Generative AI can help businesses in many sectors increase efficiency and boost their bottom-lines, not just tech giants. A UBS report analyzes well-positioned firms.


Making things that think.



Demand for AI via consumer mobile apps has been climbing, with market leader OpenAI’s ChatGPT mobile app topping half a million downloads in its first six days. Now, another AI app is touting its own launch success, as the a16z-backed Character. AI app is claiming to have pulled in over 1.7 million new installs in less than a week on the market. The AI app maker, which announced a whopping $150 million in Series A funding earlier this year, valuing its business at $1 billion, offers customizable AI companions with distinct personalities, as well as the ability for users to create their own characters.
While there are a number of these AI character generators available on today’s app stores, interest in Character. AI has a lot to do with its founders. The Palo Alto–based startup was created by Noam Shazeer and Daniel De Freitas, AI experts who previously led a team of researchers at Google that built LaMDA (Language Model for Dialogue Applications), a language model that helps power conversational AI experiences.
At Google, the founders had become frustrated with the company’s hesitancy to roll out AI chatbots to other researchers and the general public, including through integrations with other Google products, like Assistant, The Wall Street Journal reported. Believing AI would revolutionize search and other areas, the duo ultimately decided to leave Google in late 2021, despite pleas from CEO Sundar Pichai to stay and continue their work on LaMDA. That same November, Shazeer and De Freitas founded Character Technologies, now home to Character. AI.

The U.S.-China decoupling is giving rise to a divided tech landscape between the two major economies, shaping the development of the red-hot area of generative AI, which turns text into various forms of content like prose, images, and videos.
China, in order to reduce dependence on the U.S. technological foundation, has been pursuing its own large language models that match OpenAI’s GPT models. But unlike the U.S., some of its most advanced AI endeavors are happening at established internet juggernauts, such as Baidu.
The search engine and autonomous driving giant rolled out its counterpart to ChatGPT in March. Now the 23-year-old firm wants to have a stake in other AI startups, too. The company aims to have a stake in other AI startups. During a JPMorgan summit in China this week, Baidu’s co-founder and CEO Robin Li announced the launch of a billion yuan ($145 million) fund to back generative AI companies.

GM’s Cruise aims to turn self-driving into a billion-dollar business.

Missed the GamesBeat Summit excitement? Don’t worry! Tune in now to catch all of the live and virtual sessions here.
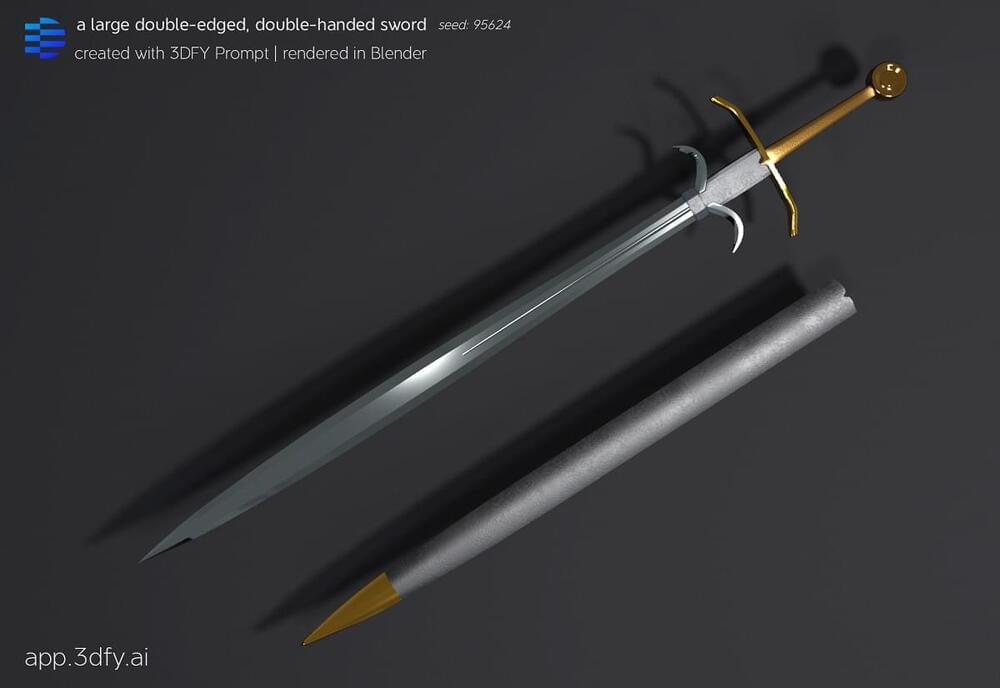
3DFY.ai announced the launch of 3DFY Prompt, a generative AI that lets developers and creators build 3D models based on text prompts.
The Tel Aviv, Israel-based company said the tech democratizes professional-quality 3D model creation, enabling anyone to use text prompts to create high-quality models that can be used in gaming, design or virtual environments.