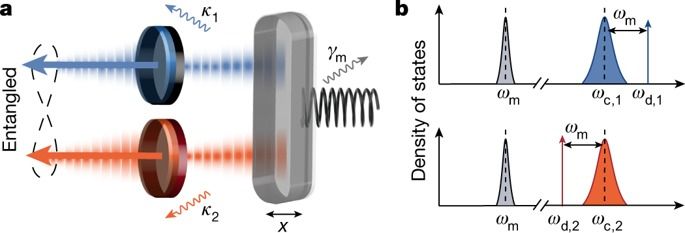
Researchers at MIT have developed a system for converting the molecular structures of proteins, the basic building blocks of all living beings, into audible sound that resembles musical passages. Then, reversing the process, they can introduce some variations into the music and convert it back into new proteins never before seen in nature. Credit: Zhao Qin and Francisco Martin-Martinez.
Want to create a brand new type of protein that might have useful properties? No problem. Just hum a few bars.
In a surprising marriage of science and art, researchers at MIT have developed a system for converting the molecular structures of proteins, the basic building blocks of all living beings, into audible sound that resembles musical passages. Then, reversing the process, they can introduce some variations into the music and convert it back into new proteins never before seen in nature.
Although it’s not quite as simple as humming a new protein into existence, the new system comes close. It provides a systematic way of translating a protein’s sequence of amino acids into a musical sequence, using the physical properties of the molecules to determine the sounds. Although the sounds are transposed in order to bring them within the audible range for humans, the tones and their relationships are based on the actual vibrational frequencies of each amino acid molecule itself, computed using theories from quantum chemistry.