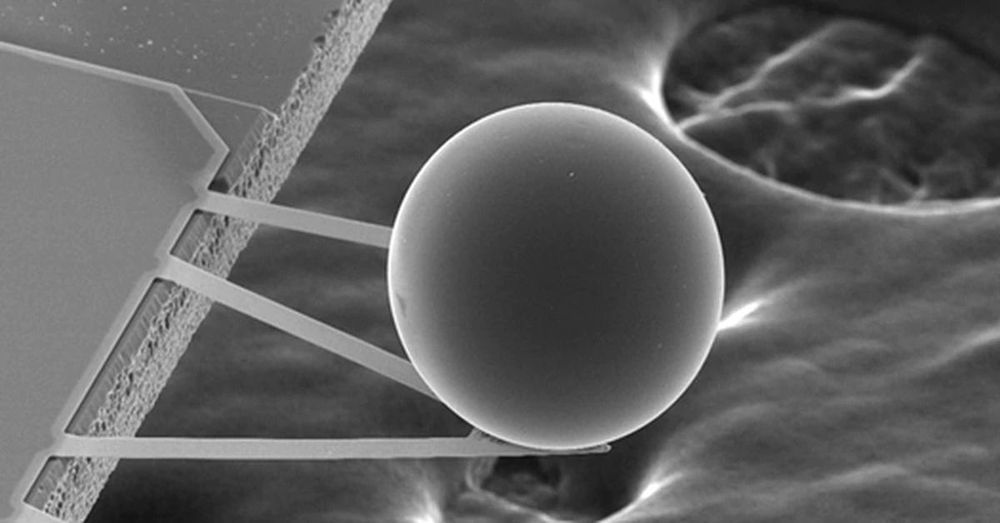
Quantum computers exist today, although they’re limited, cut-down versions of what we hope fully blown quantum computers are going to be able to do in the future.
But now, researchers have developed hardware for a ‘probabilistic computer’ – a device that might be able to bridge the gap between genuine quantum computers and the standard PCs and Macs we have today.
The special trick that a probabilistic computer can do is to solve quantum problems without actually going quantum, as it were. It does this using a p-bit, which the team behind this research describes as a “poor man’s qubit”.