:ooooooo.
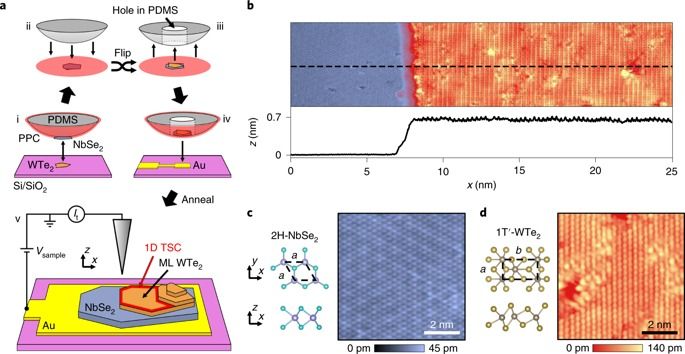
The quantum spin Hall insulator is characterized by a bandgap in the two-dimensional (2D) interior and helical 1D edge states1,2,3. Inducing superconductivity in the helical edge state results in a 1D topological superconductor, a highly sought-after state of matter at the core of many proposals for topological quantum computing4. In the present study, we report the coexistence of superconductivity and the quantum spin Hall edge state in a van der Waals heterostructure, by placing a monolayer of 1T′-WTe2, a quantum spin Hall insulator1,2,3, on a van der Waals superconductor, NbSe2. Using scanning tunnelling microscopy and spectroscopy (STM/STS), we demonstrate that the WTe2 monolayer exhibits a proximity-induced superconducting gap due to the underlying superconductor and that the spectroscopic features of the quantum spin Hall edge state remain intact. Taken together, these observations provide conclusive evidence for proximity-induced superconductivity in the quantum spin Hall edge state in WTe2, a crucial step towards realizing 1D topological superconductivity and Majorana bound states in this van der Waals material platform.