In 2005, the obituary of physicist Asher Peres in the magazine Physics Today told us that when a journalist asked him if quantum teleportation could transport a person’s soul as well as their body, the scientist replied: “No, not the body, just the soul.” More than just a simple joke, Peres’ response offers a perfect explanation, encoded in a metaphor, of the reality of a process that we have seen countless times in science fiction. In fact, teleportation does exist, although in the real world it is quite different from the famous “Beam me up, Scotty!” associated with the Star Trek series.
Teleportation in real science began to take shape in 1993 thanks to a theoretical study published by Peres and five other researchers in Physical Review Letters, which laid the foundation for quantum teleportation. Apparently, it was co-author Charles Bennett’s idea to associate the proposed phenomenon with the popular idea of teleportation, but there is an essential difference between fiction and reality: in the latter it’s not matter that travels, but rather information, which transfers properties from the original matter to that of the destination matter.
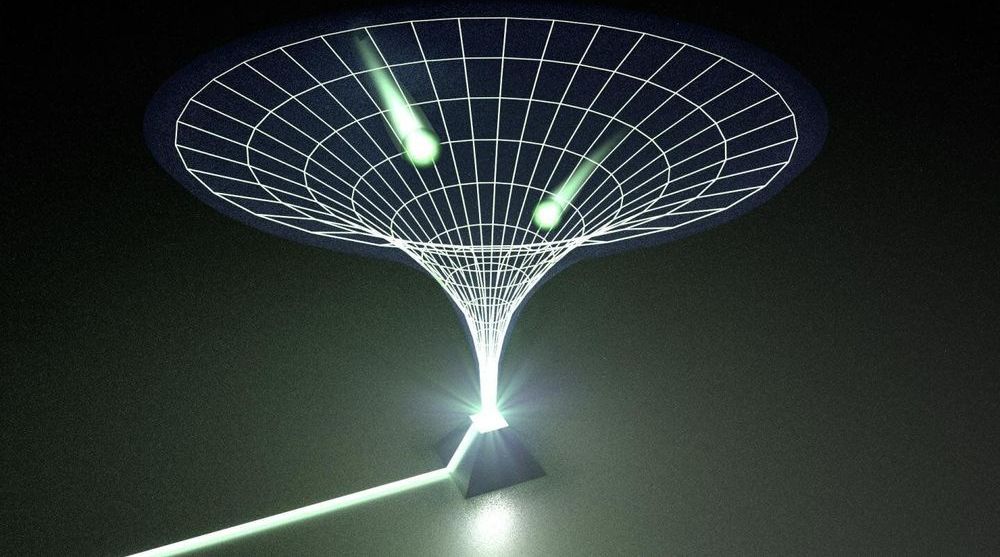
Quantum teleportation is based on a hypothesis described in 1935 by physicist Albert Einstein and his colleagues Boris Podolsky and Nathan Rosen, known as the EPR paradox. As a consequence of the laws of quantum physics, it was possible to obtain two particles and separate them in space so that they would continue to share their properties, as two halves of a whole. Thus, an action on one of them (on A, or Alice, according to the nomenclature used) would instantaneously have an effect on the other (on B, or Bob). This “spooky action at a distance”, in Einstein’s words, would seem capable of violating the limit of the speed of light.