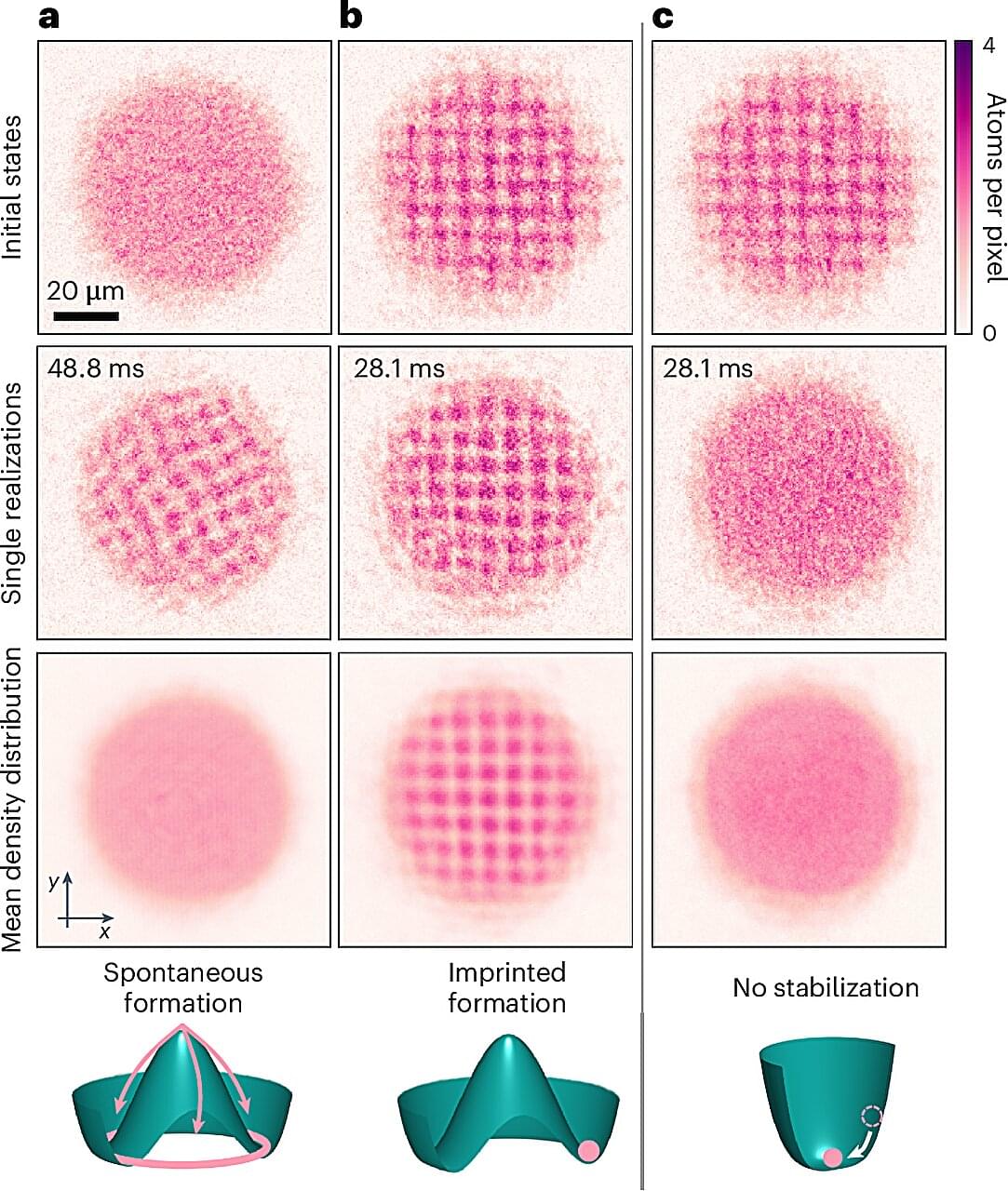
In everyday life, all matter exists as either a gas, liquid, or solid. In quantum mechanics, however, it is possible for two distinct states to exist simultaneously. An ultracold quantum system, for instance, can exhibit the properties of both a fluid and a solid at the same time.
The Synthetic Quantum Systems research group at Heidelberg University has now demonstrated this phenomenon using a new experimental approach, by feeding a small amount of energy into a superfluid. They showed that, in a driven quantum system of this kind, sound waves propagate at two different speeds, which points toward coexisting liquid and solid states, a hallmark of supersolidity. The work is published in the journal Nature Physics.
This surprising and seemingly contradictory behavior of two states of matter existing at the same time does not occur at room temperature. But at ultralow temperatures, quantum mechanics takes over, and matter can exhibit fundamentally different properties. When atoms are cooled to such low temperatures, their wave-like nature is dominant. If brought close enough together, many particles merge into one large wave, known as a Bose-Einstein condensate. This state is a superfluid, a fluid that flows without friction.