Project offers new step toward study of emergence, ‘materials by design,’ and future nanomagnets.
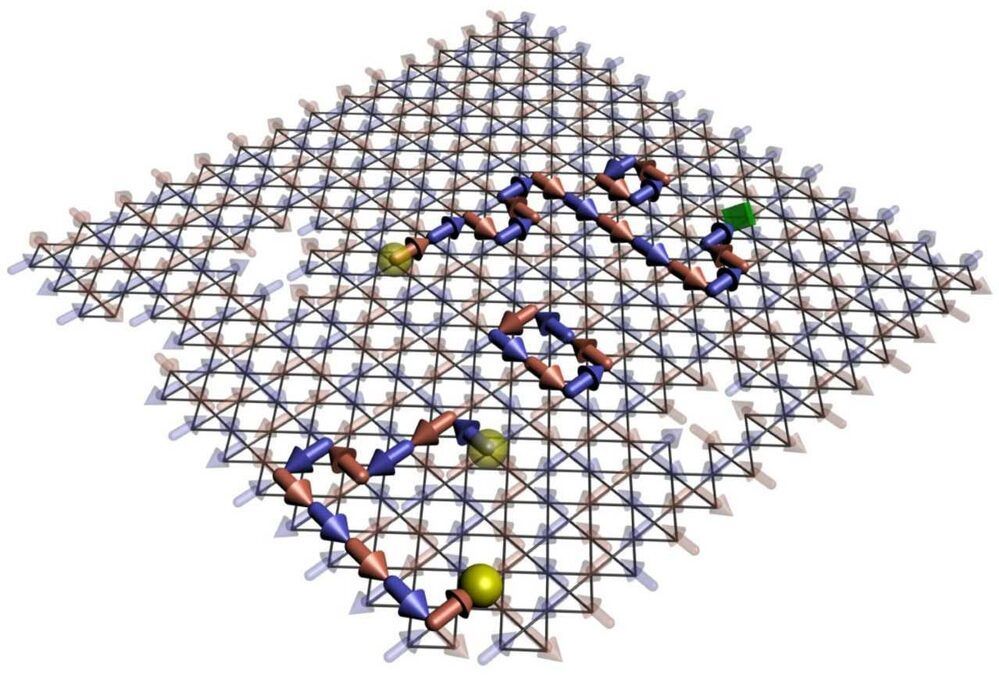
Using a D-Wave quantum-annealing computer as a testbed, scientists at Los Alamos National Laboratory have shown that it is possible to isolate so-called emergent magnetic monopoles, a class of quasiparticles, creating a new approach to developing “materials by design.”
“We wanted to study emergent magnetic monopoles by exploiting the collective dynamics of qubits,” said Cristiano Nisoli, a lead Los Alamos author of the study. “Magnetic monopoles, as elementary particles with only one magnetic pole, have been hypothesized by many, and famously by Dirac, but have proved elusive so far.”