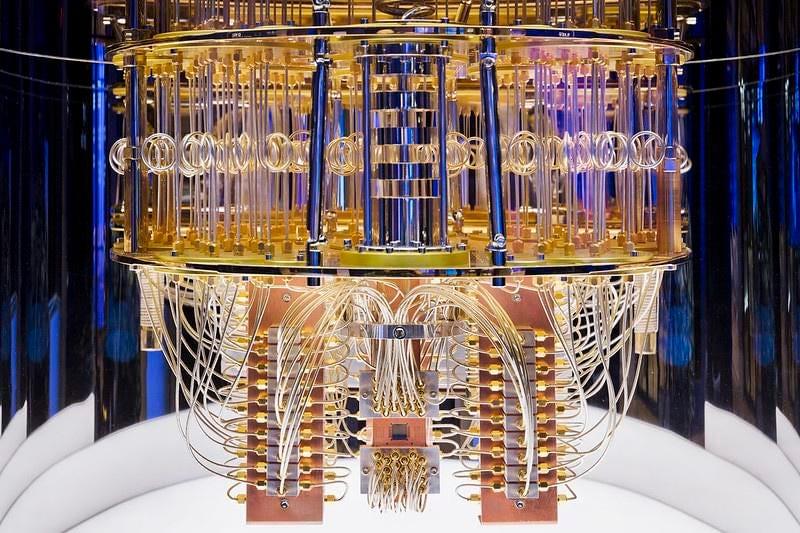
IBM has just announced a partnership with the Government of Quebec to create the Quebec-IBM Discovery Accelerator in Bromont, Quebec. The accelerator will focus on using quantum computing, Artificial Intelligence (AI), and High-Performance Computing (HPC) to develop new projects, business/scientific/academia collaborations, and skills-building initiatives in research areas including energy, life sciences (genomics and drug discovery), new materials development, and sustainability. This is the fourth such center that IBM has announced. The three previously announced partnerships are with Cleveland Clinic, the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, and the UK’s Science and Technology Facilities Council Hartree Centre. IBM’s formal mission statement for these Discovery Accelerators is: “Accelerate scientific discovery and societal impact with a convergence of AI, quantum, and hybrid cloud in a community of discovery with research, academic, industry, startup, and government organizations working together.” IBM’s formal mission statement for these Discovery Accelerators is:
“Accelerate scientific discovery and societal impact with a convergence of AI, quantum, and hybrid cloud in a community of discovery with research, academic, industry, startup, and government organizations working together.”
In addition, the company has developed individual mission statements for each of the four Discovery Accelerators: