Using just a handful of quantum bits, researchers have used a quantum computer to simulate an infinite line of electron-like particles. The technique could be used to better understand the behaviour of molecules in materials.


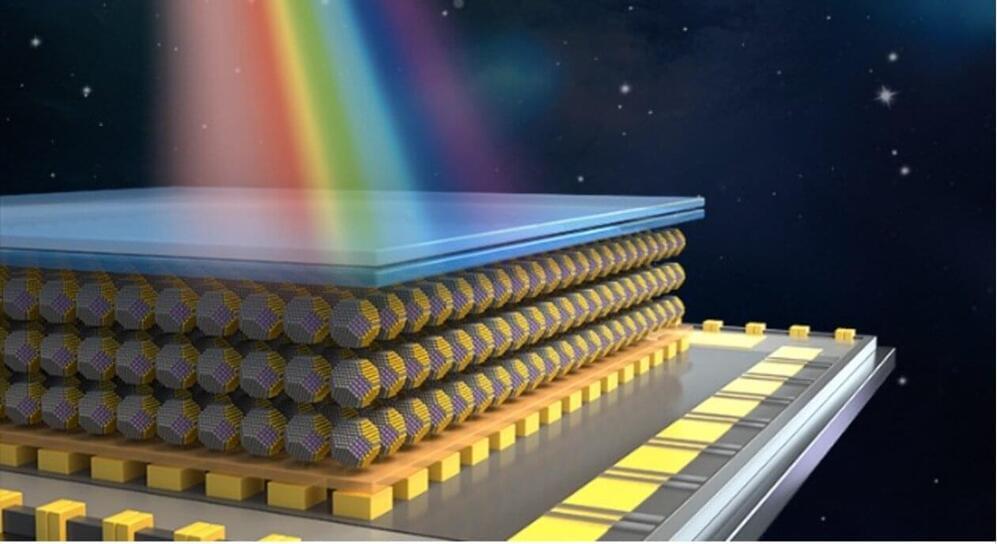
Advances in the fields of robotics, autonomous driving and computer vision have increased the need for highly performing sensors that can reliably collect data in different environmental conditions. This includes imagers that can operate at near-infrared wavelengths (i.e., 0.7–1.4 µm), thus potentially collecting high resolution images in complex or unfavorable atmospheric conditions, such as in the presence of rain, fog and smoke.
Researchers at Huazhong University of Science and Technology (HUST), HiSilicon Optoelectronics Co. Limited, and Optical Valley Laboratory have recently developed a near-infrared colloidal quantum dot (CQD) imager. This highly efficient imager was presented in a paper published in Nature Electronics.
“Our group was founded at Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, HUST in 2012 and continuously conducts research on CQD materials and devices with Associate Prof. Jianbing Zhang,” Liang Gao, one of the researchers involved in the study, told TechXplore.


Tiny crystals, known as quantum dots, have enabled an international team to achieve a quantum efficiency exceeding 100 percent in the photocurrent generated in a hybrid inorganic-organic semiconductor.
Perovskites are exciting semiconductors for light-harvesting applications and have already shown some impressive performances in solar cells. But improvements in photo-conversion efficiency are necessary to take this technology to a broader market.
Light comes in packets of energy known as photons. When a semiconductor absorbs a photon, the electromagnetic energy is transferred to a negatively charged electron and its positively charged counterpart, known as a hole. An electric field can sweep these particles in opposite directions, thereby allowing a current to flow. This is the basic operation of a solar cell. It might sound simple, but optimizing the quantum efficiency, or getting as many electron-hole pairs from the incoming photons as possible, has been a long-standing goal.

Physicists have been trying to determine the ground states of 2D electron systems at extremely low densities and temperatures for many decades now. The first theoretical predictions for these ground states were put forward by physicists Felix Bloch in 1929 and Eugene Wigner in 1934, both of whom suggested that interactions between electrons could lead to ground states that had never been observed before.
Researchers at Princeton University have been conducting studies in this area of physics for several years now. Their most recent work, featured in Physical Review Letters, gathered evidence of a new state that had been predicted by Wigner, known as a disordered Wigner solid (WS).
“The phase predicted by Wigner, an ordered array of electrons (the so-called Wigner crystal or WS), has fascinated scientists for decades,” Mansour Shayegan, principal investigator for the study, told Phys.org. “Its experimental realization is extremely challenging, as it requires samples with very low densities and with appropriate parameters (large effective mass and small dielectric constant) to enhance the role of interaction.”

View insights.
The University of Innsbruck, Austria, realized a quantum computer that breaks out of this paradigm and unlocks additional computational resources, hidden in almost all of today’s quantum devices. Computers are well-known for operating with binary information, or zeros and ones, which has led to computers powering so much. This new approach results in more computational power with fewer quantum particles.
Quantum computers work with more than zero and one and digital computers work with zeros and ones, also called binary information. Quantum computers are also designed with binary information processing in mind. In fact, it was so successful that computers now power everything from coffee makers to self-driving cars, and it’s hard to imagine life without them. Restricting researchers to binary systems prevent these devices from living up to their true potential.
The research team succeeded in developing a quantum computer that can perform arbitrary calculations with so-called quantum digits, thereby unlocking more computational power with fewer quantum particles. Unlike the classical method, the new method that utilizes more states does not negatively impact the reliability of the computer. The researchers have developed a quantum computer that can make use of the full potential of these atoms.
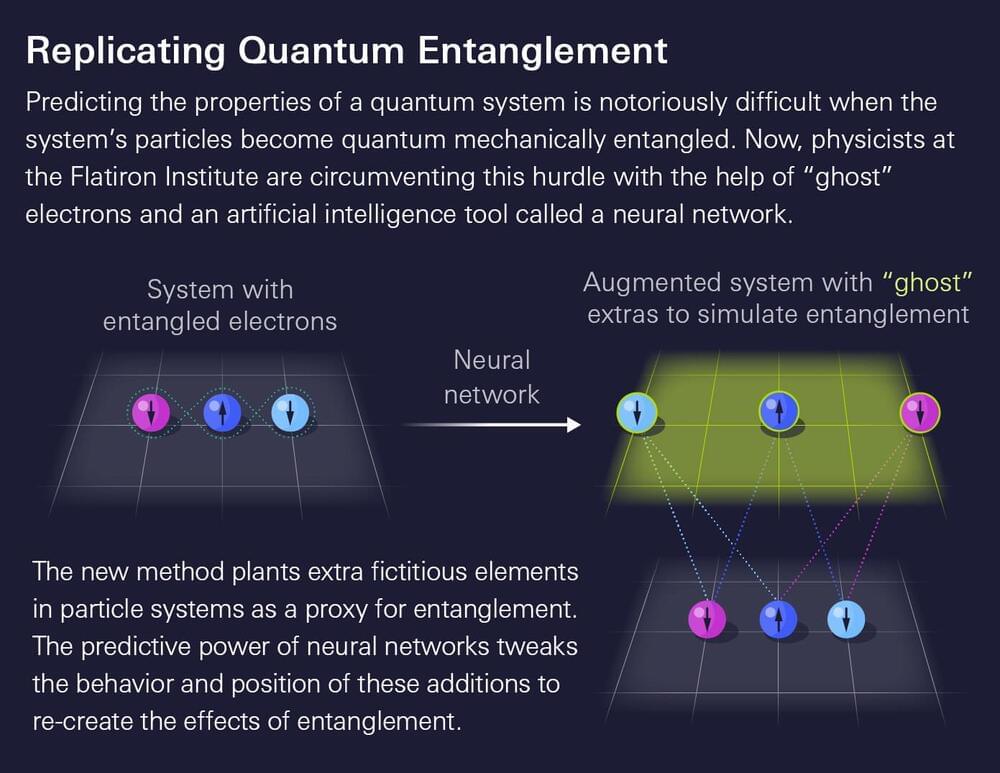
Physicists are (temporarily) augmenting reality to crack the code of quantum systems.
Predicting the properties of a molecule or material requires calculating the collective behavior of its electrons. Such predictions could one day help researchers develop new pharmaceuticals or design materials with sought-after properties such as superconductivity. The problem is that electrons can become “quantum mechanically” entangled with one another, meaning they can no longer be treated individually. The entangled web of connections becomes absurdly tricky for even the most powerful computers to unravel directly for any system with more than a handful of particles.
Now, quantum physicists at the Flatiron Institute’s Center for Computational Quantum Physics (CCQ) in New York City and the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) in Switzerland have sidestepped the problem. They created a way to simulate entanglement by adding to their computations extra “ghost” electrons that interact with the system’s actual electrons.

A special bonding state between atoms has been created in the laboratory for the first time: With a laser beam, atoms can be polarized so that they are positively charged on one side and negatively charged on the other. This makes them attract each other creating a very special bonding state—much weaker than the bond between two atoms in an ordinary molecule, but still measurable. The attraction comes from the polarized atoms themselves, but it is the laser beam that gives them the ability to do so—in a sense, it is a “molecule” of light and matter.
Theoretically, this effect has been predicted for a long time, but now scientists at the Vienna Center for Quantum Science and Technology (VCQ) at TU Wien, in cooperation with the University of Innsbruck, have succeeded in measuring this exotic atomic bond for the first time. This interaction is useful for manipulating extremely cold atoms, and the effect could also play a role in the formation of molecules in space. The results have now been published in the scientific journal Physical Review X.