A nano-scale sensor technology records precise signatures of light striking a surface.


By Robert Davis and Desiree Vogt-Lee
Quantum computing is notoriously counterintuitive; it challenges us to grapple with concepts that can be difficult to imagine. We often rely on our sense of sight to make those concepts a little easier to grasp, by representing quantum information with visualization models like the Q-sphere or the circuit diagram, and even creative visual arts projects like the recent Quantum Circuit Disks series. But what happens when we represent quantum using not only imagery, but also sound?
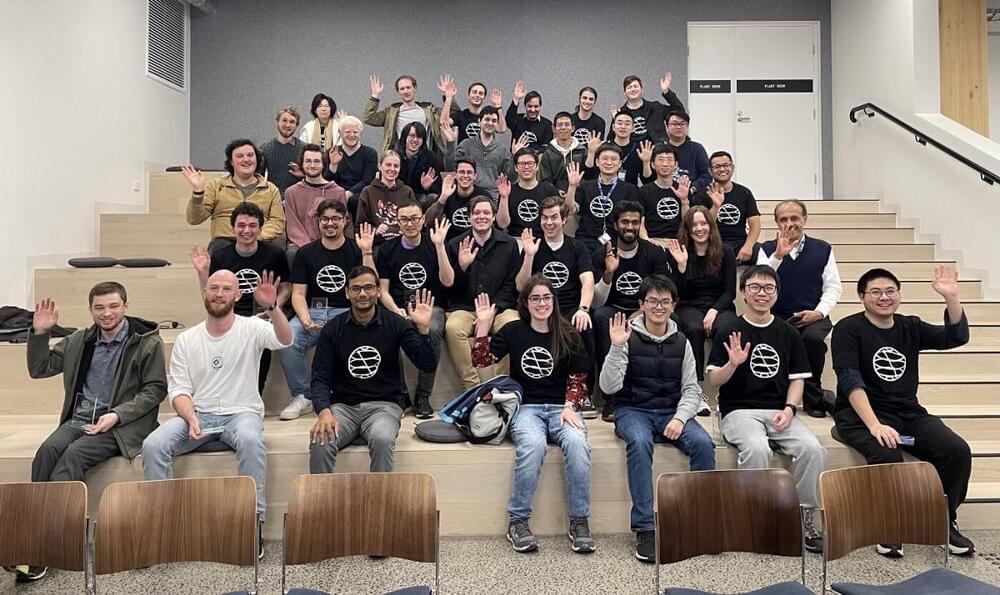
One team of Australian researchers is showing the world exactly what that looks like with a project that turns quantum circuits into music videos. That project, which the creators have named “qMuVi” (“quantum Music Video”), earned the titles of both 1st place winner and Community Choice winner at the recent Qiskit Hackathon Melbourne, a hybrid in-person and virtual event held in early July that marked the first ever Qiskit Hackathon in Australia. The event brought together 35 participants over four days to learn about quantum computing and Qiskit, and to use their new knowledge to hack together a diverse array of novel quantum computing projects. The event as a whole was a tremendous success. But before we talk about that, let’s take a closer look at that winning quantum music videos project.

Many heart problems, including tachycardia and fibrillation, mainly originate from imperfections in the way electric currents propagate through the heart. Unfortunately, it is difficult for doctors to study these imperfections. This is because measuring these currents involves highly invasive procedures and exposure to X-ray radiation.
Luckily, there are other options. For example, magnetocardiography (MCG) is a promising alternative approach to measuring heart currents indirectly. The technique involves sensing minute changes in the magnetic field near the heart caused by cardiac currents. This can be done in a completely contactless manner. To this end, various types of quantum sensors suitable for this purpose have been developed. However, their spatial resolution is limited to centimeter scales, which is not good enough to detect cardiac currents that propagate at millimeter scales. Furthermore, each of these sensors has a fair share of its practical limitations, such as size and operating temperature.
In a new study published today (August 23, 2022) in Communications Physics, a team of scientists developed a novel setup to perform MCG at higher resolutions. Their approach is based on a diamond quantum sensor comprising nitrogen vacancies, which act as special magnetic “centers” that are sensitive to the weak magnetic fields produced by heart currents. The researchers were led by Associate Professor Takayuki Iwasaki of Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech), Japan.
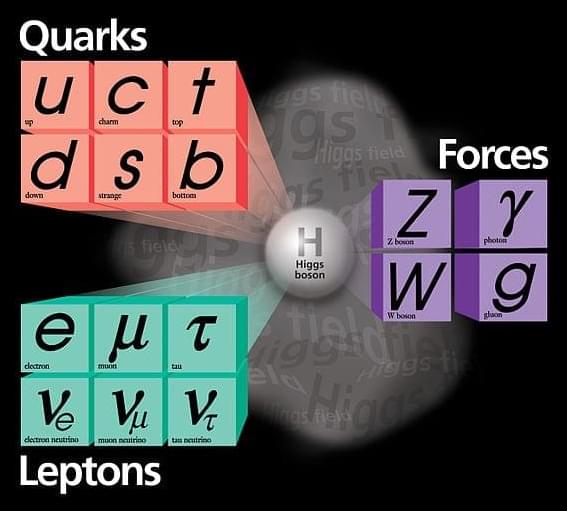
What are the most fundamental structures of the Universe?
In this article, we’ll explore the mysteries that scientists have been scratching their heads about for hundreds of years. Mysteries that have only partly been resolved and that lead us towards understanding the fundamental structures of Nature. Mysteries that turned out to be so bizarre that it took more than a hundred years to appreciate the true power of this amazing theory.
The hunt for simplicity has been going on for centuries, but where are we now? What is our best bet at how Nature really works and what do we still not understand?
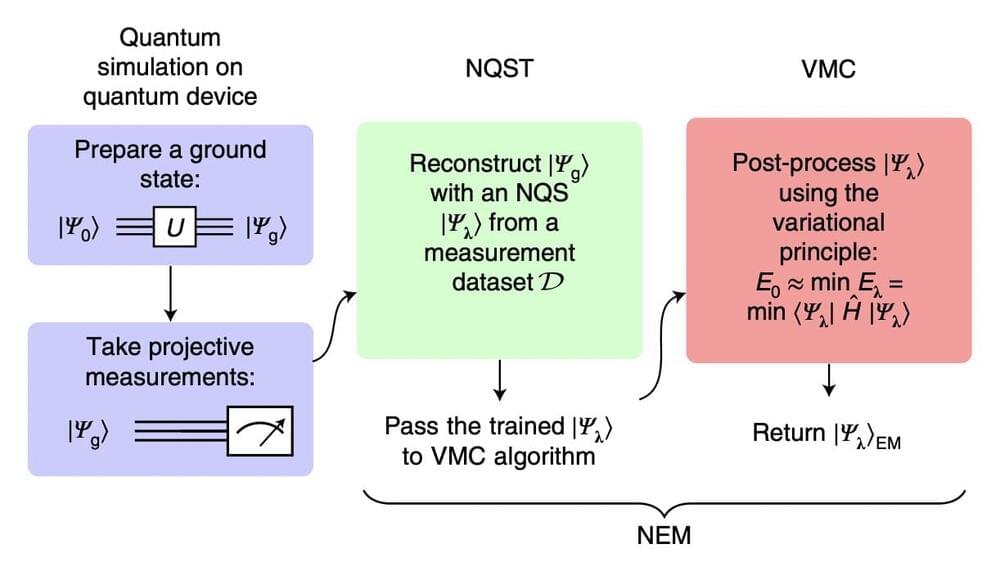
Near-term quantum computers, quantum computers developed today or in the near future, could help to tackle some problems more effectively than classical computers. One potential application for these computers could be in physics, chemistry and materials science, to perform quantum simulations and determine the ground states of quantum systems.
Some quantum computers developed over the past few years have proved to be fairly effective at running quantum simulations. However, near-term quantum computing approaches are still limited by existing hardware components and by the adverse effects of background noise.
Researchers at 1QB Information Technologies (1QBit), University of Waterloo and the Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics have recently developed neural error mitigation, a new strategy that could improve ground state estimates attained using quantum simulations. This strategy, introduced in a paper published in Nature Machine Intelligence, is based on machine-learning algorithms.

Exactly like a quasicrystal, this arrangement is ordered without repetition. Similar to a quasicrystal, it’s a single-dimensional representation of a 2-dimensional pattern. As a consequence of the flattening of dimensions, the system is given two time symmetries instead of just one: the system is given another dimension of time that does not exist.
Nevertheless, quantum computers remain extremely complex experimental systems, so it is not yet known whether the benefits of the theory will hold true in actual qubits.
The experientialists tested the theory using Quantinuum’s quantum computer. Periodically and using Fibonacci sequences, laser light was pulsed at the computer’s qubits.
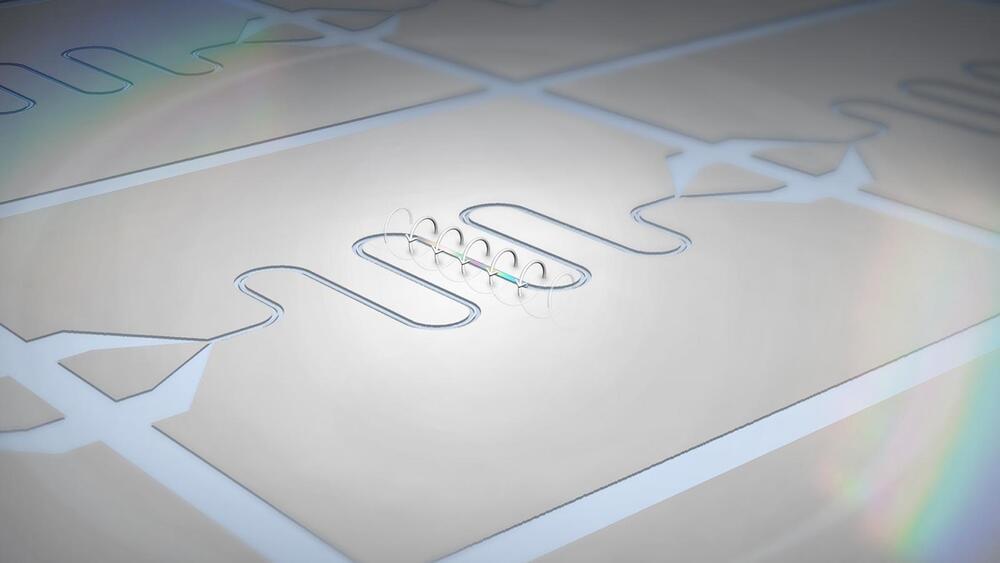

In new research from the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory, scientists have achieved efficient quantum coupling between two distant magnetic devices, which can host a certain type of magnetic excitations called magnons. These excitations happen when an electric current generates a magnetic field. Coupling allows magnons to exchange energy and information. This kind of coupling may be useful for creating new quantum information technology devices.
“Remote coupling of magnons is the first step, or almost a prerequisite, for doing quantum work with magnetic systems,” said Argonne senior scientist Valentine Novosad, an author of the study. “We show the ability for these magnons to communicate instantly with each other at a distance.”
A team of Chinese scientists report on a new method for entangling photons that they say could make quantum networks and quantum computing more practical, according to the South China Post.
In a study published in Nature Photonics, the team from the University of Science and Technology of China said that the new way to produce entangled photons is extremely efficient. The work was led by Jian-Wei Pan, one of the world’s leading quantum researcher from the Hefei National Research Center for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, the University of Science and Technology of China and CAS Center for Excellence in Quantum Information and Quantum Physics, University of Science and Technology of China.
Entangled photons are needed for certain forms of quantum communication and computing. These technologies require the ability to efficiently produce large numbers of particles — in this case, photons — that can remain entangled even when separated by vast distances to process and protect information. Specifically, the technology could be used in quantum relays that are used in long-distance, attack-proof quantum communication, the newspaper reports.

[Editor’s note: “Quantum Computing Will Be Bigger Than the Discovery of Fire!” was previously published in June 2022. It has since been updated to include the most relevant information available.]
It’s commonly appreciated that the discovery of fire was the most profound revolution in human history. And yesterday, I read that a major director at Bank of America (BAC) thinks a technology that hardly anyone is talking about these days could be more critical for humankind than fire!
Google AI announced the launch of the Google Research YouTube channel today. The channel is set to focus on a wide range of subjects like AI/ML, robotics, theory and algorithms, quantum computing, health and bioscience.