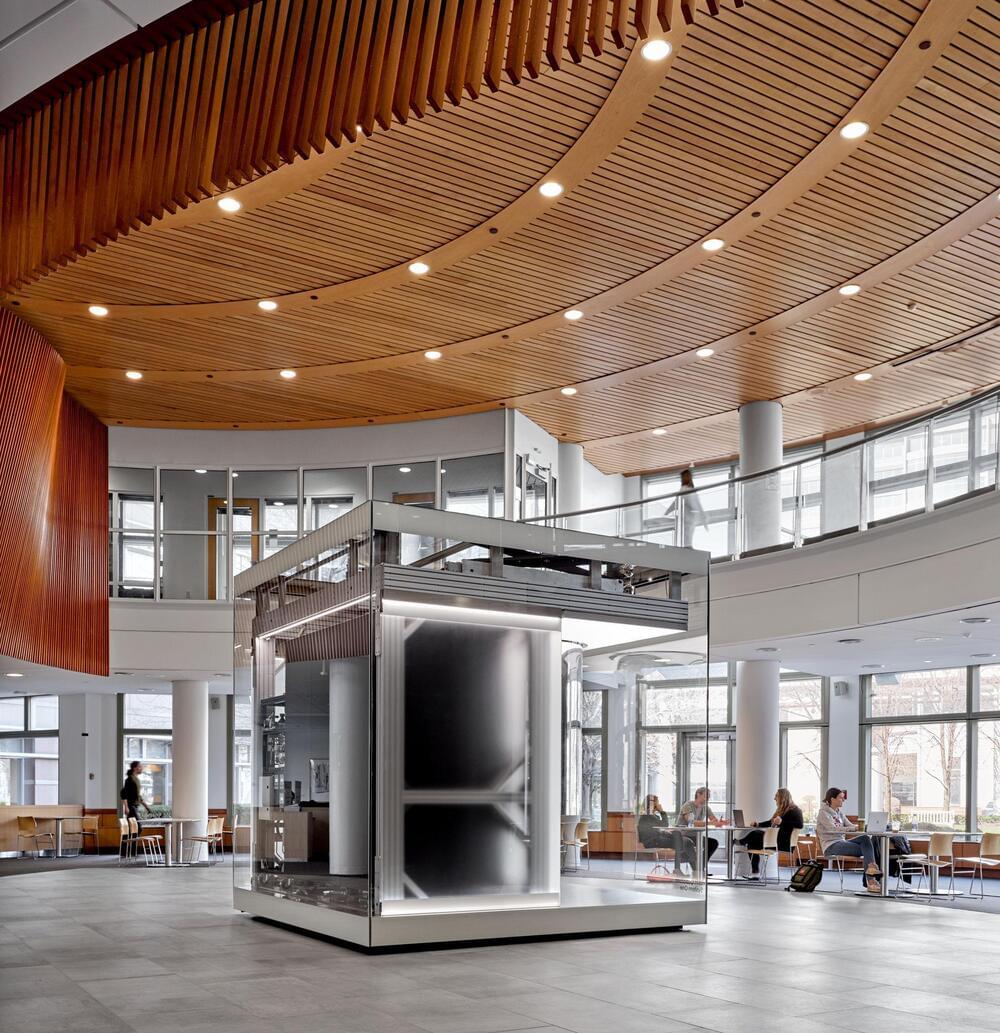
This appears to be the year that IBM’s Quantum Computing program reaches the tipping point. IBM and the Cleveland Clinic Foundation just announced the first deployment of an onsite, private sector, IBM-managed quantum computer in the United States. However, beyond the placement of a 127-qubit IBM Eagle quantum processor in a cafeteria at Cleveland Clinic’s main campus, this announcement signals a major leap forward for quantum computing applications.
Of course, the most immediate question is, why install a quantum computer in a cafeteria? Although this may seem like a frivolous question, it gets to a major point of this article. The IBM Eagle class quantum processor has been installed in a highly visible location in the Cleveland Clinic so that biomedical researchers and physicians can start thinking about the most productive ways to use this resource. These are very early days for the development of quantum computing applications, so installing the IBM Eagle quantum processor in the cafeteria, visited daily by nearly everyone working at the Cleveland Clinic, seems like an extremely creative way of keeping the machine ever present in the minds of people working at the facility.
Dr Lara Jehi, who became Cleveland Clinic’s first Chief Research Information Officer in 2020, said that there are many areas of interest in medical research with computational ceilings that block further advances. Quantum processing may help break through those ceilings. Researchers at Cleveland Clinic, working with IBM data scientists, combed through the possible avenues for research, discipline by discipline, to identify the projects most likely to bear fruit when matched to quantum processing’s current capabilities. “Quantum is still a nascent technology,” said Jehi.