To operate reliably a quantum computer needs to correct the errors introduced into the system by noise in its hardware. Error-correction approaches typically use “logical” qubits, which are qubits made up of as many as a few thousand “physical” qubits. Logical qubits are much less error prone than physical qubits, but the hardware overhead complicates the realization of fault-tolerant quantum computers based on this approach. Now a team led by Harry Levine and Oskar Painter of the Amazon Web Services Center for Quantum Computing in California has demonstrated a new qubit design with built-in error-detection ability [1]. Painter says this qubit could serve as an alternative building block for error-correcting schemes, substantially reducing complexity.
The demonstrated qubit is an “erasure” qubit, one in which the most likely error type involves the loss, or erasure, of the qubit’s state [2]. This error is easier to spot and correct for than other qubit errors, such as those that flip the qubit’s state. Researchers have previously demonstrated erasure qubits made from single atoms. The new study makes the leap to transmons, the superconducting qubit used in the quantum processors developed by Google and IBM.
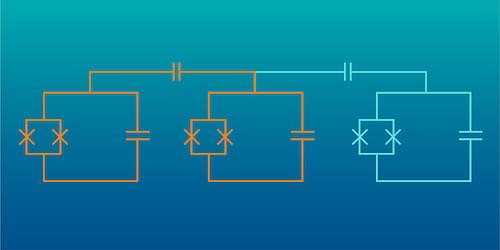
The erasure qubit of Levine, Painter, and colleagues contains three transmons. Two of the transmons are coupled together and store a qubit’s worth of information in a single, shared microwave photon. The third transmon reveals the loss of the photon—the erasure—through a shift in its operating frequency. The researchers show that in this qubit erasure errors are the dominant error type and can be detected in real time. The researchers now plan to use their new qubit to build logic gates and error-correcting circuits.