Physicist Pan Jianwei outlines timetable for quantum-based ultra-secure networks that will have coverage across the world.
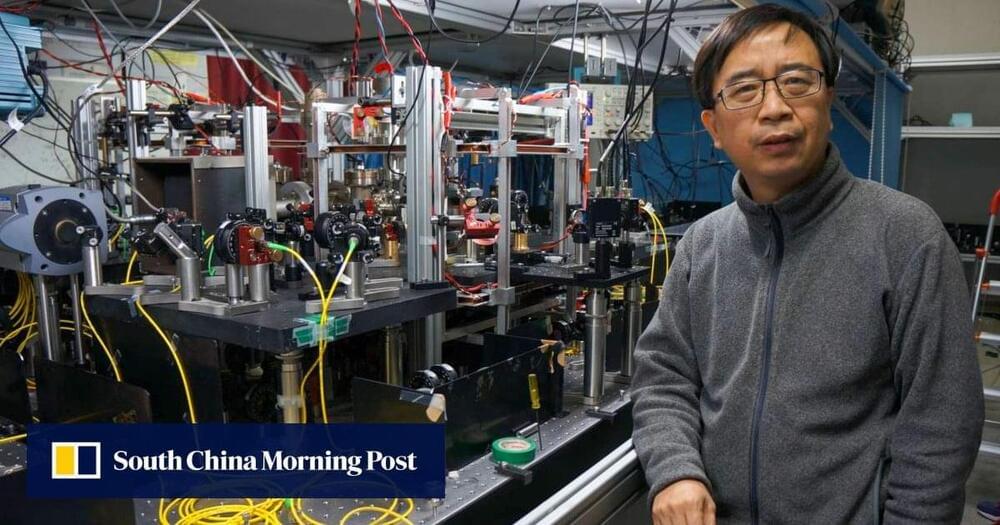

It’s not your ordinary pocket watch: The researchers showed that, at least under a narrow range of conditions, their clock could beat a benchmark for precision called the “standard quantum limit”—what physicist Adam Kaufman refers to as the “Holy Grail” for optical atomic clocks.
“What we’re able to do is divide the same length of time into smaller and smaller units,” said Kaufman, senior author of the new study and a fellow at JILA, a joint research institute between CU Boulder and NIST. “That acceleration could allow us to track time more precisely.”
The team’s advancements could lead to new quantum technologies. They include sensors that can measure subtle changes in the environment, such as how Earth’s gravity shifts with elevation.

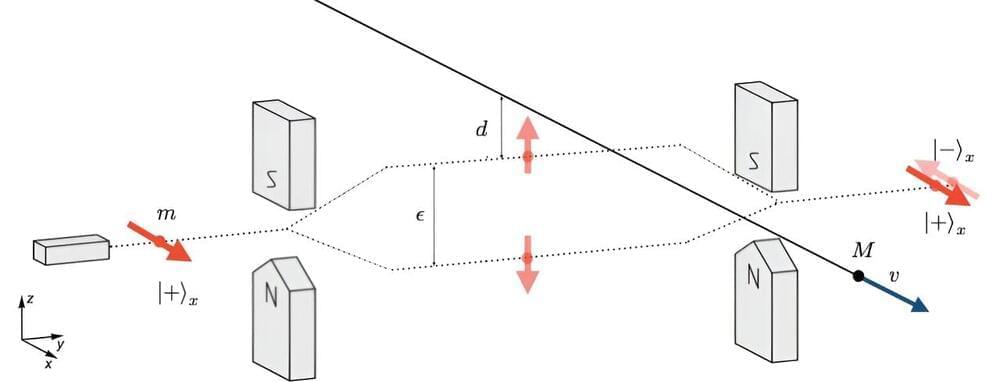
Scientists have devised a method to detect nuclear decay through the subtle movement of microparticles, enhancing our understanding of elusive particles like neutrinos.
This breakthrough paves the way for improved nuclear monitoring tools and could be enhanced by future quantum technologies.
Radioactivity is all around us, even in everyday items. For example, bananas contain trace amounts of radioactive potassium, with approximately 10 nuclei decaying every second in a typical banana. While these tiny amounts of radioactivity are not dangerous, there is growing scientific interest in enhancing the precision of tools for detecting such nuclear decays.

Quantum computers and quantum communication are groundbreaking technologies that enable faster and more secure data processing and transmission compared to traditional computers. In quantum computers, qubits serve as the fundamental units of information, functioning as the quantum mechanical equivalent of bits in classical computing.
Where, for example, laser pulses in a glass fiber transport information from A to B in classical digital communication, quantum mechanics uses individual photons. In principle, this makes it impossible to intercept the transmitted data. Qubits that are optically addressable (can be controlled or read out with light) are suitable for storing the photons’ information and processing it in quantum computers. The qubits can store and process quantum states, and absorb and emit them in the form of photons.
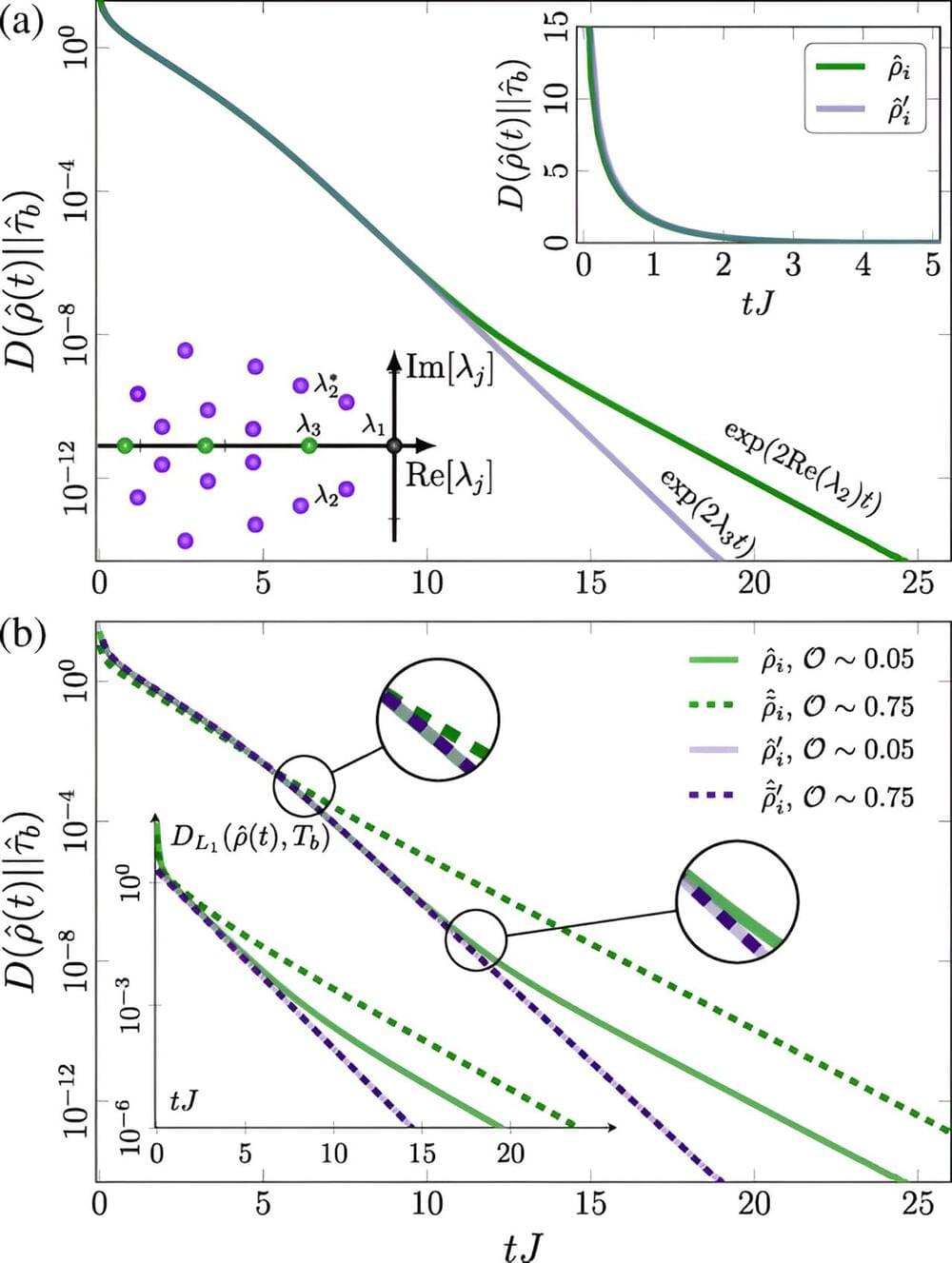
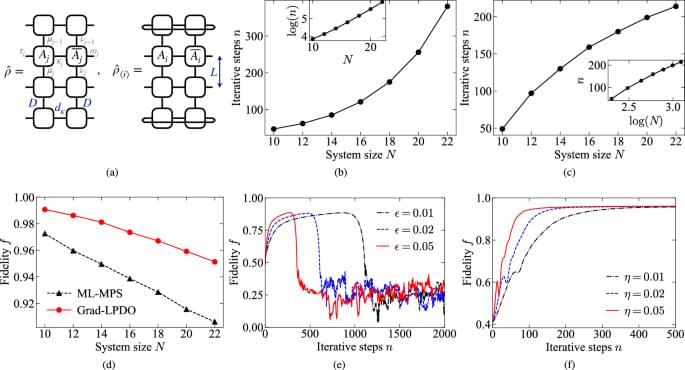
Quantum state tomography plays a fundamental role in characterizing and evaluating the quality of quantum states produced by quantum devices. It serves as a crucial element in the advancement of quantum hardware and software, regardless of the underlying physical implementation and potential applications1,2,3. However, reconstructing the full quantum state becomes prohibitively expensive for large-scale quantum systems that exhibit potential quantum advantages4,5, as the number of measurements required increases exponentially with system size.
Recent protocols try to solve this challenge through two main steps: efficient parameterization of quantum states and utilization of carefully designed measurement schemes and classical data postprocessing algorithms. For one-dimensional (1D) systems with area law entanglement, the matrix product state (MPS)6,7,8,9,10,11,12 provides a compressed representation. It requires only a polynomial number of parameters that can be determined from local or global measurement results. Two iterative algorithms using local measurements, singular value thresholding (SVT)13 and maximum likelihood (ML)14, have been demonstrated in trapped-ion quantum simulators with up to 14 qubits15. However, SVT is limited to pure states and thus impractical for noisy intermediate-scale quantum (NISQ) systems. Meanwhile, although ML can handle mixed states represented as matrix product operators (MPOs)16,17, it suffers from inefficient classical data postprocessing.
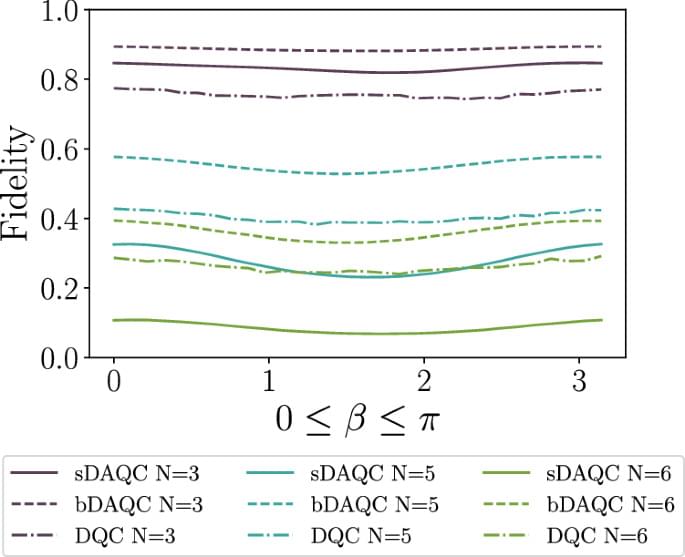
The authors explore the digital-analog quantum computing paradigm, which combines fast single-qubit gates with the natural dynamics of quantum devices. They find the digital-analog paradigm more robust against certain experimental imperfections than the standard fully-digital one and successfully apply error mitigation techniques to this approach.

China’s efforts to scale up the manufacture of superconducting quantum computers have gathered momentum with the launch of the country’s independently developed third-generation Origin Wukong, said industry experts on Monday.
The latest quantum computer, which is powered by Wukong, a 72-qubit indigenous superconducting quantum chip, has become the most advanced programmable and deliverable superconducting quantum computer currently available in China.
The chip was developed by Origin Quantum, a Hefei, Anhui province-based quantum chip startup. The company has already delivered its first and second generations of superconducting quantum computers to the Chinese market.
