Navier-Stokes equations are shown to emerge from a generalized hydrodynamics description for nearly integrable 1D models.
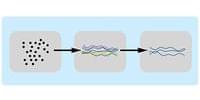


Supersolids are strange materials that behave like both a solid and a fluid due to quantum effects – and now researchers have created an intriguing new type of supersolid from laser light.

In this work, I present a coherent and comprehensive argument for the nature of consciousness as the inherent ground of phenomena backed by experimental evidence confirming the predictions make by this hypothesis.
This argument makes its point by establishing an equivalence between all observers, generating a set of observational and mathematical predictions which were then tested and confirmed.
Furthermore, when the core tenet of the argument is accepted, it provides clear, testable explanations for most of the curently unresolved questions regarding consciousness, intelligence, and the nature of observed phenomena.
In human engineering, we design systems to be predictable and controlled. By contrast, nature thrives on systems where simple rules generate rich, emergent complexity. The computational nature of the universe explains how simplicity can generate the complexity we see in natural phenomena. Imagine being able to understand everything about the universe and solve all its mysteries by a computational approach that uses very simple rules. Instead of being limited to mathematical equations, using very basic computational rules, we might be able to figure out and describe everything in the universe, like what happened at the very beginning? What is energy? What’s the nature of dark matter? Is traveling faster than light possible? What is consciousness? Is there free will? How can we unify different theories of physics into one ultimate theory of everything?
This paradigm goes against the traditional notion that complexity in nature must arise from complicated origins. It claims that simplicity in fundamental rules can produce astonishing complexity in behavior. Entering the Wolfram’s physics project: The computational universe!
Thousands of hours have been dedicated to the creation of this video. Producing another episode of this caliber would be difficult without your help. If you would like to see more, please consider supporting me on / disculogic, or via PayPal for a one-time donation at https://paypal.me/Disculogic.
Chapters:
00:00 Intro.
01:48 Fundamentally computational.
08:51 Computational irreducibility.
13:14 Causal invariance.
16:16 Universal computation.
18:44 Spatial dimensions.
21:36 Space curvature.
23:52 Time and causality.
27:12 Energy.
29:38 Quantum mechanics.
31:31 Faster than light travel.
34:56 Dark matter.
36:30 Critiques.
39:15 Meta-framework.
41:19 The ultimate rule.
44:21 Consciousness.
46:00 Free will.
48:02 Meaning and purpose.
49:09 Unification.
55:14 Further analysis.
01:02:30 Credits.
#science #universe #documentary


Researchers discovered how Floquet Majorana fermions can improve quantum computing by controlling superconducting currents, potentially reducing errors and increasing stability. A new study has revealed significant insights into the behavior of electric current flow in superconductors, which could contribute to advancements in controlled quantum information processing.

Although Navier–Stokes equations are the foundation of modern hydrodynamics, adapting them to quantum systems has so far been a major challenge. Researchers from the Faculty of Physics at the University of Warsaw, Maciej Łebek, M.Sc. and Miłosz Panfil, Ph.D., Prof., have shown that these equations can be generalized to quantum systems, specifically quantum liquids, in which the motion of particles is restricted to one dimension.
This discovery opens up new avenues for research into transport in one-dimensional quantum systems. The resulting paper, published in Physical Review Letters, was awarded an Editors’ Suggestion.
Liquids are among the basic states of matter and play a key role in nature and technology. The equations of hydrodynamics, known as the Navier–Stokes equations, describe their motion and interactions with the environment. Solutions to these equations allow us to predict the behavior of fluids under various conditions, from the ocean currents and the blood flow in blood vessels, to the dynamics of quark-gluon plasma on subatomic scales.

In a new study published in Physical Review D, Professor Ginestra Bianconi, Professor of Applied Mathematics at Queen Mary University of London, proposes a new framework that could revolutionize our understanding of gravity and its relationship with quantum mechanics.
The study, titled “Gravity from Entropy,” introduces a novel approach that derives gravity from quantum relative entropy, bridging the gap between two of the most fundamental yet seemingly incompatible theories in physics: quantum mechanics and Einstein’s general relativity.
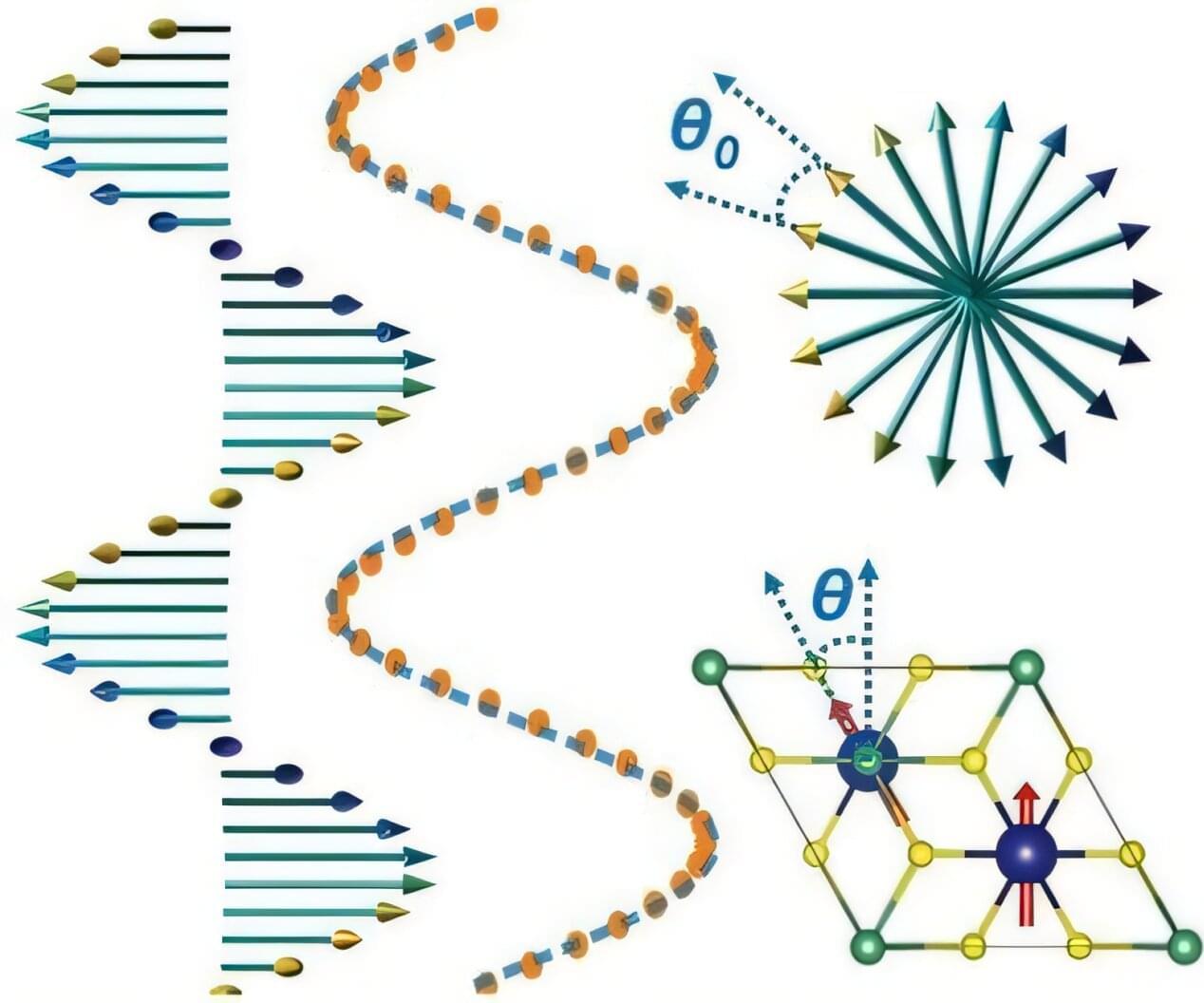
Deep within certain magnetic molecules, atoms arrange their spins in a spiral pattern, forming structures called chiral helimagnets. These helical spin patterns have intrigued researchers for years due to their potential for powering next-generation electronics. But decoding their properties has remained a mystery—until now.
Researchers at the University of California San Diego have developed a new computational approach to accurately model and predict these complex spin structures using quantum mechanics calculations. Their work was published on Feb. 19 in Advanced Functional Materials.
“The helical spin structures in two-dimensional layered materials have been experimentally observed for over 40 years. It has been a longstanding challenge to predict them with precision,” said Kesong Yang, professor in the Aiiso Yufeng Li Family Department of Chemical and Nano Engineering at the UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering and senior author of the study. “The helical period in the layered compound extends up to 48 nanometers, making it extremely difficult to accurately calculate all the electron and spin interactions at this scale.”
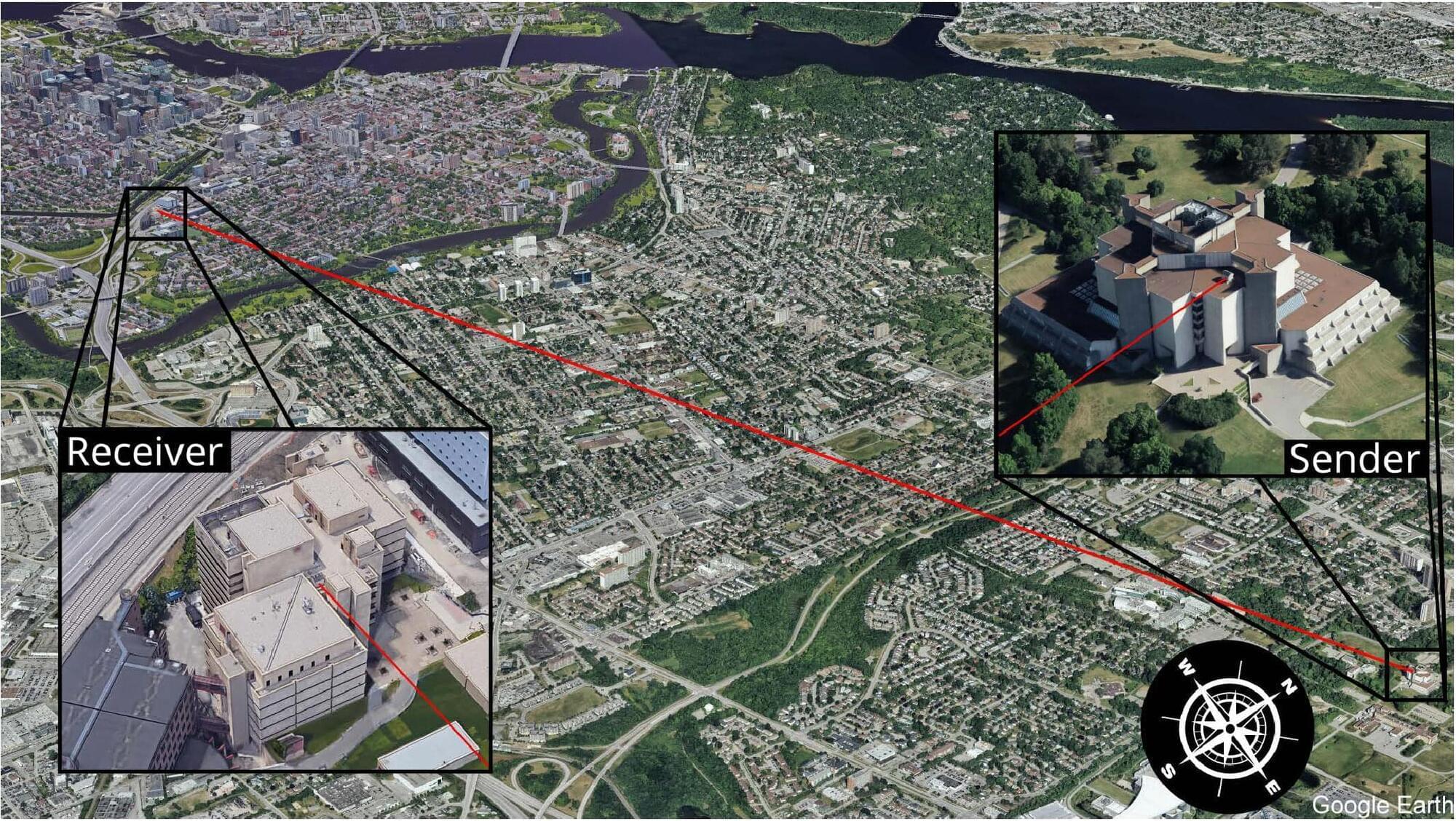
In the quest for ultra-secure, long-range quantum communication, two major challenges stand in the way: the unpredictable nature of atmospheric turbulence and the limitations of current optical wavefront correction techniques. Researchers at the University of Ottawa, under the supervision of Professor Ebrahim Karimi, the director of Nexus for Quantum Technologies, in collaboration with the National Research Council Canada (NRC) and the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Light (Germany), have made significant advances in overcoming both obstacles.
Their two latest breakthroughs—an AI-powered turbulence forecasting tool called TAROQQO and a high-speed Adaptive Optics (AO) system for correcting turbulence in quantum channels—represent a turning point in developing free-space quantum networks.
These advancements, published in Optics Express and Communication Physics, offer complementary solutions to the fundamental issue of atmospheric turbulence that distorts and diminishes photonic quantum states as they traverse through the air.