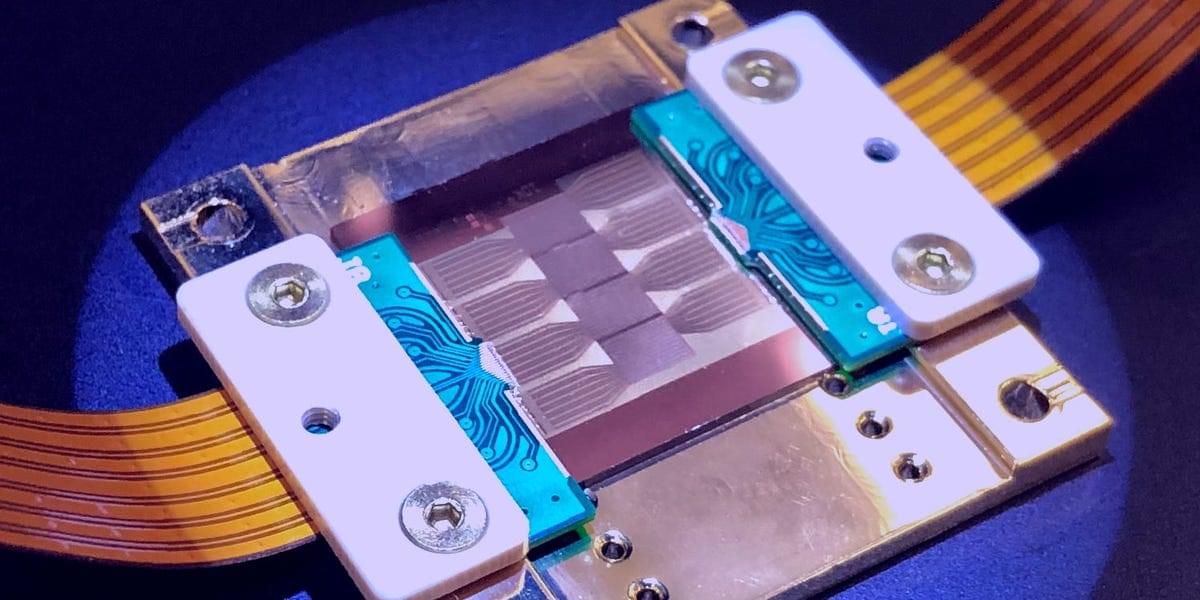
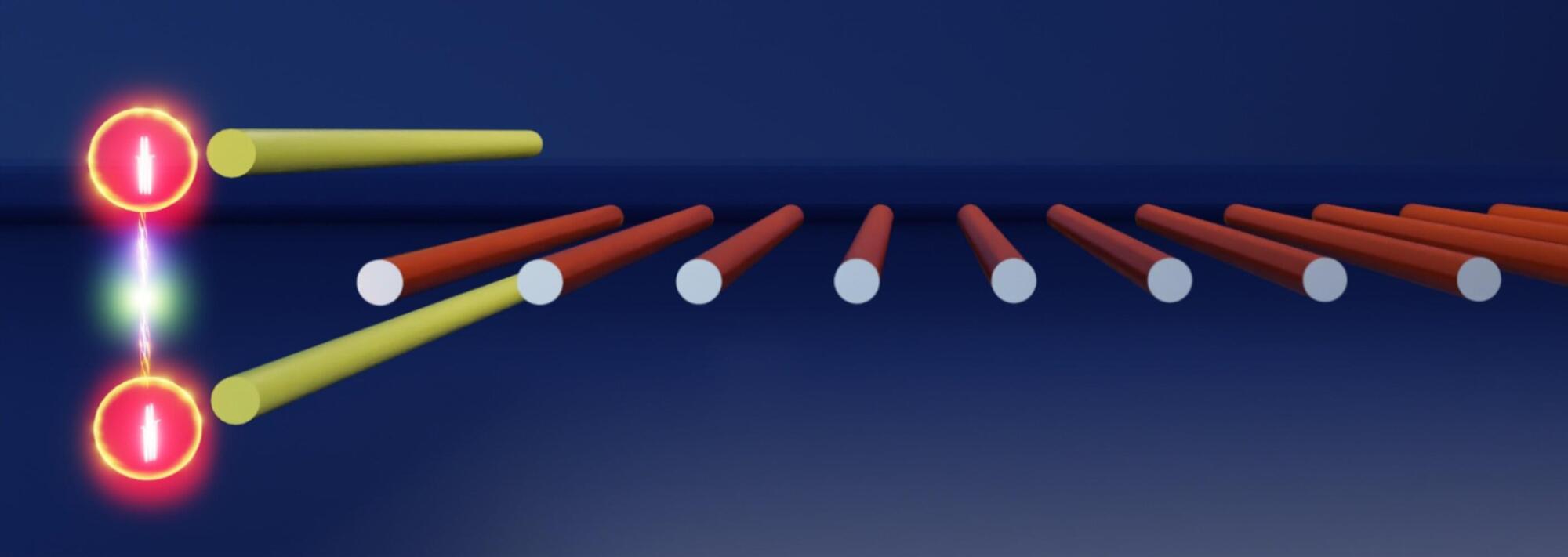
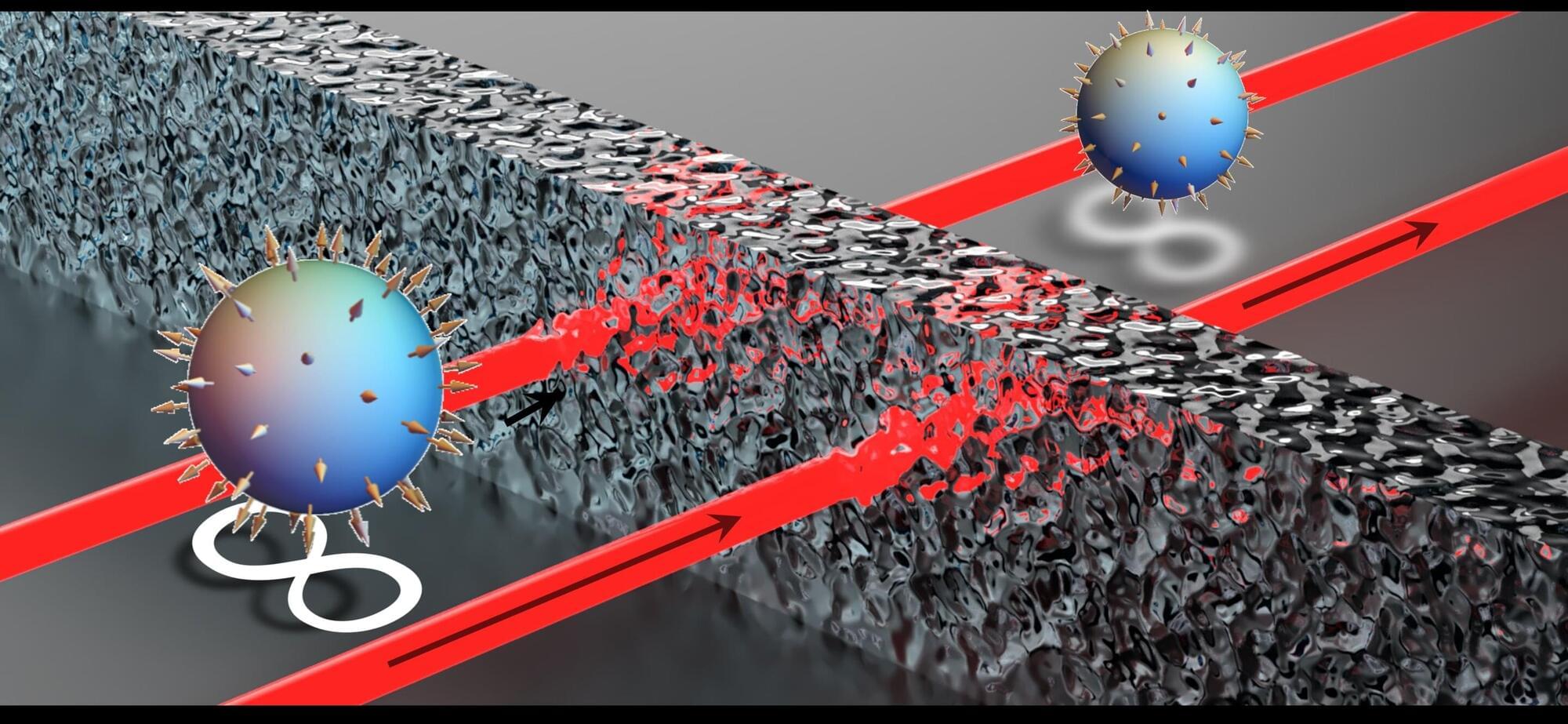
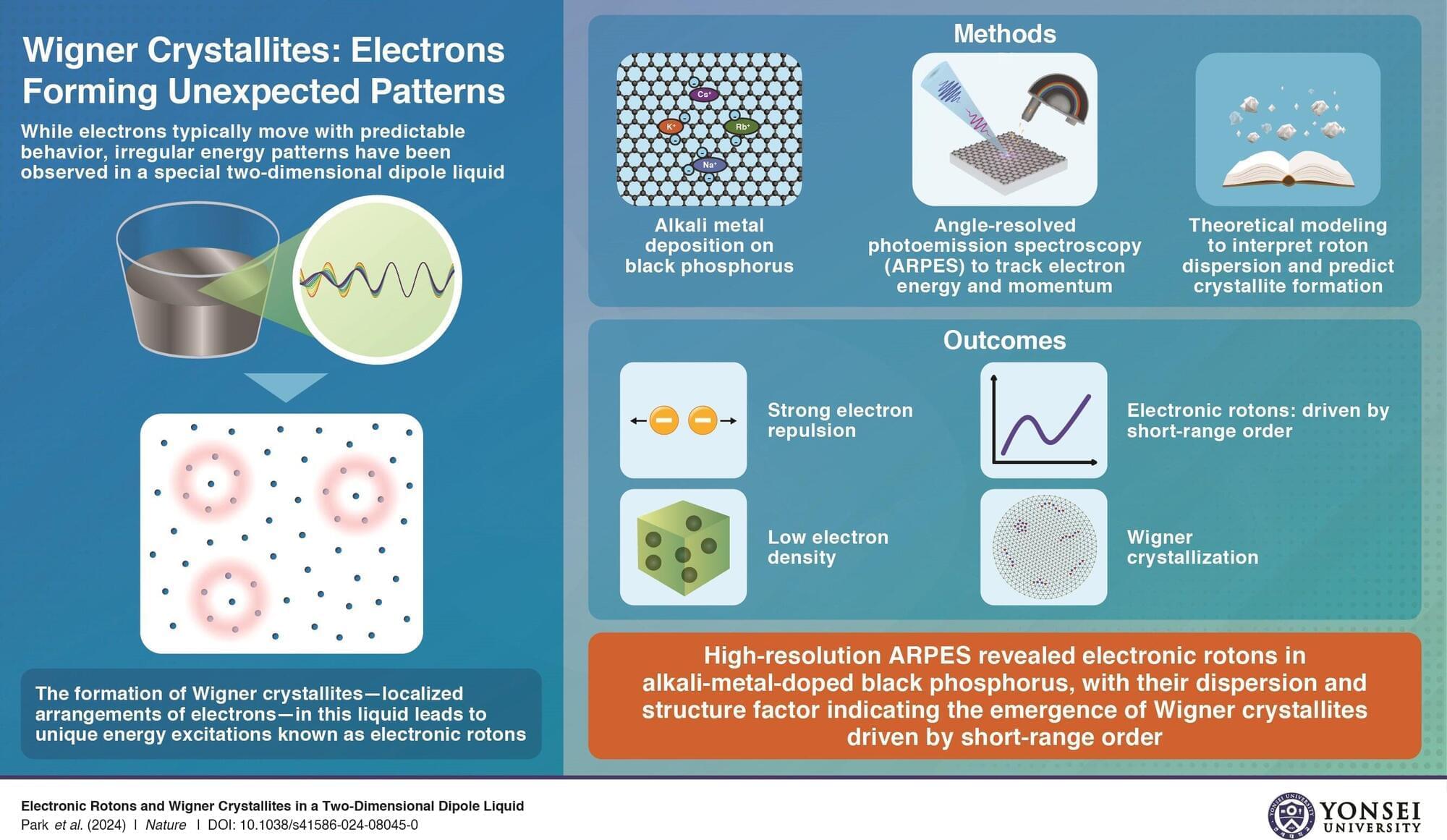
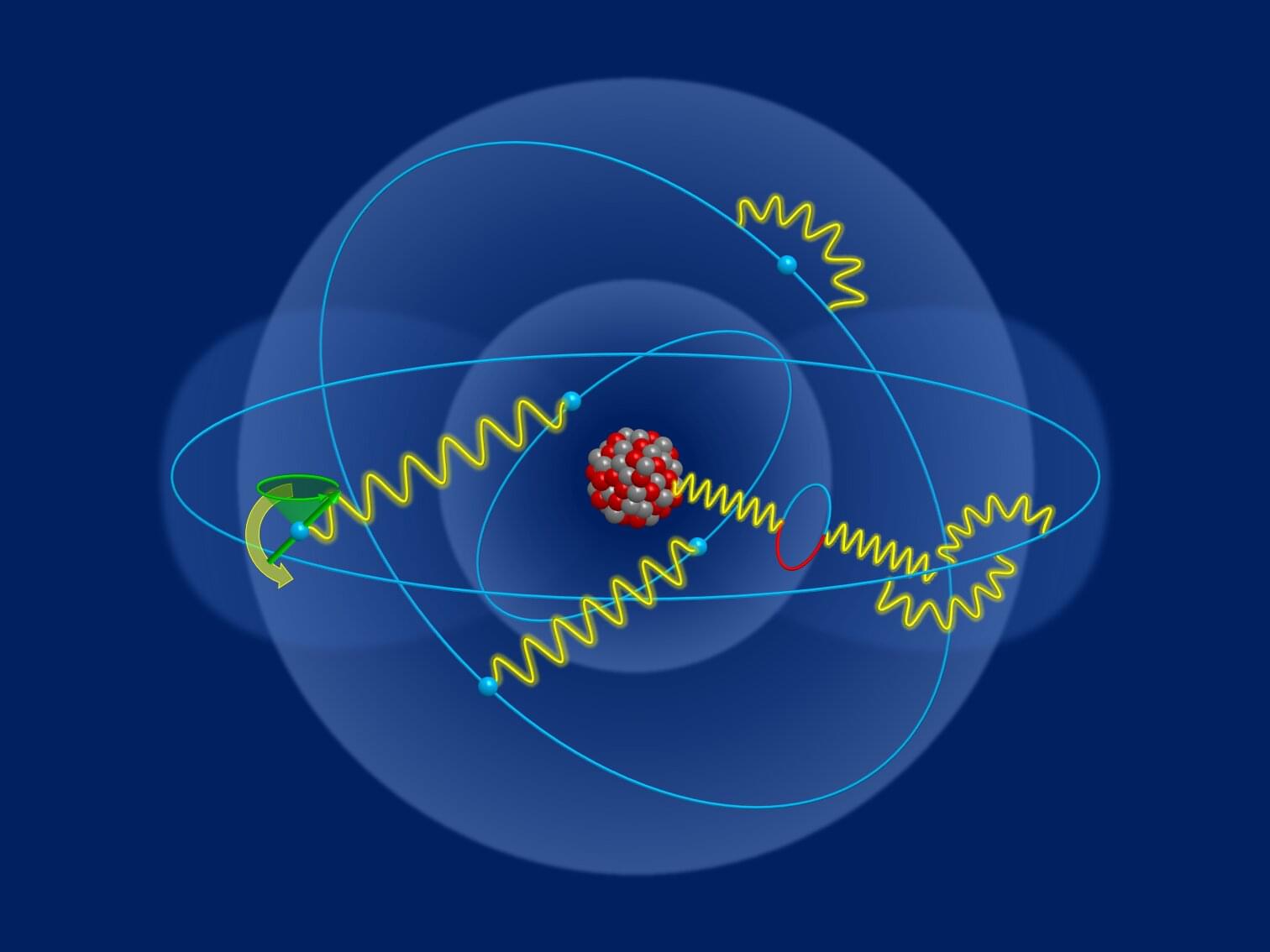
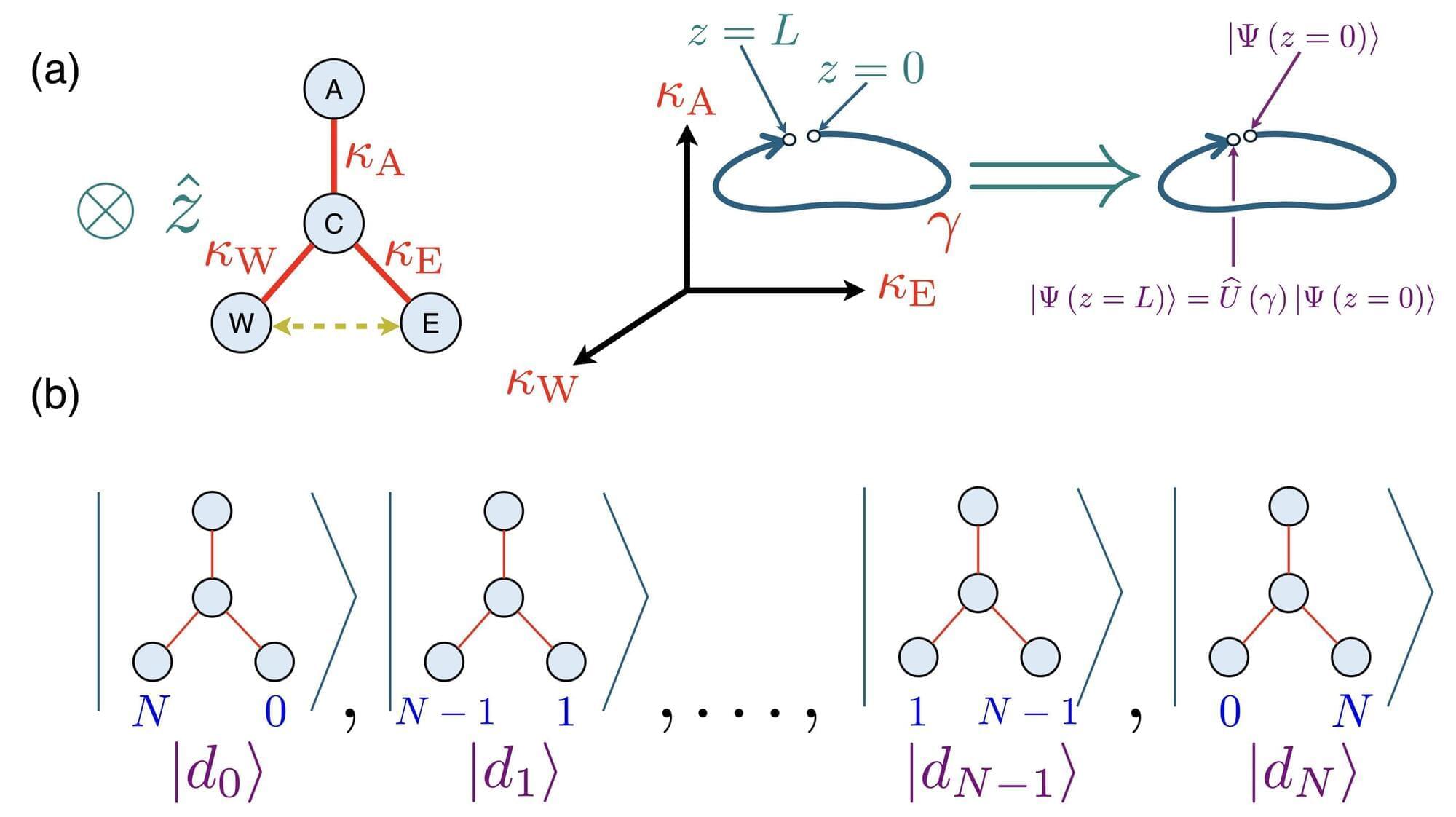
Together with an international team of researchers from the Universities of Southern California, Central Florida, Pennsylvania State and Saint Louis, physicists from the University of Rostock have developed a novel mechanism to safeguard a key resource in quantum photonics: optical entanglement. Their discovery is published in Science.
Declared as the International Year of Quantum Science and Technology by the United Nations, 2025 marks 100 years since the initial development of quantum mechanics. As this strange and beautiful description of nature on the smallest scales continues to fascinate and puzzle physicists, its quite tangible implications form the basis of modern technology as well as material science, and are currently in the process of revolutionizing information science and communications.
A key resource to quantum computation is so-called entanglement, which underpins the protocols and algorithms that make quantum computers exponentially more powerful than their classical predecessors. Moreover, entanglement allows for the secure distribution of encryption keys, and entangled photons provide increased sensitivity and noise resilience that dramatically exceed the classical limit.