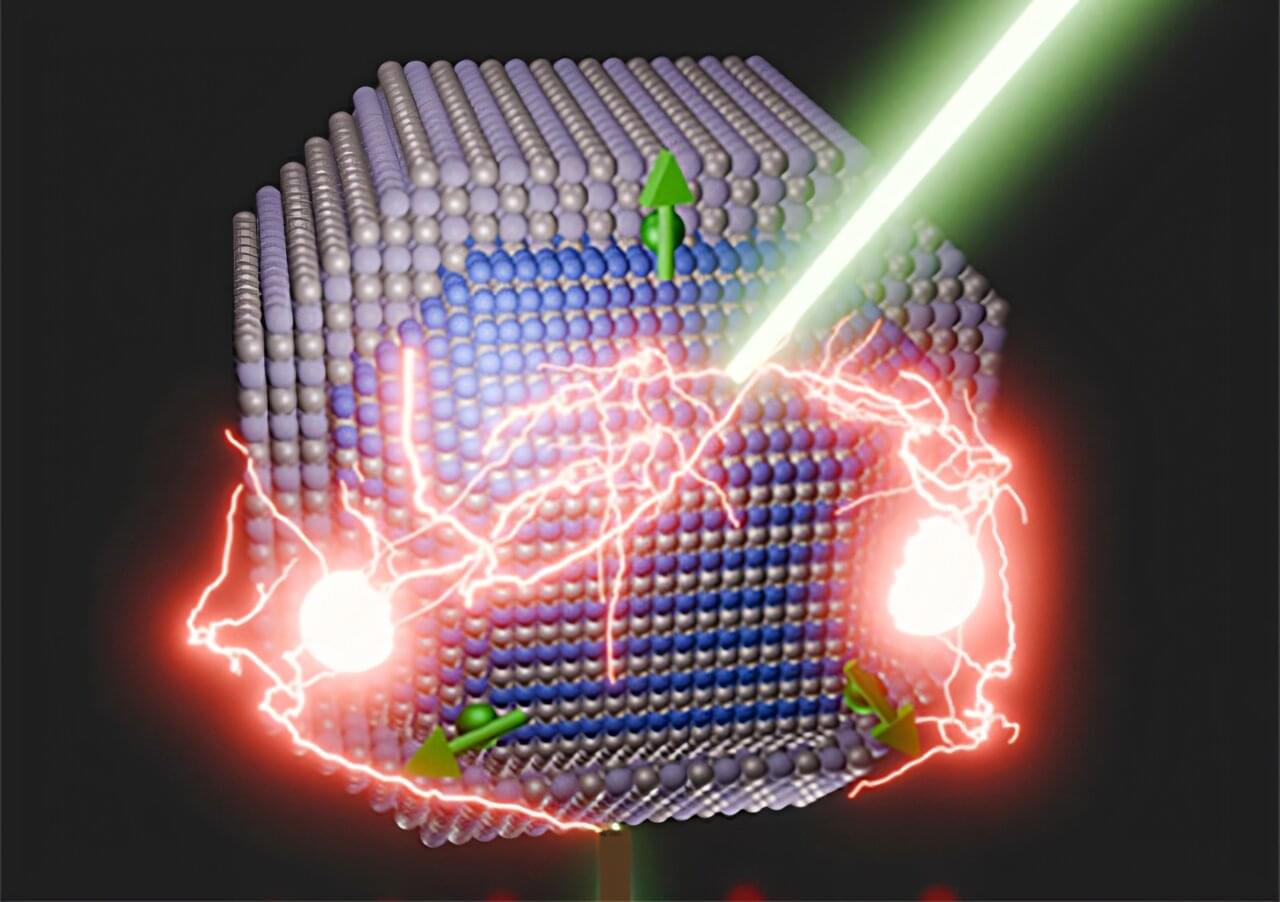
Quantum dots are microscopic semiconductor crystals developed in the lab that share many properties with atoms, including the ability to absorb or emit light, a technology that Los Alamos researchers have spent nearly three decades evolving. Through carrier multiplication, in which a single absorbed photon generates two electron-hole pairs, called excitons, quantum dots have the unique ability to convert photons more efficiently to energy.
“Our work demonstrates how purely quantum mechanical spin-exchange interactions can be harnessed to enhance the efficiency of photoconversion devices or photochemical reactions,” says Victor Klimov, the team’s principal investigator at the Lab. “This not only deepens our fundamental understanding of quantum mechanical phenomena but also introduces a new paradigm for designing advanced materials for energy applications.”
In this latest research, published in the journal Nature Communications, Los Alamos researchers improved this ability by introducing magnetic manganese impurities into quantum dots. This novel approach to highly efficient carrier multiplication leverages ultrafast spin-exchange interactions mediated by manganese ions to capture the energy of energetic (hot) carriers generated by incident photons and convert it into additional excitons.