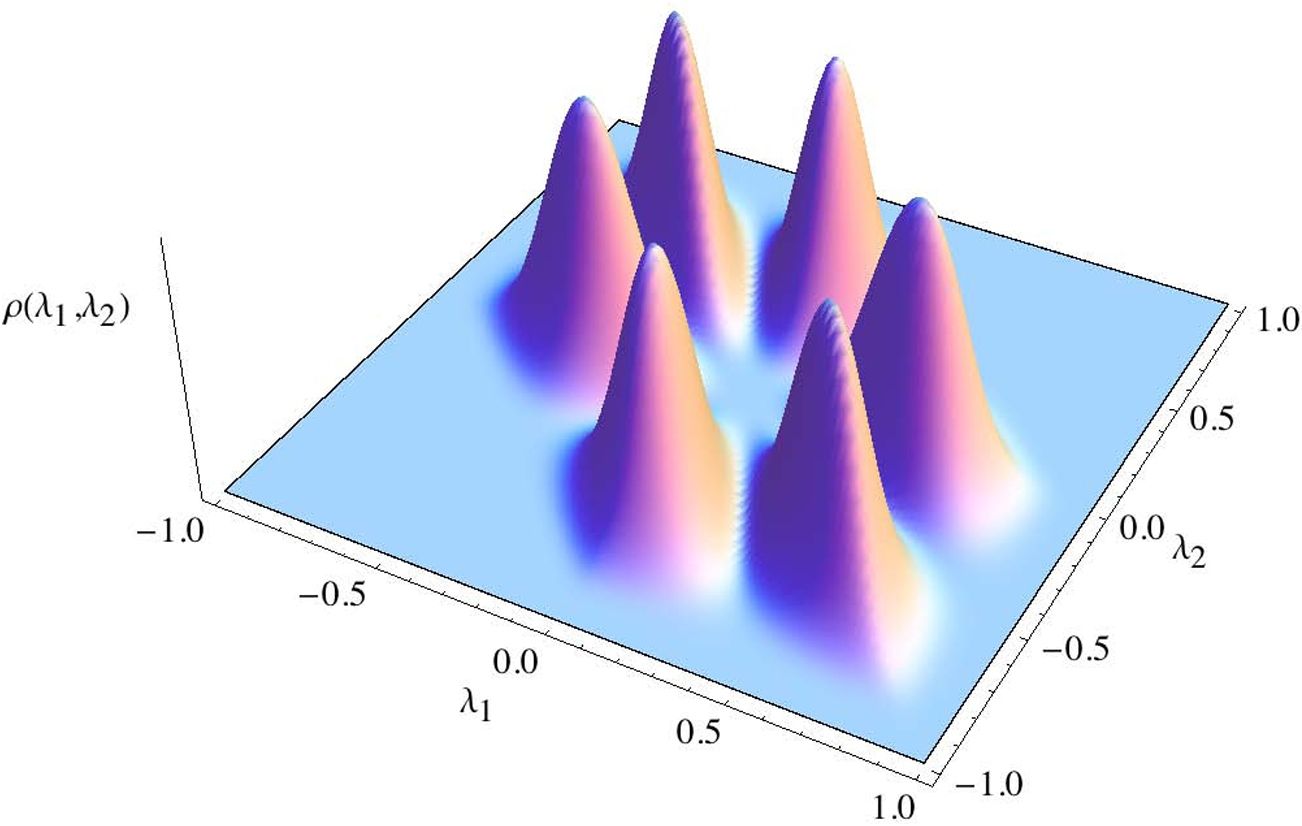
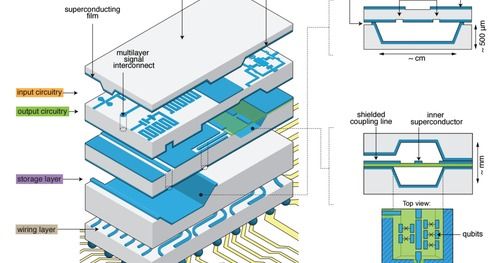
Quantum will be the most important technology in 2017; as it will touch everything as well as change everything. Until we see a better integration of AR in Enterprise Apps, platforms, and published services; AR like VR will remain a niche market gadget.
I do know companies like Microsoft, SAP, and Oracle have been looking at ways to leverage AR in their enterprise platforms and services such as ERP and CRM as well as Big Data Analytics; however, to see the volume of sales needed to make VR or AR have staying power on a large scale; the vendors will need to it a pragmatic useful device on multiple fronts. And, yes it is great that we’re using VR and AR in healthcare, defense, engineering, and entertainment (includes gaming); we just need to make it an every consumer device that people canot live with out.
2016 has been a remarkable year that’s brought continued growth and awareness to the worlds of Augmented, Virtual and Mixed Reality. Set to become a $165 Billion dollar industry by 2020, there’s still a common question that lingers among many newcomers trying to understand this fast moving digital phenomena we are just beginning to watch evolve: What’s the difference between them and how will it impact the digital world as I currently know it?
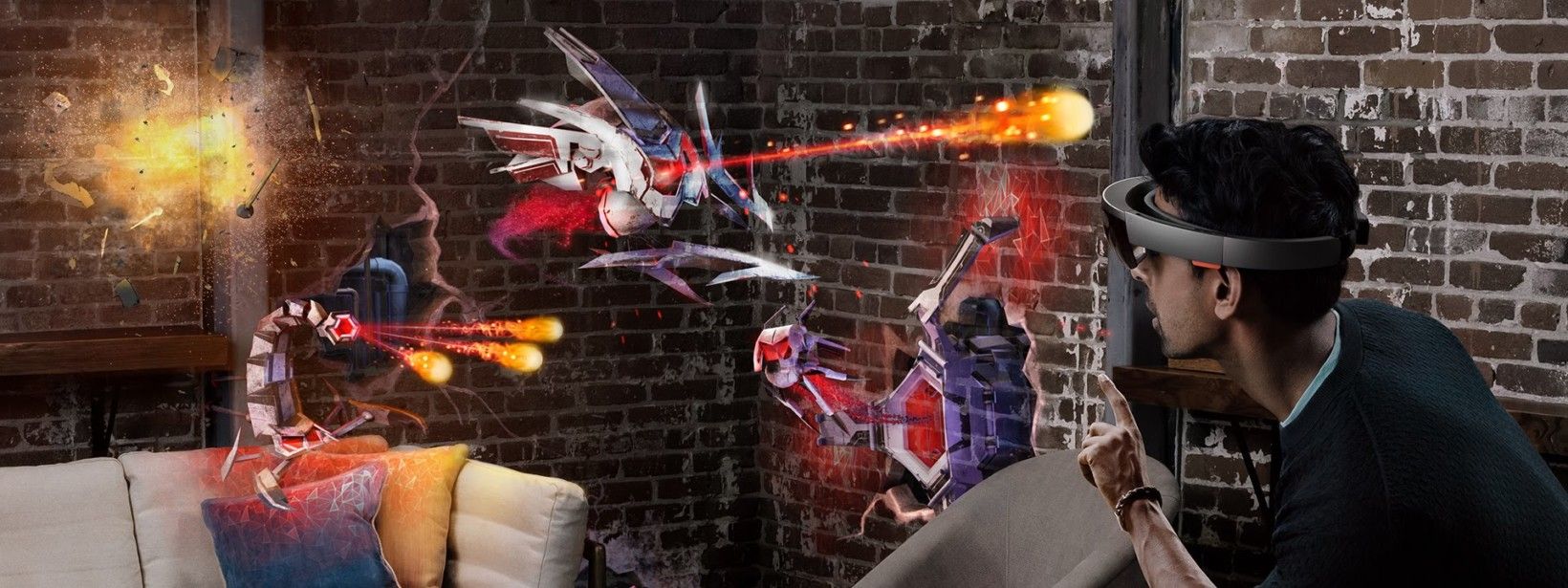
Before we jump into the mind-blowing future Mixed Reality is set to usher in over the course of 2017, let’s first discuss the distinctions between Virtual and Augmented Reality. Their technologies are very similar but have some fundamental differences.
TNW is at CES 2017! Get the low-down on the latest and most insane tech being showcased in Las Vegas.