I’m not that interested in this on the movie end, because i think most movies already suck, and couldnt really get any worse.
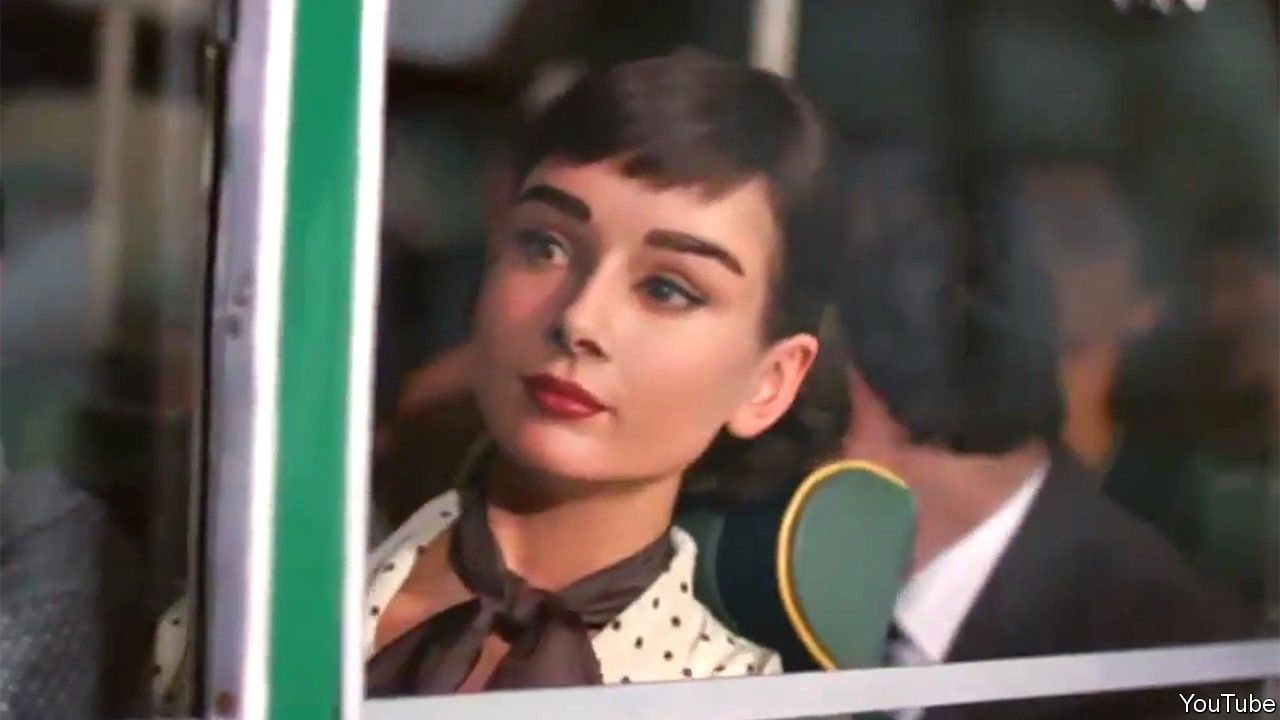
AUDREY HEPBURN DIED in 1993, but in 2013 she nevertheless starred in an advertisement for Galaxy, a type of chocolate bar. She was shown riding a bus along the Amalfi coast before catching the eye of a passing hunk in a convertible. In 2016 Peter Cushing, who died in 1994, reprised his role as the villainous Grand Moff Tarkin in the Star Wars film “Rogue One”. Such resurrections are not new, but they are still uncommon enough to count as news. Yet advances in special effects—and, increasingly, in artificial intelligence (AI)—are making it ever easier to manufacture convincing forgeries of human beings.
In recent months this has led to concern that propagandists will use the technology to generate videos in which political figures appear to say compromising things. A video created by BuzzFeed, a news website, in April shows Barack Obama apparently saying “We’re entering an era in which our enemies can make it look like anyone is saying anything at any point in time,” for example. In May a Belgian political party produced a fake video of Donald Trump saying implausible things about Belgium’s climate policy. In both cases the video looks slightly off, and the voice is provided by an impersonator. But the technology is improving fast, prompting a dozen AI researchers to place bets on whether a fake video will disrupt America’s midterm elections later this year. (Tim Hwang, a Harvard academic, is overseeing the wager.)
Whatever happens in the arena of fake news, the same techniques are sure to revolutionise fiction of a different kind, in the form of film and television. In future, actors need not be creatures of flesh and blood, but could, like so many other things in an increasingly digitised world, exist as nothing more than long strings of 1s and 0s. Such digital actors would sit quietly in digital storage systems until their services were needed—there would be no need for luxury trailers, chefs and make-up people.