With just an iPad, students in any classroom across the world could soon reimagine the ordinary diagrams in any physics textbook—transforming these static images into 3D simulations that run, leap or spin across the page.
Category: physics – Page 91
The Mind of the Body: A Window into Embodiment and our Future
Metaphysics and the Matter with Things: Thinking with Iain McGilchrist was a collaborative conference put on by the Center for Process Studies (CPS) and the California Institute of Integral Studies (CIIS) in March of 2024. This three-day conference brought leading process thinkers across various disciplines, including physics, neuroscience, psychology, philosophy, and theology into critical dialogue with McGilchrist’s work in a collegial effort to assess, question, extend, and apply it. For more information on the conference and to purchase recordings, please visit https://ctr4process.org/mcgilchrist-conference/
How Physicists Broke the Solar Efficiency Record
This solar breakthrough just changed everything.
Thanks to Opera for sponsoring this video. Click here https://opr.as/Opera-browser-DrBenMiles to upgrade your browser for FREE!
Last month, Oxford PV’s breakthrough solar cell broke the efficiency world record and is the world’s first commercially available Perovskite solar panel.
How does it work? And what does this mean for the future of solar?
Thanks you so much to the team for allowing me behind the scenes into their development facility and for the free Halloween costume.
#solar #efficiency #breakthrough #physics #perovskite.
Chapters.
0:00 The Solar Power Breakthrough.
3:25 Humanity’s Journey to Capture the Sun.
8:46 How We Broke the Limit of Solar Efficiency.
13:15 Building the World’s First Perovskite Solar Panel.
17:23 The Future of Solar.
🚀 JOIN US for members-only content: https://www.patreon.com/DrBenMiles.


1992, 31 October
On this day in 1992, the Vatican admitted that Galileo was correct in believing that the earth went around the sun.
2. In the first place, I wish to congratulate the Pontifical Academy of Sciences for having chosen to deal, in its plenary session, with a problem of great importance and great relevance today: the problem of ‘the emergence of complexity in mathematics, physics, chemistry and biology’
The emergence of the subject of complexity probably marks in the history of the natural sciences a stage as important as the stage which bears relation to the name of Galileo, when a univocal model of order seemed to be obvious. Complexity indicates precisely that, in order to account for the rich variety of reality, we must have recourse to a number of different models.
This realisation poses a question which concerns scientists, philosophers and theologians: how are we to reconcile the explanation of the world – beginning with the level of elementary entities and phenomena – with the recognition of the fact that ‘the whole is more than the sum of its parts’?
Cosmic Inflation Explained | Cosmology 101 Episode 6
In this episode of Cosmology 101, we learn how the detection of the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) validated the Big Bang Theory and led to the development of the concept of cosmic inflation.
Explore the challenges and ongoing debates in cosmology as scientists seek to uncover the true nature of the early universe and the origins of cosmic structure.
Join Katie Mack, Perimeter Institute’s Hawking Chair in Cosmology and Science Communication, on an incredible journey through the cosmos in our new series, Cosmology 101.
Sign up for our newsletter and download exclusive cosmology posters at: https://landing.perimeterinstitute.ca…
Follow the edge of theoretical physics on our social media:
/ pioutreach.
https://twitter.com/perimeter.
/ perimeterinstitute.
/ perimeter-institute.
Follow our host \.
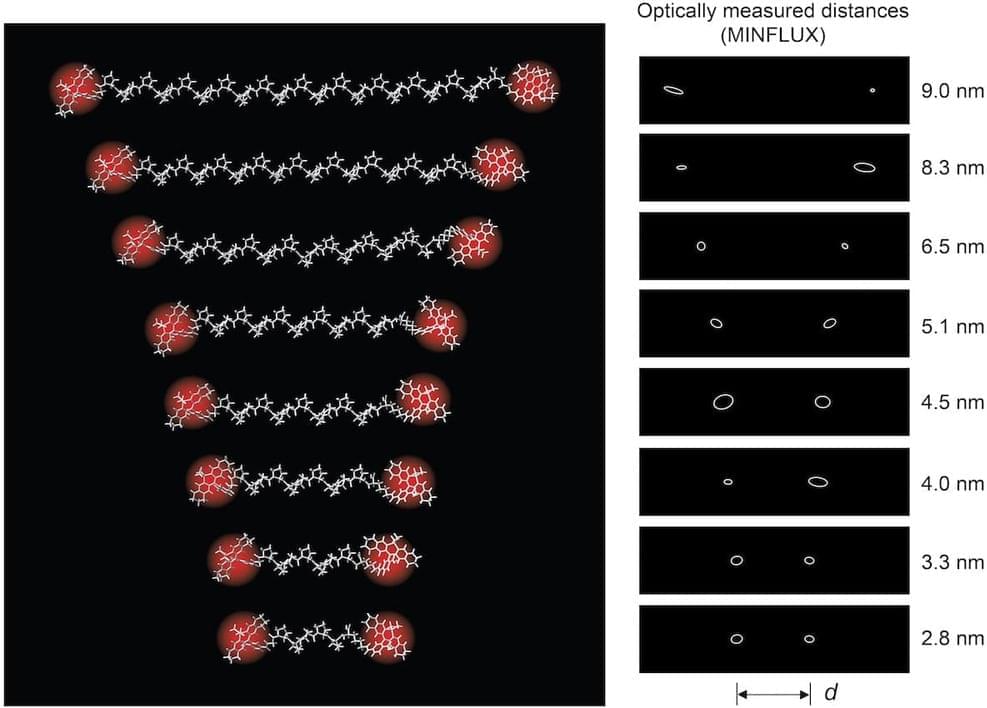
Optical technique measures intramolecular distances with angstrom precision
Physicists in Germany have used visible light to measure intramolecular distances smaller than 10 nm thanks to an advanced version of an optical fluorescence microscopy technique called MINFLUX. The technique, which has a precision of just 1 angstrom (0.1 nm), could be used to study biological processes such as interactions between proteins and other biomolecules inside cells.
In conventional microscopy, when two features of an object are separated by less than half the wavelength of the light used to image them, they will appear blurry and indistinguishable due to diffraction. Super-resolution microscopy techniques can, however, overcome this so-called Rayleigh limit by exciting individual fluorescent groups (fluorophores) on molecules while leaving neighbouring fluorophores alone, meaning they remain dark.
One such technique, known as nanoscopy with minimal photon fluxes, or MINFLUX, was invented by the physicist Stefan Hell. First reported in 2016 by Hell’s team at the Max Planck Institute (MPI) for Multidisciplinary Sciences in Göttingen, MINFLUX first “switches on” individual molecules, then determines their position by scanning a beam of light with a doughnut-shaped intensity profile across them.
Is There Really a Hard Problem of Consciousness? — Joscha Bach, Artificial Intelligence Researcher
Joscha Bach is a German artificial intelligence researcher and cognitive scientist who works on on cognitive architectures, mental representation, emotion, social modeling, and multi-agent systems. We got connected over the hard problem of consciousness — namely, why do people seem to think it’s so hard? During our conversation we deal with the foundational questions of the technological future being built in Silicon Valley, the fever dream of machine intelligence, and try to understand why people seem to think that there’s even such a thing as the hard problem of consciousness in the first place.
Support the scientific revolution by joining our Patreon: https://bit.ly/3lcAasB
Tell us what you think in the comments or on our Discord: https://discord.gg/MJzKT8CQub.
00:00:00 Go!
00:04:09 Career Advice.
00:11:31 Beauty, Grace, & Hotness.
00:13:48 Putting on Airs.
00:22:32 Patreon Ask.
00:22:33 Winning for the sake of winning.
00:29:35 Transformative experiences.
00:36:25 Speciation event, or crap again?
00:42:17 Who is Joscha Bach.
00:52:39 Physics & Causality.
01:00:52 Physics vs Biology.
01:12:16 Life vs Cells.
01:20:14 Biosynthetic AGI
01:28:15 Creativity & Novelty.
01:38:52 Wetware & Neuromorphic computing.
01:50:46 The Limits of Hardware.
02:05:07 The value of Agency.
02:15:47 Layers of Society.
02:35:03 Chimp Empire.
02:52:31 Collapse.
03:05:13 The Hard Problem.
03:43:28 Computer Imagination.
04:02:52 How reasoning works.
04:14:28 Reward Functions.
04:20:01 Consciousness dreams.
04:25:35 The heart of the disagreement.
04:30:15 Consensus.
#AGI #consciousness #machinelearning.
Check our short-films channel, @DemystifySci: https://www.youtube.com/c/DemystifyingScience.

Research team achieves first-ever acceleration of positive muons to 100 keV
A team of engineers and physicists affiliated with a host of institutions across Japan, working at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, has demonstrated acceleration of positive muons from thermal energy to 100 keV—the first time muons have been accelerated in a stable way. The group has published a paper describing their work on the arXiv preprint server.
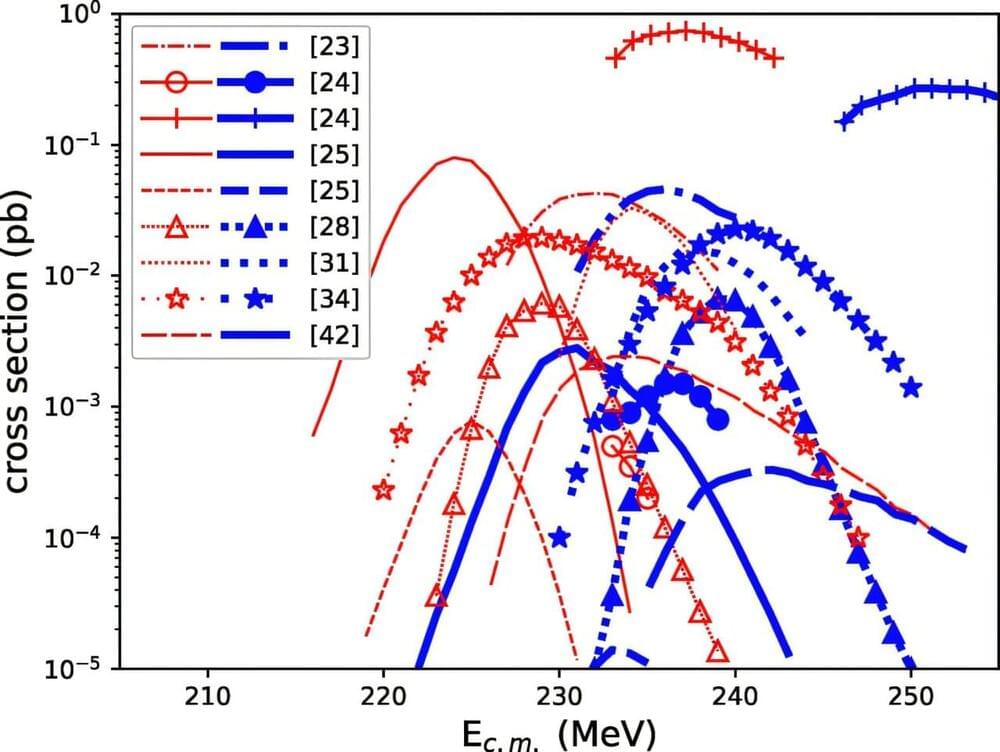
Successful experiment paves the way for discovery of a new element
The search for new elements comes from the dream of finding a variant that is sufficiently stable to be long-lived and not prone to immediate decay. There is a theory in nuclear physics about an island of stability of superheavy elements. This is a potential zone in the upper part of the periodic table of as-yet-undiscovered elements that could remain stable for longer than just a few seconds. The aim is to explore the limits of stability of atomic nuclei.