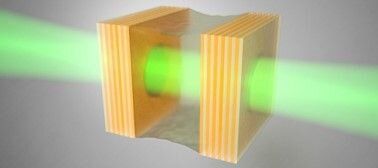
A simple drop of olive oil in a system of photons bouncing between two mirrors has revealed universal aspects of phase transitions in physics. Researchers at AMOLF used an oil-filled optical cavity in which light undergoes phase transitions similar to those in boiling water. The system they studied has memory because the oil causes photons to interact with themselves. By varying the distance between the two mirrors and measuring the transmission of light through the cavity, they discovered a universal law describing phase transitions in systems with memory. These results are published on April 15th in Physical Review Letters.
The Interacting Photons research group at AMOLF studies nonlinearity and noise in photonic systems. One of such systems is a cavity, formed by two mirrors facing each other at a close distance. Within the cavity, light bounces back and forth as it is reflected by the mirrors. Putting something inside such an optical cavity, changes the properties of the system. “We created a system with memory by placing a drop of olive oil inside the cavity,” says group leader Said Rodriguez. “The oil mediates effective photon-photon interactions, which we can see by measuring the transmission of laser light through this cavity.”