The next big questions in particle physics, a talk by CERN’s Director-General, Fabiola Gianotti.
- Set-up: regular talk with wash out lights and with one hand mic — ppt Presentation no sound — English translated to FR.
The next big questions in particle physics, a talk by CERN’s Director-General, Fabiola Gianotti.
- Set-up: regular talk with wash out lights and with one hand mic — ppt Presentation no sound — English translated to FR.
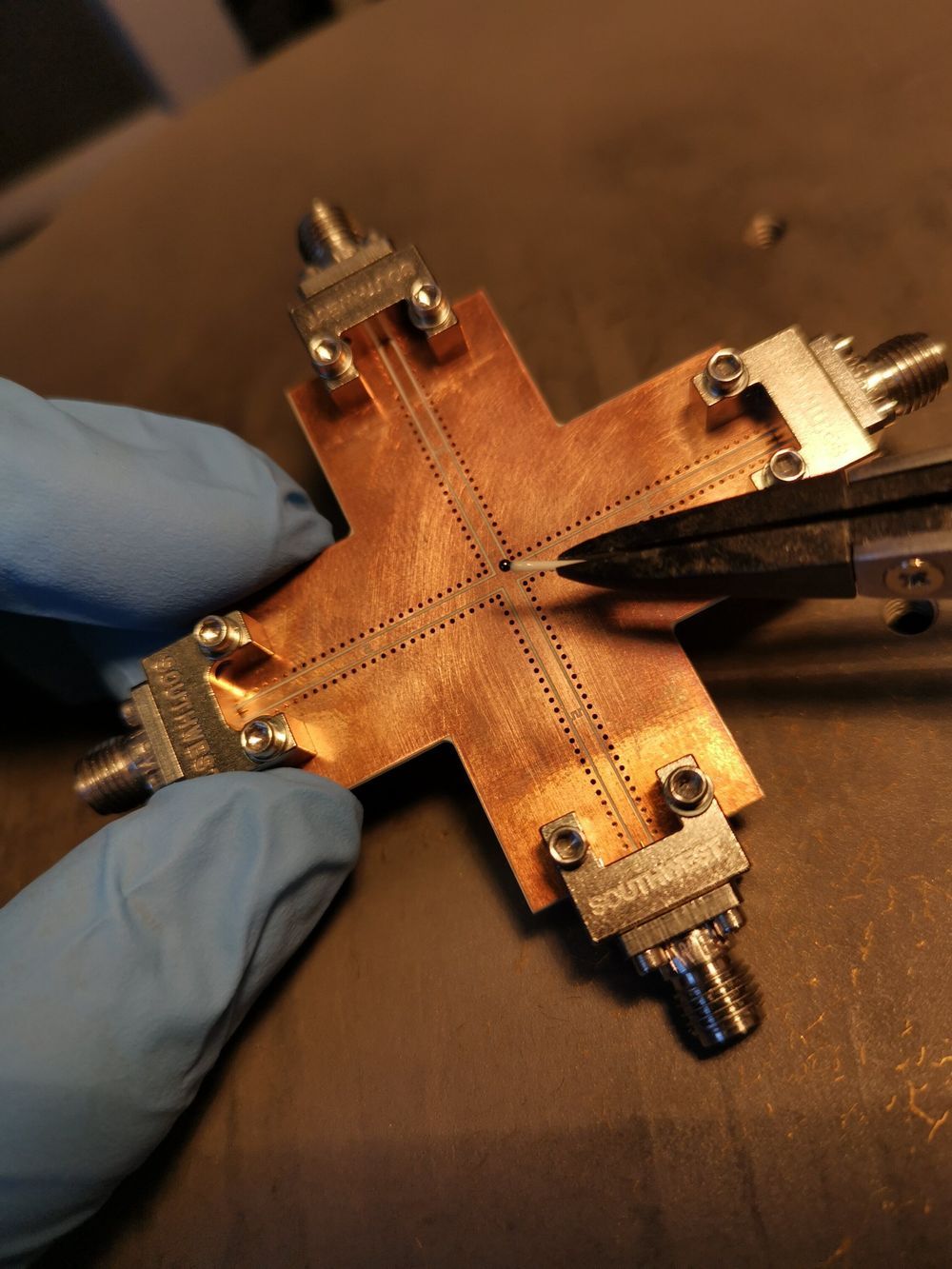

As quantum objects are susceptible to their surrounding environment, quantum coherence and quantum states can easily be destroyed due to the impact of external signals, which can include thermal noise and backscattered signals in the measurement circuit. Researchers have thus been trying to develop techniques to enable nonreciprocal signal propagation, which could help to block the undesired effects of backward noise.
In a recent study, members of the dynamic spintronics group at the University of Manitoba in Canada have proposed a new method to produce dissipative coupling in hybrid quantum systems. Their technique, presented in a paper published in Physical Review Letters, enables nonreciprocal signal propagation with a substantial isolation ratio and flexible controllability.
“Our recent work on nonreciprocity in cavity magnonics is grounded in a research area combining cavity spintronics and hybrid quantum systems, which holds promise for constructing new quantum information processing platforms,” Yi-Pu Wang, a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Manitoba who was involved in the study, told Phys.org.
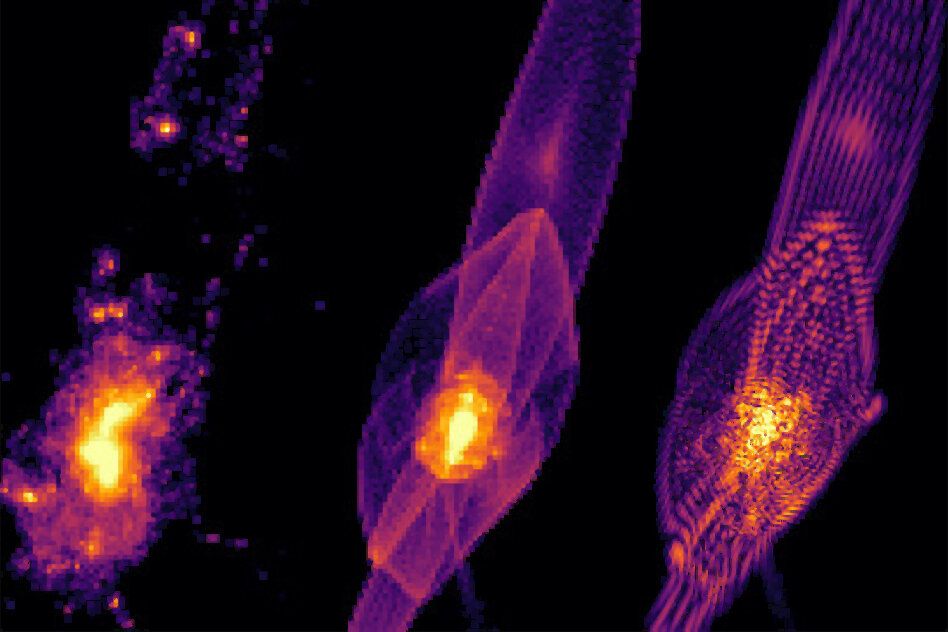
Dark matter was likely the starting ingredient for brewing up the very first galaxies in the universe. Shortly after the Big Bang, particles of dark matter would have clumped together in gravitational “halos,” pulling surrounding gas into their cores, which over time cooled and condensed into the first galaxies.
Although dark matter is considered the backbone to the structure of the universe, scientists know very little about its nature, as the particles have so far evaded detection.
Now scientists at MIT, Princeton University, and Cambridge University have found that the early universe, and the very first galaxies, would have looked very different depending on the nature of dark matter. For the first time, the team has simulated what early galaxy formation would have looked like if dark matter were “fuzzy,” rather than cold or warm.
After counting all the normal, luminous matter in the obvious places of the universe – galaxies, clusters of galaxies and the intergalactic medium – about half of it is still missing. So not only is 85 percent of the matter in the universe made up of an unknown, invisible substance dubbed “dark matter”, we can’t even find all the small amount of normal matter that should be there.
This is known as the “missing baryons” problem. Baryons are particles that emit or absorb light, like protons, neutrons or electrons, which make up the matter we see around us. The baryons unaccounted for are thought to be hidden in filamentary structures permeating the entire universe, also known as “the cosmic web”.
But this structure is elusive and so far we have only seen glimpses of it. Now a new study, published in Science, offers a better view that will enable us to help map what it looks like.


Energy is a quantity that must always be positive—at least that’s what our intuition tells us. If every single particle is removed from a certain volume until there is nothing left that could possibly carry energy, then a limit has been reached. Or has it? Is it still possible to extract energy even from empty space?
Quantum physics has shown time and again that it contradicts our intuition, which is also true in this case. Under certain conditions, negative energies are allowed, at least in a certain range of space and time. An international research team at the TU Vienna, the Université libre de Bruxelles (Belgium) and the IIT Kanpur (India) have now investigated the extent to which negative energy is possible. It turns out that no matter which quantum theories are considered, no matter what symmetries are assumed to hold in the universe, there are always certain limits to “borrowing” energy. Locally, the energy can be less than zero, but like money borrowed from a bank, this energy must be “paid back” in the end.
Investigating the heaviest elements known is rewriting our knowledge of chemistry and may even mean the end of the periodic table itself, writes Kit Chapman.
In 2018, Peter Schwerdtfeger published a paper that turned chemistry on its head. According to calculations he and his colleagues performed, oganesson – element 118, the heaviest known – was not a noble gas as you would expect from its position in the periodic table, but a highly reactive solid. Even stranger, it didn’t seem to have electron shells.1
‘Well, that statement is oversimplified,’ says Schwerdtfeger, a theoretical chemist at Massey University in New Zealand. ‘You can still build up the electron densities from orbitals describing individual shells. What happens is that for oganesson the shell structure is barely visible, approaching an electron gas.’
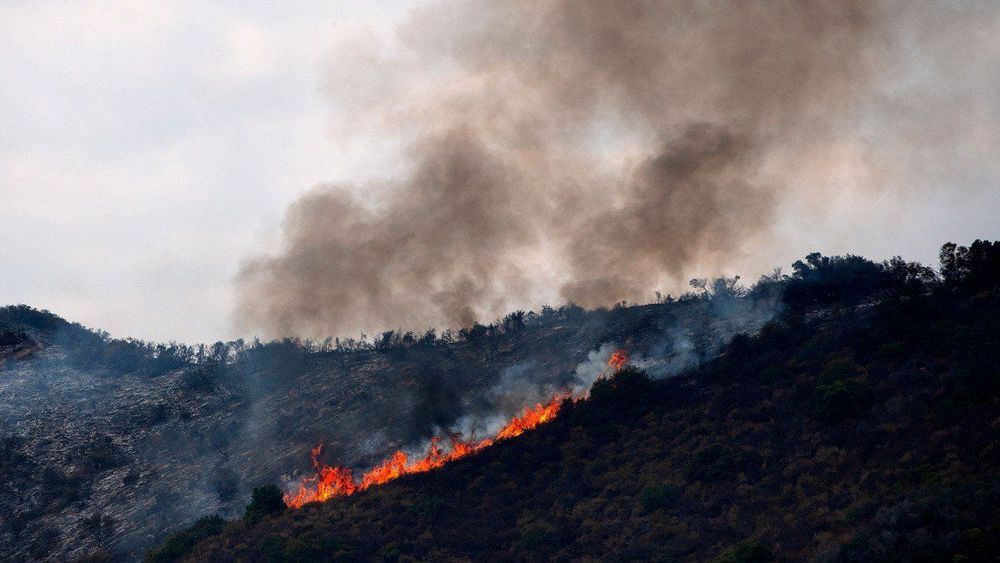

The news: A gel developed by Stanford researchers could be sprayed on forests and vegetation to make them fire-resistant, helping to stop wildfires from spreading. It’s made from cellulose polymers (extracted from plants) and particles of silica, which are chemically identical to sand, mixed with a flame-retardant fluid.
How to use it: Fire-fighting sprays are currently used on wildfires only in emergencies: this new approach would deploy them protectively before any fires can break out. In a paper in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the researchers say the gel is nontoxic and biodegradable.
Rain-resistant: The team tested the gel on plants in the laboratory and then on patches of grass by a road in California, supervised by local firefighters. They found it can withstand wind and up to half an inch of rain, so iy only needs to be applied once per fire season (if it rains more than that, the risk of wildfires plummets anyway).
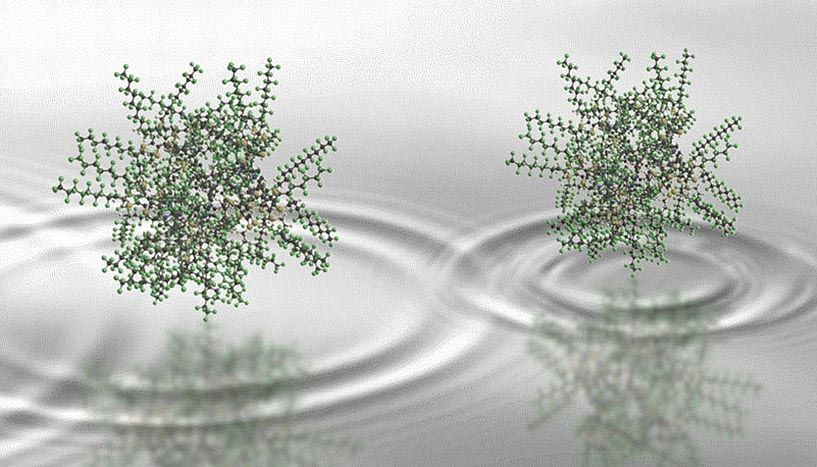
The quantum superposition principle has been tested on a scale as never before in a new study by scientists at the University of Vienna in collaboration with the University of Basel. Hot, complex molecules composed of nearly two thousand atoms were brought into a quantum superposition and made to interfere. By confirming this phenomenon – “the heart of quantum mechanics”, in Richard Feynman’s words – on a new mass scale, improved constraints on alternative theories to quantum mechanics have been placed. The work was published in Nature Physics on September 23, 2019.
Quantum to classical?
The superposition principle is a hallmark of quantum theory which emerges from one of the most fundamental equations of quantum mechanics, the Schrödinger equation. It describes particles in the framework of wave functions, which, much like water waves on the surface of a pond, can exhibit interference effects. But in contrast to water waves, which are a collective behavior of many interacting water molecules, quantum waves can also be associated with isolated single particles.

Geneva. Arts at CERN announces two open calls for art residencies – Collide Geneva/Dance and Accelerate Finland – and the arrival of the winners of Collide International, Rosa Menkman, and Collide Pro Helvetia, Christina Hemauer and Roman Keller. The art residency programmes are based on the particle physics laboratory’s cultural strategy, which aims to foster networks between local and international organisations through platforms that engage art and science.
“Arts at CERN plays an important role in augmenting the interest seen in the interaction of the arts and sciences in recent years. By inviting artists and scientists to have a dialogue in the Laboratory, the programme shows how the two fields impact one another. I am proud to announce new opportunities for participation, and to welcome artists-in-residence this autumn,” says Mónica Bello, head of Arts at CERN.
For the sixth Collide Geneva residency, Arts at CERN, the Republic and Canton of Geneva and the City of Geneva have joined forces. The three-month fully funded residency award will be granted to a Geneva-based artist or artist collective working in the field of dance. The winner will have the opportunity to carry out their research at CERN and work together with particle physicists, engineers and IT professionals. Collide Geneva/Dance encourages applications from dance artists inspired by scientific ideas or technological concepts, with innovative approaches in their artistic expression.