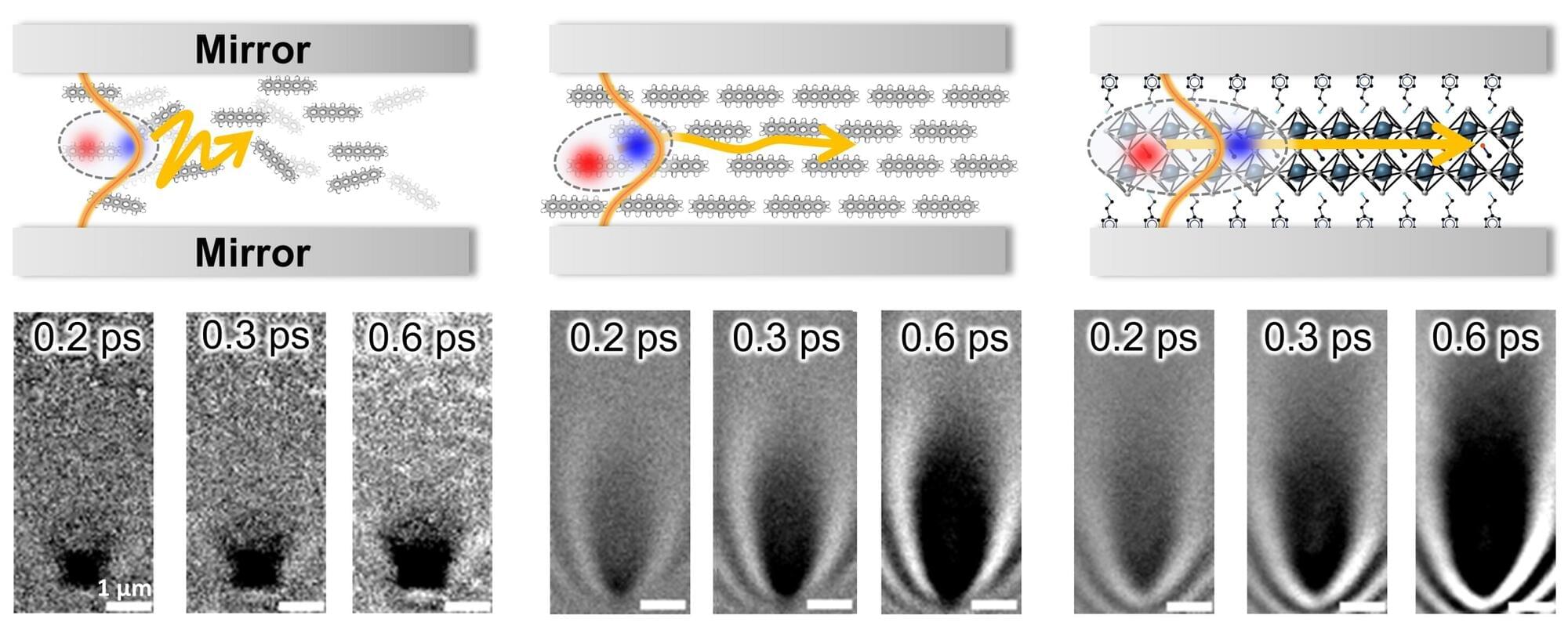
Imagine industrial processes that make materials or chemical compounds faster, cheaper, and with fewer steps than ever before. Imagine processing information in your laptop in seconds instead of minutes or a supercomputer that learns and adapts as efficiently as the human brain. These possibilities all hinge on the same thing: how electrons interact in matter.
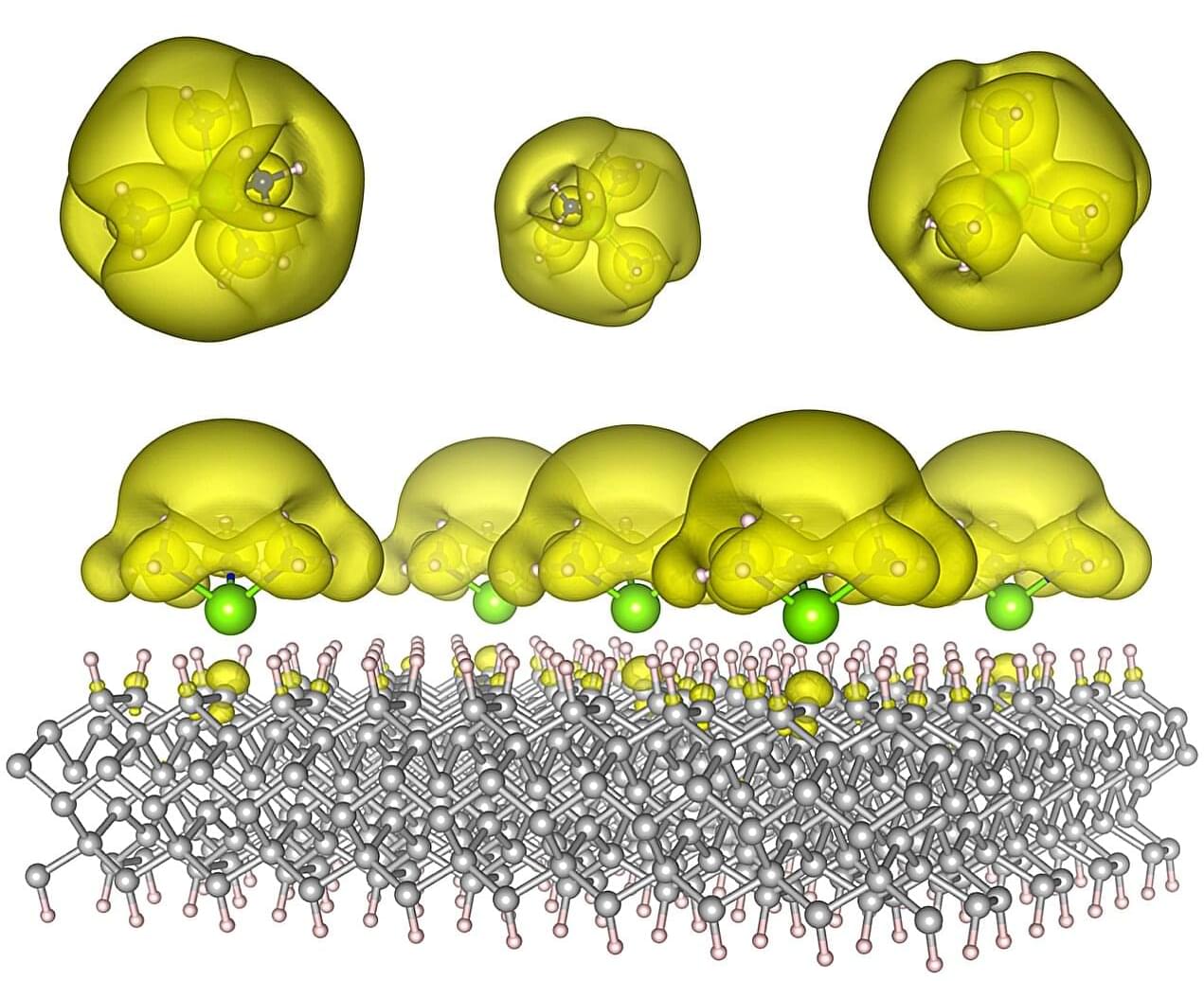
A team of Auburn University scientists has now designed a new class of materials that gives scientists unprecedented control over these tiny particles. Their study, published in ACS Materials Letters, introduces the tunable coupling between isolated-metal molecular complexes, known as solvated electron precursors, where electrons aren’t locked to atoms but instead float freely in open spaces.
From their key role in energy transfer, bonding, and conductivity, electrons are the lifeblood of chemical synthesis and modern technology. In chemical processes, electrons drive redox reactions, enable bond formation, and are critical in catalysis. In technological applications, manipulating the flow and interactions between electrons determines the operation of electronic devices, AI algorithms, photovoltaic applications, and even quantum computing. In most materials, electrons are bound tightly to atoms, which limits how they can be used. But in electrides, electrons roam freely, creating entirely new possibilities.