A new imaging technique, which captured frozen lithium atoms transforming into quantum waves, could be used to probe some of the most poorly understood aspects of the quantum world.




Quantum mechanics, the most potent theory physicists have developed, doesn’t make sense. What I mean by that statement is that quantum mechanics — which was developed to describe the microworld of molecules, atoms, and subatomic particles — leaves its users without a common-sense picture of what it describes. Full of what seem to be paradoxes and puzzles, quantum physics demands, for most scientists, an interpretation: a way of making sense of its mathematical formalism in terms of a concrete description of what exists in the world and how we interact with it. Unfortunately, after a century not one but a basketful of “quantum interpretations” have been proposed. Which one is correct? Which one most clearly understands what quantum physics has been trying to tell us these past 100 years?
In light of these questions, I’m beginning a series that explores the most radical of all the quantum interpretations, the one I think gets it right, or at least is pointed in the right direction. It is a relative newcomer to the scene, so you may not have heard of it. But it has been gaining a lot of attention recently because it doesn’t just ask us to reimagine how we view the science of atoms; it asks us to reimagine the process of science itself.
The term “QBism” was shorthand for “Quantum Bayesianism” when this idea/theory/interpretation was first proposed in the late 1990s and early 2000s. The name hit the nail on the head because “Bayesianism” is a radical way of interpreting probabilities. The Bayesianist approach to what we mean by probability differs strongly from what you learned in school about coin flips and dice rolls and how frequently a particular result can be expected to appear. Since probabilities lie at the heart of quantum mechanics, QBism zeroed in on a key aspect of quantum formalism — one that other interpretations had missed or swept under the rug — because it focused squarely on how we interpret probabilities. We’re going to dig deep into all of this as we go along in this series, but since today’s column is supposed to be the introduction, let’s start with a 10,000-foot view of what’s at stake in the great “Quantum Interpretation Wars” so we can see where QBism fits in.
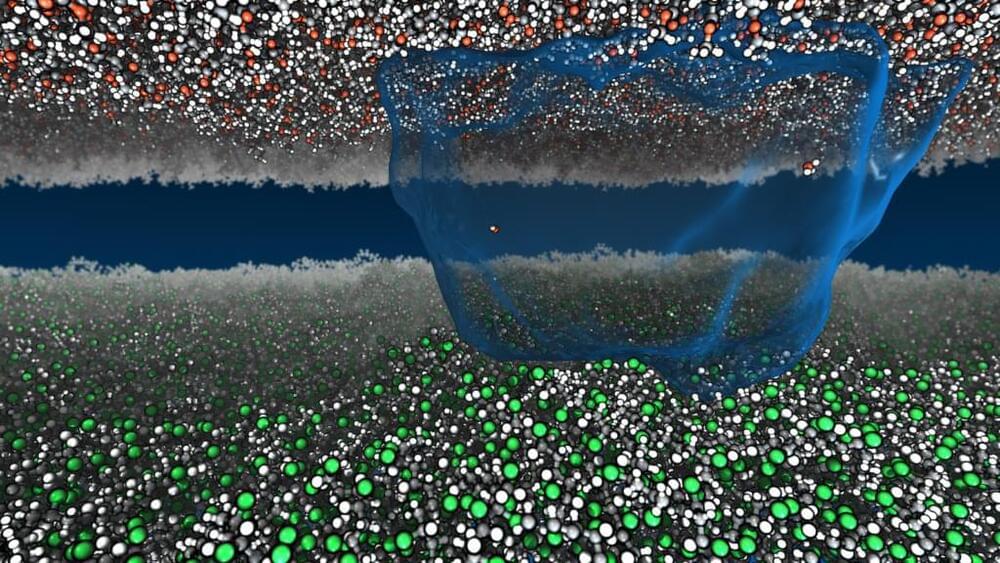
Now Princeton researchers have sparked new life into static. Using millions of hours of computational time to run detailed simulations, the researchers found a way to describe static charge atom-by-atom with the mathematics of heat and work. Their paper appeared in Nature Communications on March 23.
The study looked specifically at how charge moves between materials that do not allow the free flow of electrons, called insulating materials, such as vinyl and acrylic. The researchers said there is no established view on what mechanisms drive these jolts, despite the ubiquity of static: the crackle and pop of clothes pulled from a dryer, packing peanuts that cling to a box.
“We know it’s not electrons,” said Mike Webb, assistant professor of chemical and biological engineering, who led the study. “What is it?”
Theoretical physicists employ their imaginations and their deep understanding of mathematics to decipher the underlying laws of the universe that govern particles, forces and everything in between. More and more often, theorists are doing that work with the help of machine learning.
As might be expected, the group of theorists using machine learning includes people classified as “computational” theorists. But it also includes “formal” theorists, the people interested in the self-consistency of theoretical frameworks, like string theory or quantum gravity. And it includes “phenomenologists,” the theorists who sit next to experimentalists, hypothesizing about new particles or interactions that could be tested by experiments; analyzing the data the experiments collect; and using results to construct new models and dream up how to test them experimentally.
In all areas of theory, machine-learning algorithms are speeding up processes, performing previously impossible calculations, and even causing theorists to rethink the way theoretical physics research is done.

A team at HZB has investigated a new, simple method at BESSY II that can be used to create stable radial magnetic vortices in magnetic thin films.
In some materials, spins form complex magnetic structures within the nanometre and micrometer scale in which the magnetization direction twists and curls along specific directions. Examples of such structures are magnetic bubbles, skyrmions, and magnetic vortices.
Spintronics aims to make use of such tiny magnetic structures to store data or perform logic operations with very low power consumption, compared to today’s dominant microelectronic components. However, the generation and stabilization of most of these magnetic textures is restricted to a few materials and achievable under very specific conditions (temperature, magnetic field…).

The elegant equations of classical electromagnetism written by James Clark Maxwell in 1861 display a remarkable symmetry between electric and magnetic fields except for their sources. We know about electric charges but we have not found magnetic charges. Bar magnets are dipoles with two poles, north and south, for the magnetic field, resembling the configuration of an electric field sourced by a pair of positive and negative electric charges. However, we had never seen experimental evidence for a magnetic monopole, namely a magnetic charge with only one magnetic pole, a net north or south, from where magnetic field lines emanate, just like the electric field sourced by an electric charge. In a symmetric theory of electromagnetism, magnetic monopoles should exist.
The existence of monopoles with a net magnetic charge was proposed by Paul Dirac in 1931 to explain the quantized (discrete) values of electric charges. Dirac found that magnetic charges should be an integer multiple of a fundamental unit, g_D, equal to the electron charge, e, divided by twice the fine-structure constant, or about 68.5e.
In classical physics, the existence of magnetic monopoles restores symmetry to Maxwell’s equations. But in the broader context of quantum mechanics, Gerard ‘t Hooft and Alexander Polyakov showed in 1974 that magnetic monopoles are required in Grand Unified Theories of the strong, weak and electromagnetic interactions. Since the electric charge is quantized, magnetic charges are unavoidable in these theories. Magnetic charges with the lowest mass must be stable because magnetic charge is conserved and they cannot decay into lower-mass particles.
1,769 views • Premiered 82 minutes ago • #worldsciencefestival #quantumentanglement #briangreene
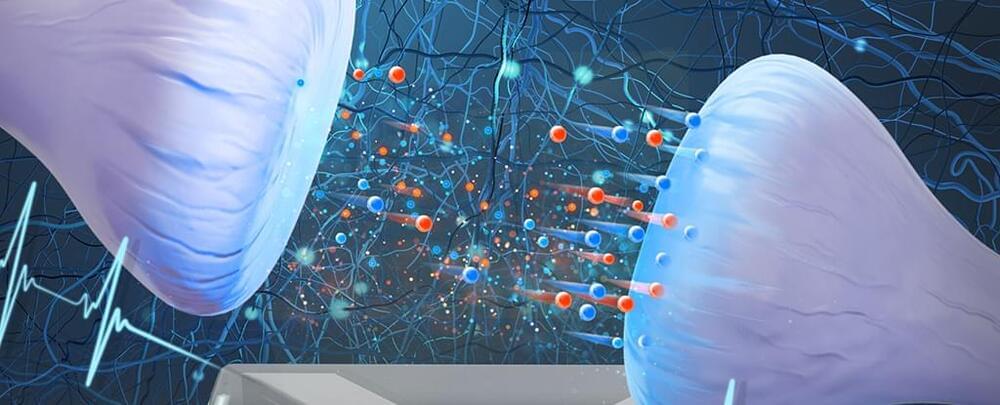
For the first time, researchers have simulated neurological junctions called synapses using the same water and salt ingredients the brain uses, contributing to an emerging field that combines biology with electronics called iontronics.
The team from Utrecht University in the Netherlands and Sogang University in South Korea claim to have been inspired by the functioning of the human brain, which also uses charged particles called ions dissolved in water to transmit signals within neurons.
An important feature of the brain’s ability to process information is synaptic plasticity, which allows neurons to adjust the strength of connections between them in response to input history.