While these findings, published in Physical Review Letters, did not lead to the observation of signals associated with these hypothetical dark matter particles, they established a new technique to search for axions using a tunable optical cavity.


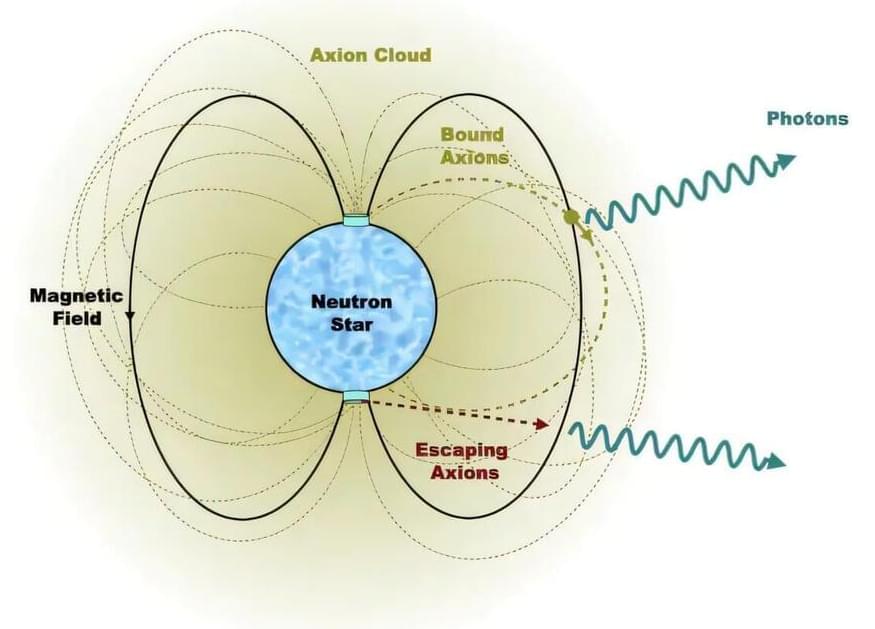
A team of physicists from the universities of Amsterdam, Princeton and Oxford have shown that extremely light particles known as axions may occur in large clouds around neutron stars. These axions could form an explanation for the elusive dark matter that cosmologists search for—and moreover, they might not be too difficult to observe.


From subatomic particles to complex molecules, quantum systems hold the key to understanding how the universe works. But there’s a catch: when you try to model these systems, that complexity quickly spirals out of control—just imagine trying to predict the behavior of a massive crowd of people where everyone is constantly influencing everyone else. Turn those people into quantum particles, and you are now facing a “quantum many-body problem.”

In their previous research, Mak and his colleagues engineered a highly tunable moiré Kondo lattice system based on MoTe2/WSe2 moiré bilayers. This material offers a unique opportunity to examine the Kondo destruction transition in a continuous manner, which has proved highly challenging in bulk heavy fermion materials.
“With this background, our Nature Physics paper studied the fate of the heavy fermions by continuously tuning the density of the itinerant carriers in the system, which tunes the effective Kondo coupling strength,” said Mak. “Near a critical density, we observed a destruction of the heavy fermions and the simultaneous emergence of a ferromagnetic Anderson insulator.”
As part of their new study, the researchers examined the Kondo lattice physics emerging in the moiré semiconductor: angle-aligned MoTe2/WSe2 heterobilayer presented in their previous paper. Their results highlight the promise of moiré Kondo lattices for studying the Kondo destruction transition using a tunable platform, as well as the possibility of realizing other exotic states of matter near such transition.

When driving though a bank of fog, car headlights are only of limited help as the light is scattered by the water particles suspended in the air. The situation is similar when you try to observe the inside of a drop of milk in water or the internal structure of an opal gem with the help of white light. In all these cases, multiple light scattering effects prevent examination of the interior.

First coherent picture of an atomic nucleus made of quarks and gluons.
For the first time, quarks and gluons were used to describe properties of atomic nuclei, which until now had been explained by the existence of protons and neutrons. The temporary pair of correlated nucleons is highlighted in purple. (Source: IFJ PAN)
The atomic nucleus is made up of protons and neutrons, particles that exist through the interaction of quarks bonded by gluons. It would seem, therefore, that it should not be difficult to reproduce all the properties of atomic nuclei hitherto observed in nuclear experiments using only quarks and gluons. However, it is only now that physicists, including those from the Institute of Nuclear Physics of the Polish Academy of Sciences in Cracow, have succeeded in doing this.
It’s almost a century since the discovery of the main components of atomic nuclei: protons and neutrons. Initially, the new particles were considered indivisible. In the 1960s, however, there was a suggestion that, at sufficiently high energies, protons and neutrons would reveal their internal structure – the presence of quarks constantly held together by gluons. Soon afterwards, the existence of quarks was confirmed experimentally. It may therefore seem surprising that, despite the passage of many decades, no one has been able to reproduce with quark-gluon models the results of nuclear experiments at low energies when only protons and neutrons are visible in atomic nuclei. This long-standing deadlock has only now been broken, in a paper published in Physical Review Letters. Its main authors are scientists from the international nCTEQ collaboration on quark-gluon distributions, including those from the Institute of Nuclear Physics of the Polish Academy of Sciences (IFJ PAN) in Cracow.
Twesh Upadhyaya, William F. Braasch, Jr., Gabriel T. Landi, and Nicole Yunger Halpern PRX Quantum 5, 030355 – Published 23 September 2024 https://journals.aps.org/prxquantum/abstract/10.1103/PRXQuantum.5.
As an ice cube melts in water, the heat exchange d by the two produces disorder. Imagine measuring the heat flow while the ice melts in each of many trials. From the measurement results, one can compute the disorder generated in each trial—the stochastic entropy production (SEP). The SEP is well understood in the case of two classical systems interacting; there is one widely accepted SEP definition that can be expressed equivalently via three formulas. But the situation is far murkier for quantum analogues, such as two atoms exchanging components of spin.
Generalizing the three SEP formulas to accommodate quantum systems, we prove that quantum effects render the three SEP formulas inequivalent. Each formula reasonably quantifies entropy production and highlights a different aspect of the underlying physics. The inequivalence of the formulas stems from the inability to simultaneously measure the exchange d quantities of the quantum systems, i.e., the uncertainty principle. This quantumness leads to negative and even nonreal entropy production. Though unusual, these entropy values herald notable physical phenomena. A negative entropy production signals superposition in the thermal initial states of the quantum systems. An imaginary entropy production witnesses contextuality, a precise notion of nonclassicality.
Our work reveals new facets of entropy production for quantum systems, with potential implications for the performance of future technologies. For example, negative entropy production could be harnessed to improve the efficiency of a quantum engine.


Overlapping two 3D lattices with a relative twist opens the door to synthesizing crystals with diverse symmetries that showcase nontrivial band structures and novel properties.
When two identical periodic lattices overlap in space, with one twisted at an angle relative to the other, they form moiré lattices. The best-known examples are formed from stacked and rotated 2D sheets. These structures can possess fascinating properties not seen in their component layers. Twisted bilayer graphene, for example, can exhibit superconductor and Mott insulator behavior [1, 2]. Ce Wang of Tongji University in China and his colleagues now propose how to construct a 3D moiré lattice using two cubic optical lattices hosting ultracold atoms [3]. The researchers mathematically describe how two simple periodic structures, twisted relative to each other, can lead to 3D optical moiré patterns (Fig. 1). The result is a crystal-like structure with emergent properties that differ from those of the underlying simple lattices.