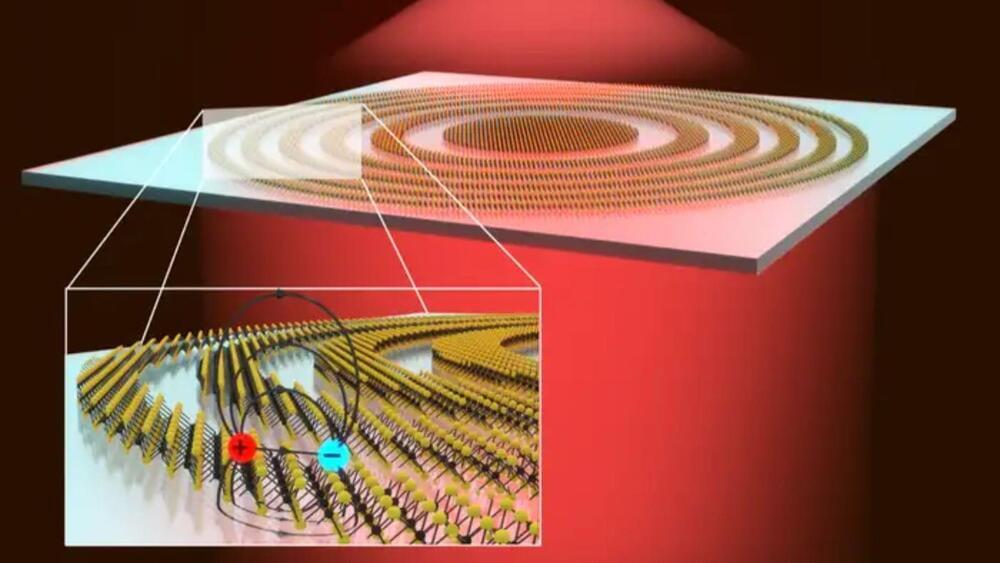
The world’s thinnest lens diffracts light of specific wavelengths instead of refracting it.
By arranging a special material in concentric rings, researchers have built the world’s thinnest lens at just three atoms thickness.
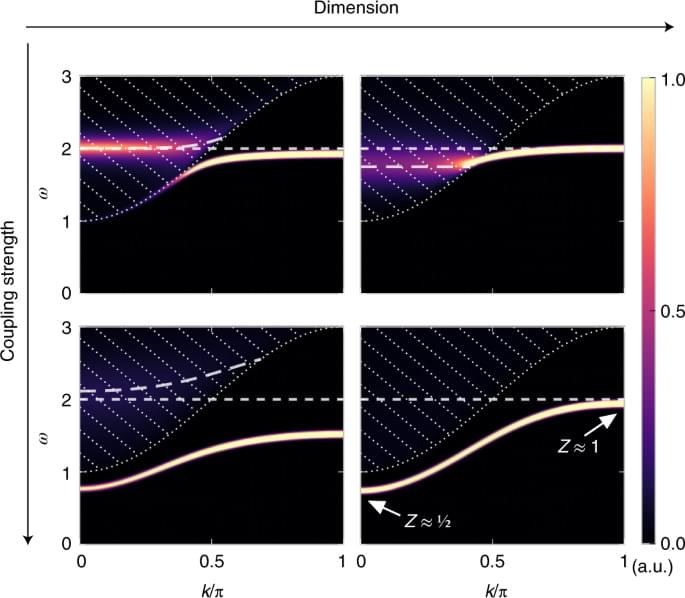
Immortality particles called quasiparticles face_with_colon_three
A collective excitation behaving as a single emergent entity, known as a quasiparticle, often becomes unstable when encountering a continuum of many-body excited states. However, under certain conditions, the result can be totally different.
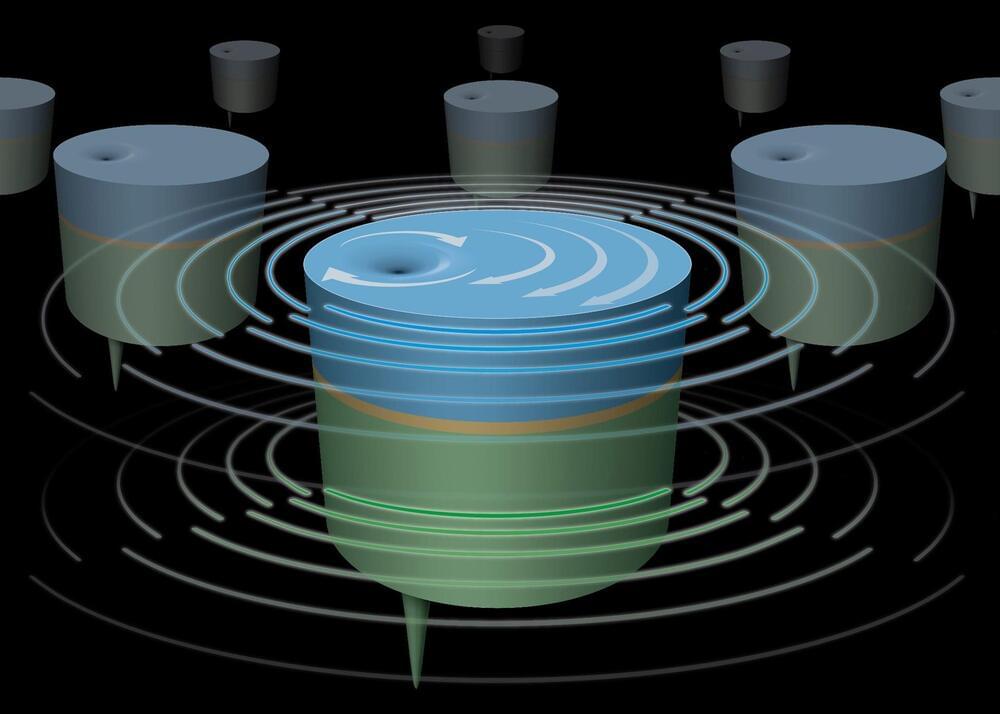
Brookhaven National Laboratory researchers are working to develop ways to synchronize the magnetic spins in nanoscale devices to build tiny signal-generating or receiving antennas and other electronics.
Upton, New York — Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Brookhaven National Laboratory are seeking ways to synchronize the magnetic spins in nanoscale devices to build tiny yet more powerful signal-generating or receiving antennas and other electronics. Their latest work, published in Nature Communications, shows that stacked nanoscale magnetic vortices separated by an extremely thin layer of copper can be driven to operate in unison, potentially producing a powerful signal that could be put to work in a new generation of cell phones, computers, and other applications.
The aim of this “spintronic” technology revolution is to harness the power of an electron’s “spin,” the property responsible for magnetism, rather than its negative charge.
New research from North Carolina State University shows that unique materials with distinct properties akin to those of gecko feet – the ability to stick to just about any surface – can be created by harnessing liquid-driven chaos to produce soft polymer microparticles with hierarchical branching on the micro-and nanoscale.
The findings, published today (October 14, 2019) in the journal Nature Materials, hold the potential for advances in gels, pastes, foods, nonwovens, and coatings, among other formulations.
The soft dendritic particle materials with unique adhesive and structure-building properties can be created from a variety of polymers precipitated from solutions under special conditions, says Orlin Velev, S. Frank and Doris Culberson Distinguished Professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at NC State and corresponding author of the paper.
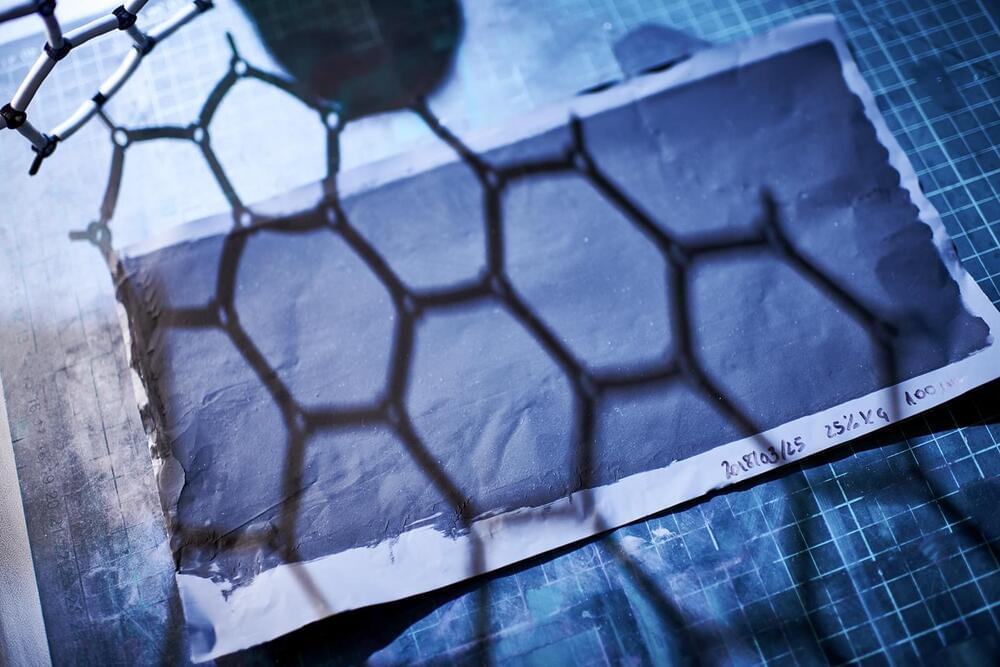


Manchester, England— On a rare sunny day in northern England, the National Graphene Institute (NGI) here gleams like a five-story block of obsidian. Squeezed into the University of Manchester’s sprawling downtown campus, the research center is clad in almost 2000 lustrous black panels with small hexagonal perforations—an architectural nod to the structure of the atom-thin sheet of carbon that gives the building its name.
NGI exists because graphene was first isolated a short walk away in a University of Manchester lab. Andre Geim and Konstantin Novoselov presented it to the world 20 years ago this month and later won a Nobel Prize for the work. Since its unveiling, billions of dollars of R&D funding have flowed to graphene, in a global race to exploit its peerless properties. It is better at carrying electricity than any metal, a superb heat conductor, and hundreds of times stronger than steel—selling points trumpeted in the marketing materials of universities and companies alike.
Early on, researchers were not shy about promising graphene breakthroughs, with predictions that it would enable superthin rollable TVs and space elevators, and even supplant silicon in computer chips. “Expectations were very, very high,” Geim says. “The companies I was involved in were mostly based on hype.”

Quantum physicists have developed a new type of optical atomic clock, using quantum entanglement among strontium atoms to achieve unprecedented precision.
This breakthrough could significantly impact quantum computing and precision sensing, although it currently operates effectively for only milliseconds.
Quantum Advances in Timekeeping.
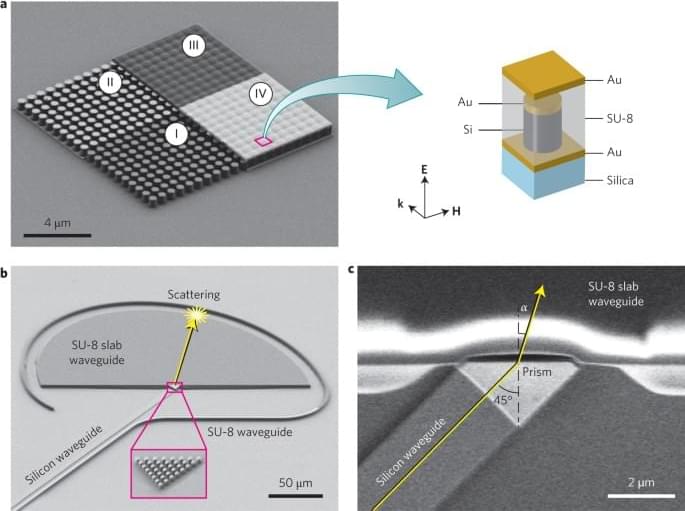
This chip has speed that defies the light speed barrier while maintaining cool temperatures using a special metamaterial that allows the light particles to go infinitely fast.
Most metamaterial experiments occur in bulk transmission geometries. Here researchers demonstrate integrated in-plane zero-index metamaterials.
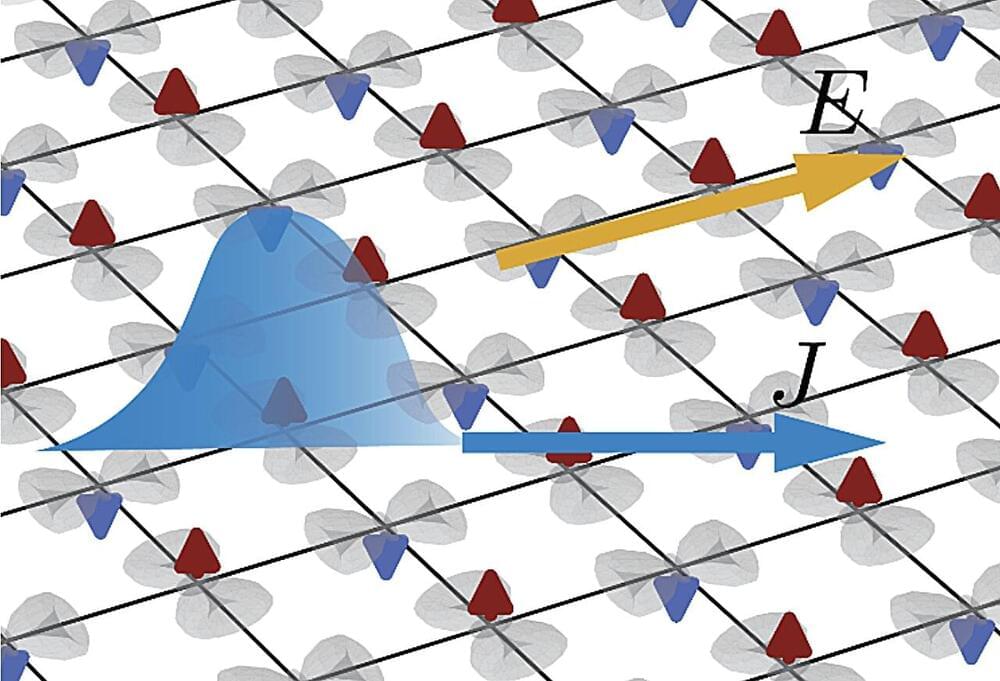
In the quantum world, materials called “altermagnets” behave in unique ways that could pave the way for new technologies.
This unique magnetism makes altermagnets highly promising for the development of new spintronic and electronic devices. It also opens new possibilities for the study of topological materials (i.e., systems with unique electronic properties originating from their electronic structure’s topology).
Researchers at Stony Brook University carried out a study aimed at better understanding the nonlinear response of planar altermagnets. Their paper, published in Physical Review Letters, reports the observation of a non-linear response in these materials derived from their quantum geometry.
“Recently, two experiments have confirmed the predicted role of quantum geometry in the second-order response of the conventional PT-symmetric antiferromagnets,” Sayed Ali Akbar Ghorashi, co-author of the paper, told Phys.org.
Imagine being able to see electrons — the tiny particles that buzz around atoms — in action, darting and swirling in their frenetic dance. This isn’t science fiction anymore.
Scientists have recently developed a state-of-the-art microscope that allows us to observe these elusive particles moving at unimaginable speeds, revealing the intricate behaviors and interactions that occur at the atomic level.
This innovative technology opens up new frontiers for research in physics and materials science, providing unprecedented insights into the fundamental building blocks of matter.