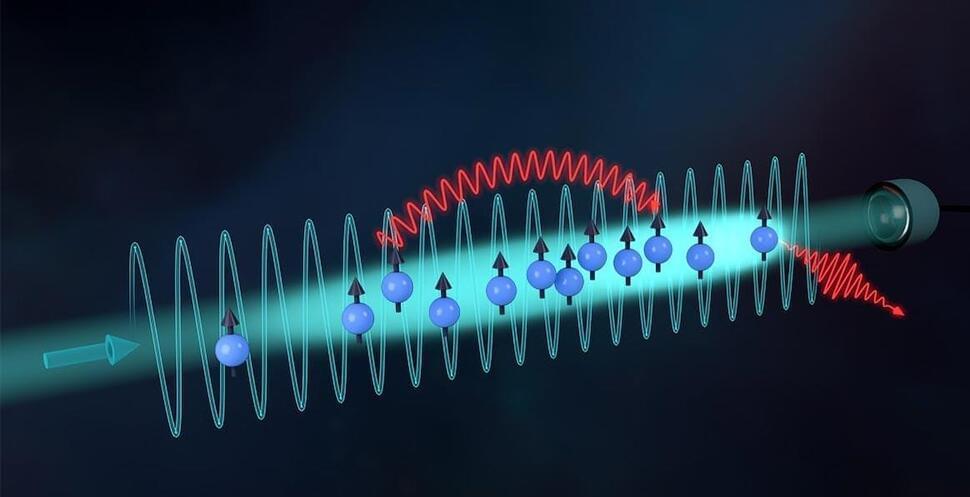
A team of researchers at the University of Birmingham in the United Kingdom has made a significant breakthrough in physics by visualizing the shape of a single photon for the first time. This achievement was facilitated by an innovative computer model that simplifies the complex interaction between light and matter, a major challenge in the fields of physics and quantum mechanics.
Photons, the particles of light, have long captivated scientists. Since their discovery, it has been proven that light behaves both as a wave and a particle, a phenomenon known as wave-particle duality. This concept, which took centuries to be accepted, has been pivotal for the advancement of quantum mechanics, the branch of physics that studies subatomic interactions.
Photons are central to many phenomena, including lighting, telecommunications, and even touchscreen technology. However, despite their significance, the precise nature of their shape remained unknown until this team of researchers discovered a new way to visualize them.