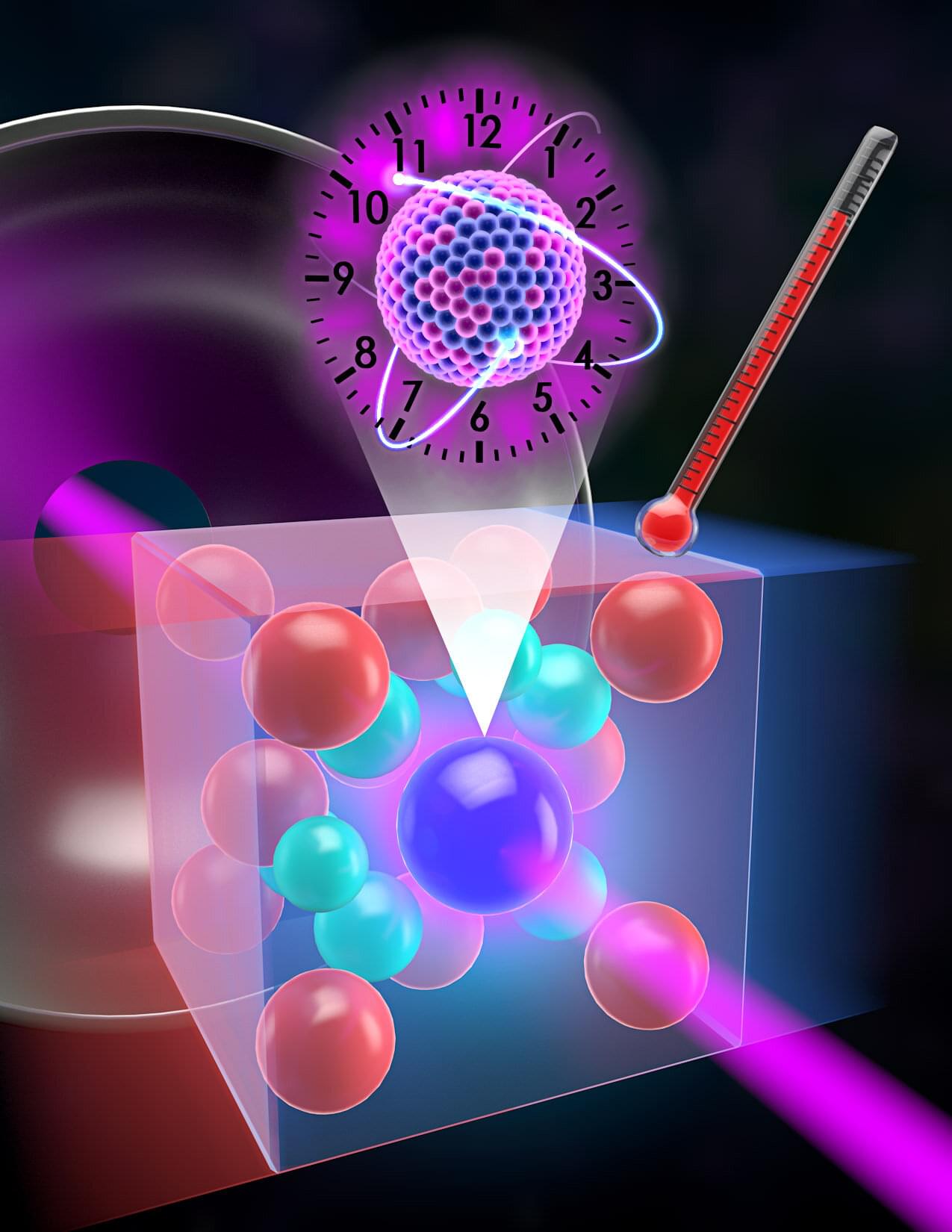
For decades, atomic clocks have been the pinnacle of precision timekeeping, enabling GPS navigation, cutting-edge physics research, and tests of fundamental theories. But researchers at JILA, led by JILA and NIST Fellow and University of Colorado Boulder physics professor Jun Ye, in collaboration with the Technical University of Vienna, are pushing beyond atomic transitions to something potentially even more stable: a nuclear clock.
This clock could revolutionize timekeeping by using a uniquely low-energy transition within the nucleus of a thorium-229 atom. This transition is less sensitive to environmental disturbances than modern atomic clocks and has been proposed for tests of fundamental physics beyond the Standard Model.
This idea isn’t new in Ye’s laboratory. In fact, work in the lab on nuclear clocks began with a landmark experiment, the results of which were published as a cover article of Nature last year, where the team made the first frequency-based, quantum-state-resolved measurement of the thorium-229 nuclear transition in a thorium-doped host crystal. This achievement confirmed that thorium’s nuclear transition could be measured with enough precision to be used as a timekeeping reference.