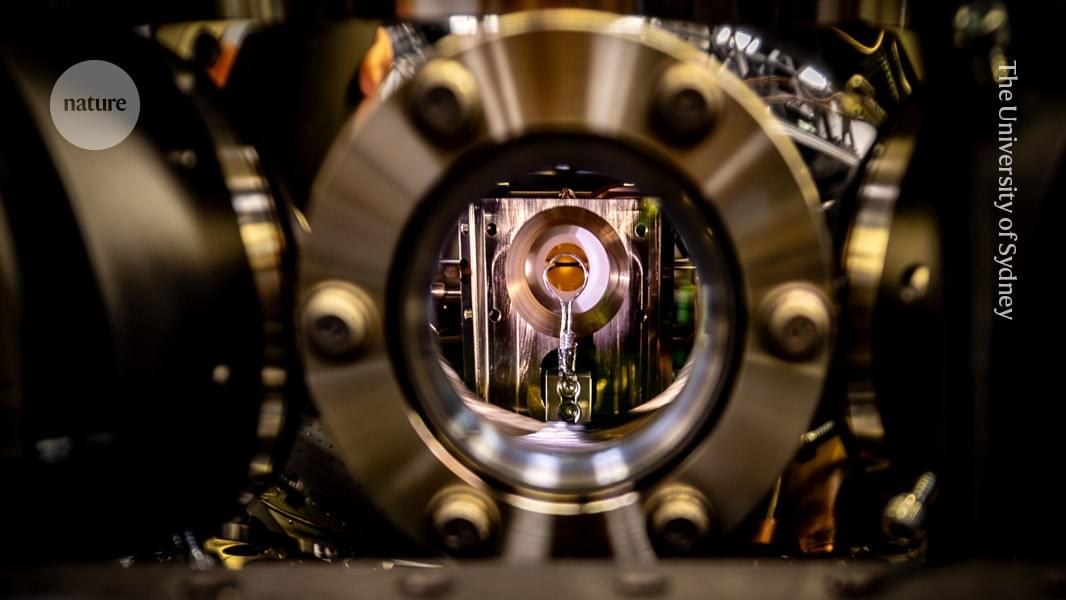
A trapped ytterbium ion can be used to model complex changes in the energy levels of organic molecules interacting with light.
Category: particle physics – Page 10
A new proposal makes the case that paraparticles—a new category of quantum particle—could be created in exotic materials.
In hyperentanglement, particle share multiple correlated properties, rather than just one seen in regular quantum entanglement.
Scientists may have discovered the most powerful particle colliders in the universe — and they’re strewn throughout our galaxy just waiting to blow.
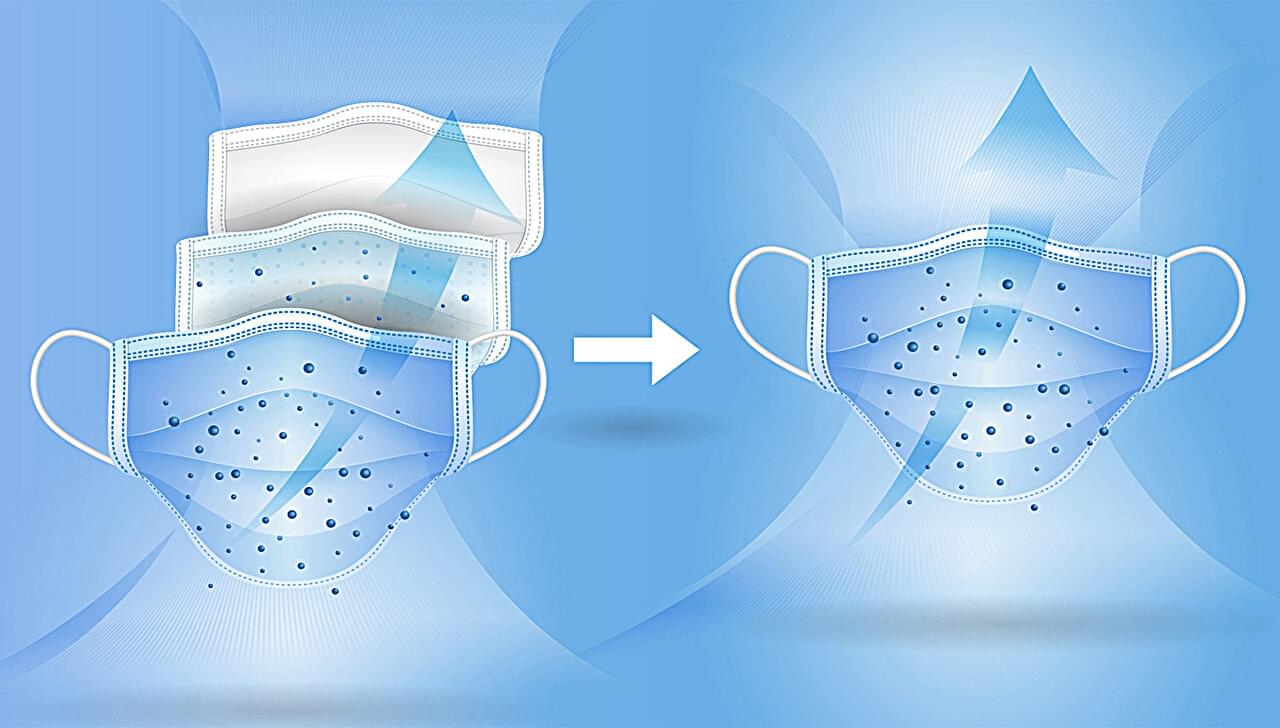
The COVID-19 pandemic increased public awareness of the importance of mask use for personal protection. However, when the mesh size of mask fabrics is small enough to capture viruses, which are usually around one hundred nanometers in size, the fabric typically also restricts air flow, resulting in user discomfort. Researchers from Japan have now developed a new filter material that effectively captures nanoparticles, although further improvements are needed to make it suitable for comfortable mask use.
In a study published this month in Materials Advances, researchers from the Institute of Industrial Science at the University of Tokyo have developed a filter capable of capturing nanoparticles such as viruses. While the filter demonstrates high filtration efficiency, its airflow resistance is currently higher than the standards required for face masks, indicating that additional development is necessary before it can be used for personal protective equipment.
The filter is constructed from nanosheets consisting of an ordered mesh composed of porphyrins, which are flat, ring-shaped molecules with a central hole. The tiny holes in the porphyrin molecules are suitably sized to allow the easy passage of the small gas molecules in air while blocking the movement of larger particles, such as viruses. The nanosheets are then supported on a fabric modified with nanofibers containing pores of several hundred nanometers to form the filter.
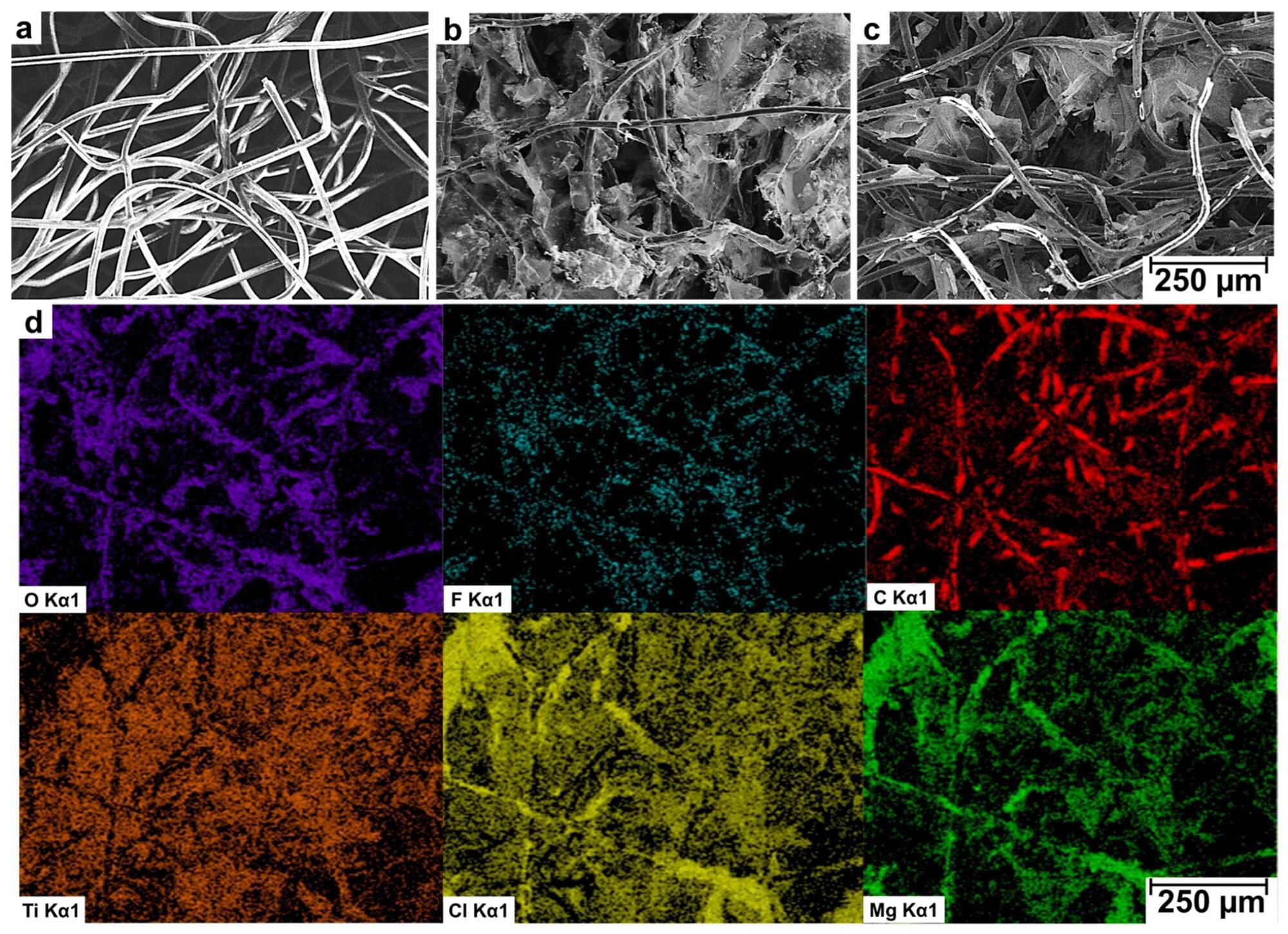
Despite improvements to air filtration technology in the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic, some of the smallest particles—those of automobile and factory emissions—can still make their way through less efficient, but common filters. An interdisciplinary team of researchers from Drexel University’s College of Engineering have introduced a new way to improve textile-based filters by coating them with a type of two-dimensional nanomaterial called MXene.
Recently published in the journal C—Journal of Carbon Research, the team’s research reports that a non-woven polyester textile—a low-cost material with low filtration efficiency—coated with a thin layer of MXene nanomaterial can turn it into a potent filter capable of pulling some of the finest nanoparticles from the air.
“It can be challenging for common filters to contend with particles less than 100 nanometers, which include those emitted by industrial processes and automobiles,” said Michael Waring, Ph.D., a professor in Drexel’s College of Engineering, and co-author of the research. “Being able to augment a filter, through a simple coating process, to make it effective against these emissions is a significant development.”
A quantum Monte Carlo calculation shows that the hydrodynamic behavior of the charge current at graphene’s charge neutrality point can emerge despite the absence of momentum flow.
A new model of quark–gluon plasma finds that the strong force was more potent in the early Universe than previously thought.
Besides particles like sterile neutrinos, axions and weakly interacting massive particles (WIMPs), a leading candidate for the cold dark matter of the universe are primordial black holes—black holes created from extremely dense conglomerations of subatomic particles in the first seconds after the Big Bang.
Primordial black holes (PBHs) are classically stable, but as shown by Stephen Hawking in 1975, they can evaporate via quantum effects, radiating nearly like a blackbody. Thus, they have a lifetime; it’s proportional to the cube of their initial mass. As it’s been 13.8 billion years since the Big Bang, only PBHs with an initial mass of a trillion kilograms or more should have survived to today.
However, it has been suggested that the lifetime of a black hole might be considerably longer than Hawking’s prediction due to the memory burden effect, where the load of information carried by a black hole stabilizes it against evaporation.
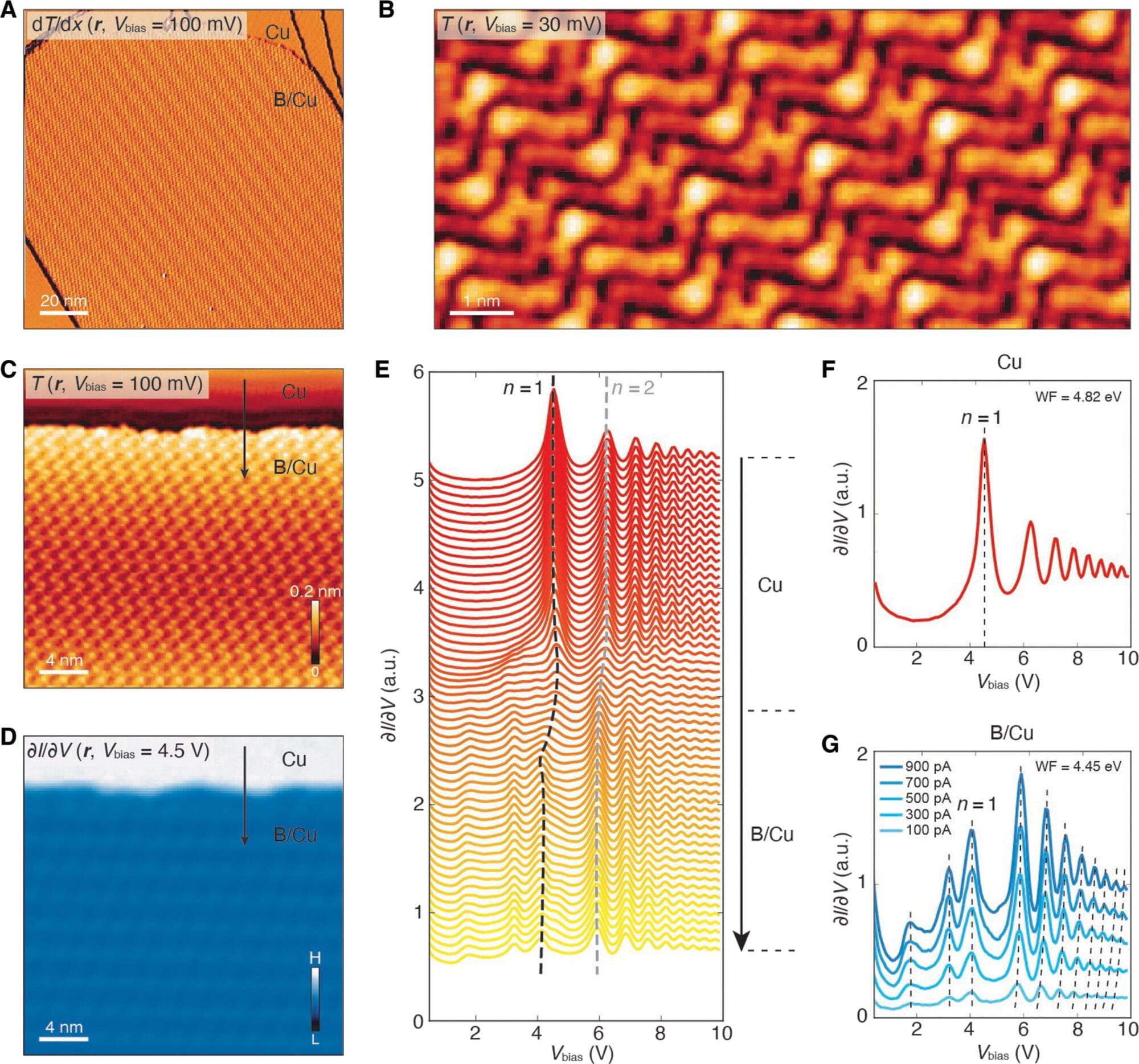
More than ten years ago, researchers at Rice University led by materials scientist Boris Yakobson predicted that boron atoms would cling too tightly to copper to form borophene, a flexible, metallic two-dimensional material with potential across electronics, energy and catalysis. Now, new research shows that prediction holds up, but not in the way anyone expected.
Unlike systems such as graphene on copper, where atoms may diffuse into the substrate without forming a distinct alloy, the boron atoms in this case formed a defined 2D copper boride ⎯ a new compound with a distinct atomic structure. The finding, published in Science Advances by researchers from Rice and Northwestern University, sets the stage for further exploration of a relatively untapped class of 2D materials.
“Borophene is still a material at the brink of existence, and that makes any new fact about it important by pushing the envelope of our knowledge in materials, physics and electronics,” said Yakobson, Rice’s Karl F. Hasselmann Professor of Engineering and professor of materials science and nanoengineering and chemistry. “Our very first theoretical analysis warned that on copper, boron would bond too strongly. Now, more than a decade later, it turns out we were right ⎯ and the result is not borophene, but something else entirely.”