Human civilization has achieved some incredible things during its short reign on this planet. Technological development over the past 5,000 years of human civilization has led our species to dominance of life on Earth and placed us on a pathway to achieving a Type I civilization.
To reach even the basic level of a “Kardashev Type 1 civilization” we must do two things:
Develop more advanced technology and share it with all responsible nations.
Make renewable energy accessible to all parts of the world.
Five hundred years ago, the Aztec civilization believed that the sun and all its power was sustained by blood from human sacrifice.
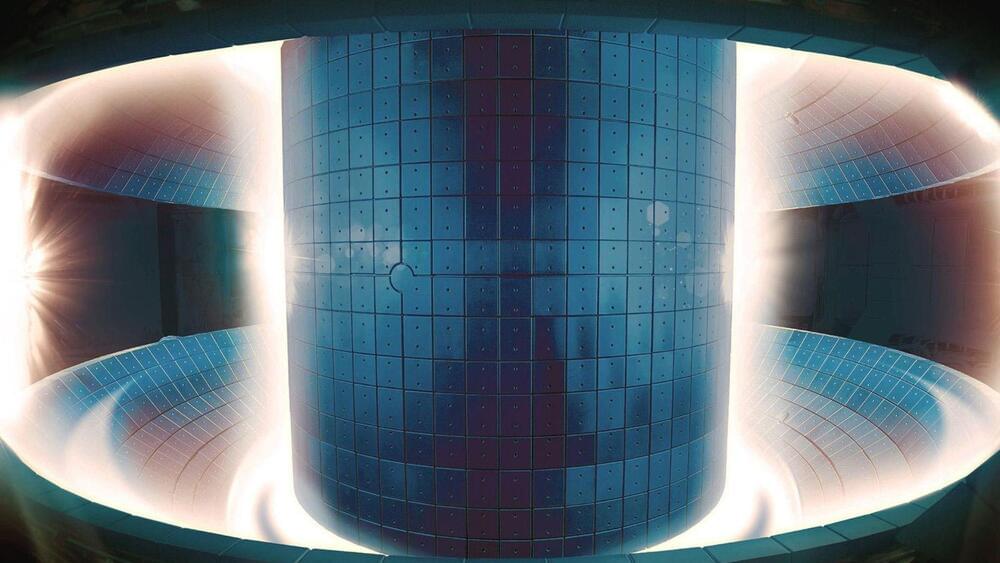
Today, we know that the sun, along with all other stars, is powered by a reaction called nuclear fusion.
Scientists and engineers have studied the Sun’s fusion process in hopes of developing a way to harness energy from fusion in machines on Earth.
What exactly is nuclear fusion, and how does it work in terms of producing electricity?
#nuclearfusion #sciencetime #kardashev.