Are brain-computer interfaces the next way we will communicate with machines and even with one another? Here are 10 companies working on decoding our thoughts.
Category: neuroscience – Page 968
Researchers improve neuronal reprogramming
The replacement of lost neurons is a holy grail for neuroscience. A new promising approach is the conversion of glial cells into new neurons. Improving the efficiency of this conversion or reprogramming after brain injury is an important step towards developing reliable regenerative medicine therapies. Researchers at Helmholtz Zentrum München and Ludwig Maximilians University Munich (LMU) have identified a hurdle towards an efficient conversion: the cell metabolism. By expressing neuron-enriched mitochondrial proteins at an early stage of the direct reprogramming process, the researchers achieved a four times higher conversion rate and simultaneously increased the speed of reprogramming.
Neurons (nerve cells) have very important functions in the brain such as information processing. Many brain diseases, injuries and neurodegenerative processes, are characterized by the loss of neurons that are not replaced. Approaches in regenerative medicine therefore aim to reconstitute the neurons by transplantation, stem cell differentiation or direct conversion of endogenous non-neuronal cell types into functional neurons.
Researchers at Helmholtz Zentrum München and LMU are pioneering the field of direct conversion of glial cells into neurons which they have originally discovered. Glia are the most abundant cell type in the brain and can proliferate upon injury. Currently, researchers are able to convert glia cells into neurons — but during the process many cells die. This means that only few glial cells convert into functional nerve cells, making the process inefficient.

3 Profound Impacts Exercise Has on The Brain
Here are just a few ways exercise changes the structure of our brain.
Memory
Many studies suggest that exercise can help protect our memory as we age. This is because exercise has been shown to prevent the loss of total brain volume (which can lead to lower cognitive function), as well as preventing shrinkage in specific brain regions associated with memory. For example, one magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan study revealed that in older adults, six months of exercise training increases brain volume.
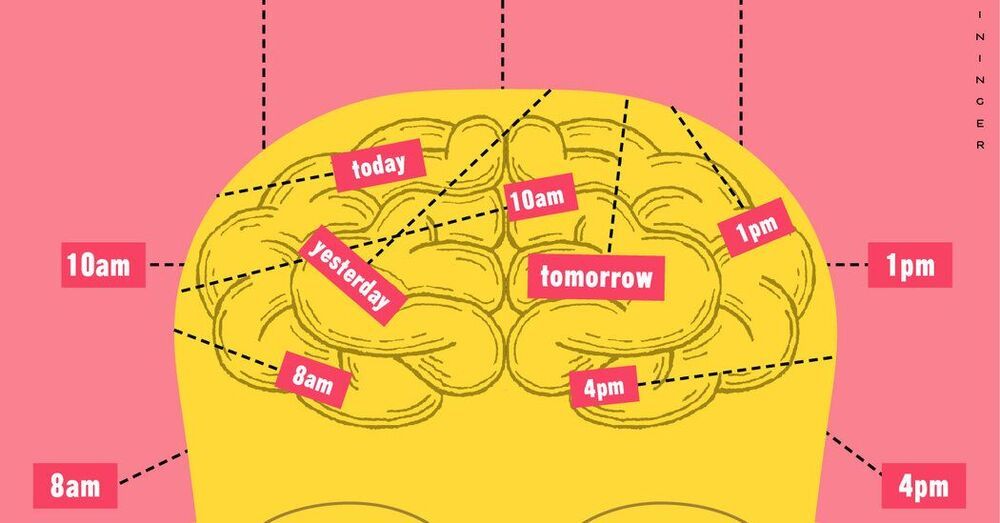
Brain Scientists Explore the How of When
Merriam-Webster’s defines a time warp as a “discontinuity, suspension or anomaly” in the otherwise normal passage of time; this year all three terms could apply. It seems like March happened 10 years ago; everyday may as well be Wednesday, and still, somehow, here come the holidays — fast, just like every year.
Some bard or novelist may yet come forth to help explain the paradoxes of pandemic time, both its Groundhog Days and the blurs of stress and fear for those on the front lines, or who had infectious people in their household. But brain science also has something to say about the relationship between perceived time and the Greenwich Mean variety, and why the two may slip out of sync.
In a new study, a research team based in Dallas reported the first strong evidence to date of so-called “time cells” in the human brain. The finding, posted by the journal PNAS, was not unexpected: In recent years, several research groups have isolated neurons in rodents that track time intervals. It’s where the scientists look for these cells, and how they identified them, that provide some insight into the subjective experiences of time.
New Chinese submersible reaches Earth’s deepest ocean trench
China livestreamed footage of its new manned submersible parked at the bottom of the Mariana Trench on Friday, part of a historic mission into the deepest underwater valley on the planet.
The “Fendouzhe”, or “Striver”, descended more than 10,000 metres (about 33,000 feet) into the submarine trench in the western Pacific Ocean with three researchers on board, state broadcaster CCTV said.
Only a handful of people have ever visited the bottom of the Mariana Trench, a crescent-shaped depression in the Earth’s crust that is deeper than Mount Everest is high and more than 2,550 kilometres (1,600 miles) long.
Supercomputer Aurora 21 will map the human brain, starting in 2021
Aurora 21 will help the US keep pace among the other nations who own the fastest supercomputers. Scientists plan on using it to map the connectome of the human brain.
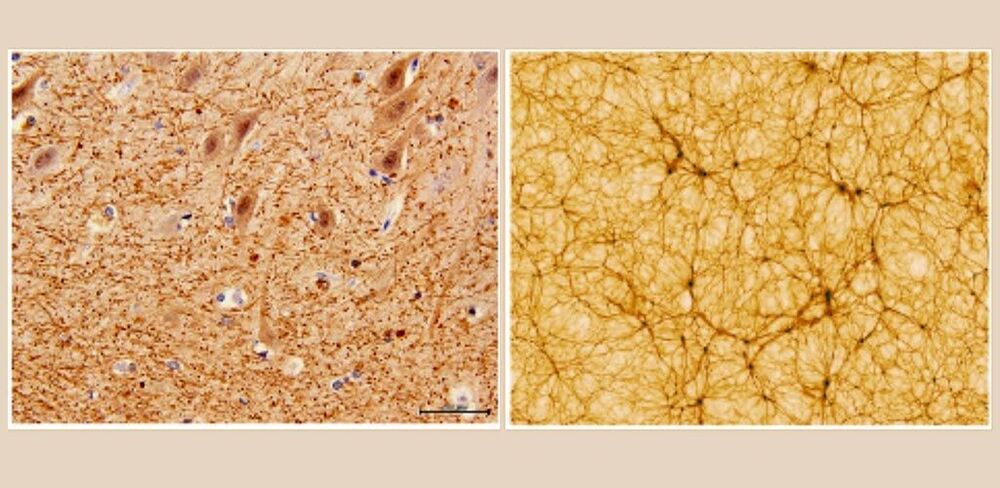
Neuroscience Meets Astrophysics: Does the Human Brain Resemble the Universe?
In their paper published in Frontiers of Physics, Franco Vazza (astrophysicist at the University of Bologna) and Alberto Feletti (neurosurgeon at the University of Verona) investigated the similarities between two of the most challenging and complex systems in nature: the cosmic network of galaxies and the network of neuronal cells in the human brain.
Despite the substantial difference in scale between the two networks (more than 27 orders of magnitude), their quantitative analysis, which sits at the crossroads of cosmology and neurosurgery, suggests that diverse physical processes can build structures characterized by similar levels of complexity and self-organization.
The human brain functions thanks to its wide neuronal network that is deemed to contain approximately 69 billion neurons. On the other hand, the observable universe can count upon a cosmic web of at least 100 billion galaxies. Within both systems, only 30% of their masses are composed of galaxies and neurons. Within both systems, galaxies and neurons arrange themselves in long filaments or nodes between the filaments. Finally, within both systems, 70% of the distribution of mass or energy is composed of components playing an apparently passive role: water in the brain and dark energy in the observable Universe.
Army-funded algorithm decodes brain signals responsible for behaviors
Like walking and breathing and could one day allow people to control prosthetics simply by thinking…
The US Army is funding a project that could lead to brain-machine interfaces. It includes an algorithm capable of isolating brain signals and linking them to specific behaviors such as walking and breathing.
Ontological Holism: The Ultimate Reality of Self-Simulating Universe, or Why We All Are One
When we apprehend reality as the entirety of everything that exists including all dimensionality, all events and entities in their respective timelines, then by definition nothing exists outside of reality, not even “nothing.” It means that the first cause for reality’s existence must lie within ontological reality itself, since there is nothing outside of it. This self-causation of reality is perhaps best understood in relation to the existence of your own mind. Self-simulated reality transpires as self-evident when you relate to the notion that a phenomenal mind, which is a web of patterns, conceives a certain novel pattern and simultaneously perceives it. Furthermore, the imminent natural God of Spinoza, or Absolute Consciousness, becomes intelligible by applying a scientific tool of extrapolation to the meta-systemic phenomenon of radical emergence and treating consciousness as a primary ontological mover, the Source if you will, not a by-product of material interactions.
#OntologicalHolism #ontology #holism #cosmology #phenomenology #consciousness #mind #evolution