Even for the brain of a worm, the best theory on offer would, she says, take several billion years to calculate. That can’t be the right answer.
Category: neuroscience – Page 960

Researchers identify promising model for studying human aging
Aging research fans might like.
“In their work, Hamiliton’s team found that the Dunkin Hartley guinea pig was a good candidate for a muscle aging model due to the animal’s tendency to develop osteoarthritis (OA) at a young age.”
There are many components to aging, both mental and physical. When it comes to the infrastructure of the human body—the musculoskeletal system that includes muscles, bones, tendons and cartilage—age-associated decline is inevitable, and the rate of that decline increases the older we get. The loss of muscle function—and often muscle mass—is scientifically known as sarcopenia or dynapenia.
For adults in their 40s, sarcopenia is hardly noticeable—about 3% muscle mass is lost each decade. For those aged 65 years and older, however, muscle decline can become much more rapid, with an average loss of 1% muscle mass each year. More importantly, sarcopenia is also marked by a decrease in strength, impaired gait, reduced physical activity, or difficulty completing everyday tasks.
The proportion of older adults aged 65+ is projected to more than double by the year 2060, driving research into the process of musculoskeletal decline. Researchers at Colorado State University’s Columbine Health Systems Center for Healthy Aging believe they have found an animal model that will help them better understand it and find ways to curtail the symptoms.
Aubrey de Grey Longevity Q&A — The last 25 years, SENS, Longevity Escape Velocity, & More
Annotated!
Aubrey David Nicholas Jasper de Grey is an English author and biomedical gerontologist. He is the Chief Science Officer of the SENS Research Foundation and VP of New Technology Discovery at AgeX Therapeutics.
Feel free to ask any related questions that you want Aubrey to try and answer!
Futurist Foundation is a non-profit organization with the goal to connect futurists and promote crowd-sourced projects in science, technology, engineering, mathematics & design.
Donate to Futurist Foundation — https://opencollective.com/future.
Donate to SENS — https://www.sens.org/get-involved/donate/
Discord: https://discord.gg/u3JM2cu.
Website: http://thefuturistfoundation.com.
Our Other Links: https://linktr.ee/futuristfoundation.
0:00 Introduction.
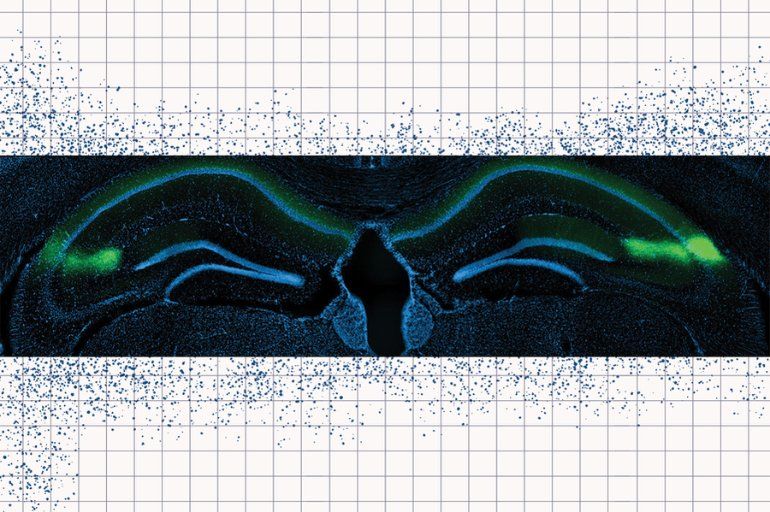
Brain Circuit That Encodes Timing of Events Identified
Summary: Pyramidal cells in the CA2 region of the hippocampus are responsible for storing critical timing information.
Source: MIT
When we experience a new event, our brain records a memory of not only what happened, but also the context, including the time and location of the event. A new study from MIT neuroscientists sheds light on how the timing of a memory is encoded in the hippocampus, and suggests that time and space are encoded separately.

One in Five Brain Cancers Fueled by Overactive Mitochondria
Summary: 20% of glioblastoma brain cancers are fueled by overactive mitochondria. Researchers say these cases may be treatable by drugs currently under trial.
Source: Columbia University.
A new study has found that up to 20% of glioblastomas–an aggressive brain cancer–are fueled by overactive mitochondria and may be treatable with drugs currently in clinical trials.

Reality Does Not Depend on the Measurer According to New Interpretation of Quantum Mechanics
For 100 years scientists have disagreed on how to interpret quantum mechanics. A recent study by Jussi Lindgren and Jukka Liukkonen supports an interpretation that is close to classical scientific principles.
Quantum mechanics arose in the 1920s – and since then scientists have disagreed on how best to interpret it. Many interpretations, including the Copenhagen interpretation presented by Niels Bohr and Werner Heisenberg and in particular von Neumann-Wigner interpretation, state that the consciousness of the person conducting the test affects its result. On the other hand, Karl Popper and Albert Einstein thought that an objective reality exists. Erwin Schrödinger put forward the famous thought experiment involving the fate of an unfortunate cat that aimed to describe the imperfections of quantum mechanics.
Scientists have restored youth to aging eyes in mice
Aging is, at least for now, inevitable, and our eyes are not immune to those changes. Vision loss is, in fact, one of the top 10 causes of disability in the US., however, shows that this might be reversible in the future.
A large team of geneticists, ophthalmologists, and other scientists used a group of molecules called Yamanaka factors to turn cells in the eyes of mature mice back to a youthful state. This reversed the damage done by aging, and the cells were then able to regenerate, connect back to the brain, and vision was restored in both models of normal aging and glaucoma.
Yamanaka factors are nothing new in neuroscience. They are named after the after Shinya Yamanaka led research using those factors to convert mature adult cells back to stem cells, kickstarting the field of induced pluripotent stem cells — cells reprogrammed with the ability to generate other types of cells.
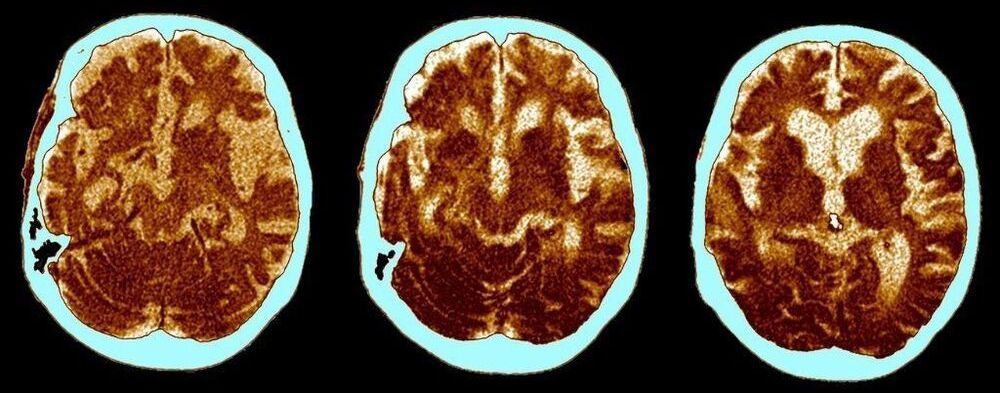
Research Says Alzheimer’s Is Actually 3 Distinct Disease Subtypes
Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) is probably more diverse than our traditional models suggest.
Postmortem, RNA sequencing has revealed three major molecular subtypes of the disease, each of which presents differently in the brain and which holds a unique genetic risk.
Such knowledge could help us predict who is most vulnerable to each subtype, how their disease might progress and what treatments might suit them best, potentially leading to better outcomes.