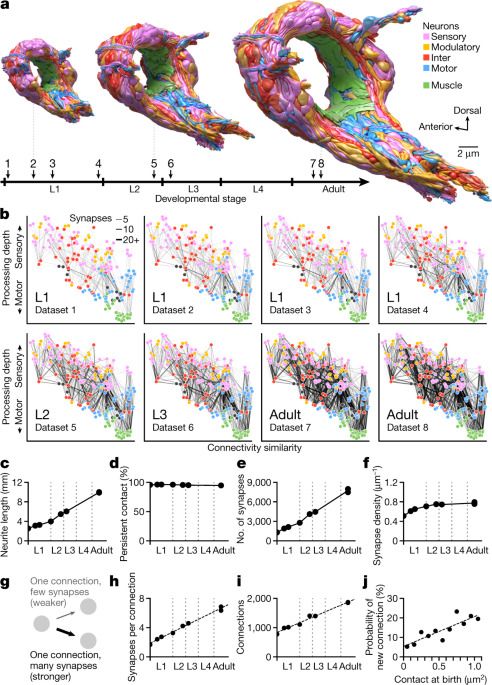
Chinese scientists have produced a 3D map of an entire rhesus monkey brain, which is 200 times larger than a mouse brain, at a resolution of just 0.001 mm (1 micron).
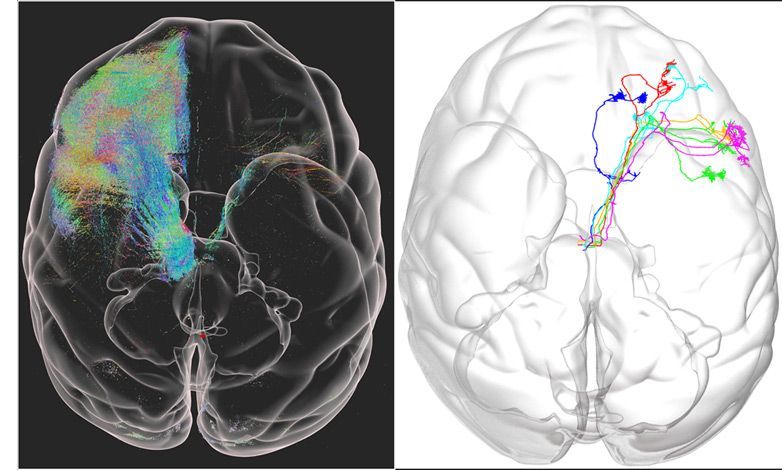


Since DNMT3A increases DNA methylation, the researchers used a natural product that donates methyl groups S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe) and to activate the retinoic acid receptor they treated the animals with vitamin A. They found that combined treatment with the methyl donor SAM and retinoic acid reversed PTSD-like behaviors.
Summary: Combining two natural products that modulate the epigenome, researchers believe they have identified a feasible approach to reversing symptoms of PTSD in animal models that could be effective in humans.
Source: Bar Ilan University
Exposure to a traumatic experience can lead to post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), an incapacitating disorder in susceptible persons with no reliable therapy. Particularly puzzling is understanding how transient exposure to trauma creates persistent long-term suffering from PTSD and why some people are susceptible to PTSD while others that were exposed to the same trauma remain resilient.
Epigenetic modifications are chemical marks on genes that program their activity. These marks are written into DNA during fetal development to correctly program how our genes function in different organs. However, research in the last two decades has suggested that these marks could also be modulated by experiences and exposures at different point of time in life.
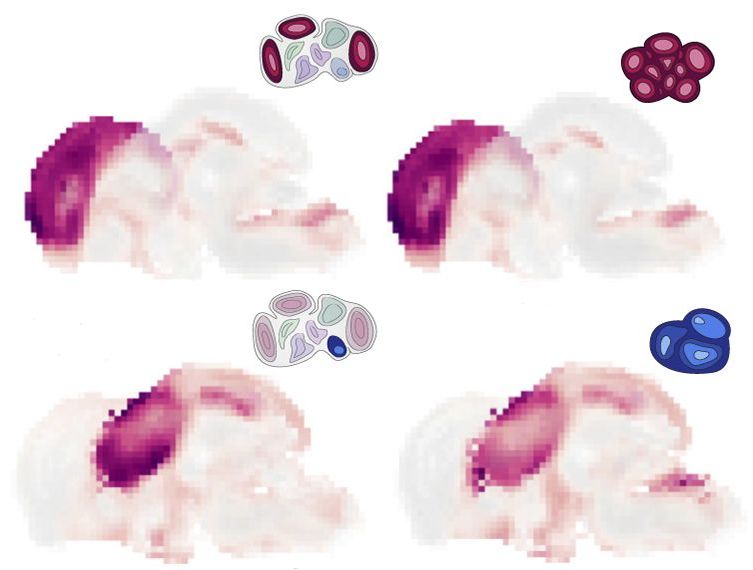
A new tool helps researchers explore the types of cells that make up brain organoids — clusters of cells that can mimic the basic structure, function and development of different parts of the brain.
The software, detailed in Cell Stem Cell, maps information about when and where genes are expressed in brain organoids onto a reference atlas of the developing mouse brain. Scientists can use the resulting overlay to develop organoids that better recapitulate the developing brain, the team says, or to uncover the effects of gene mutations and other experimental perturbations.
Brain organoids derived from the cells of people with conditions such as autism have proved useful in capturing neuronal abnormalities. But the findings are muddied by methodological differences in how researchers develop these lab-grown blobs. Advanced techniques to profile gene expression in single cells have made it easier to identify the cell types in any given organoid. But it’s remained difficult to map those cell types onto different brain regions.
Summary: Study reveals a link between corticosteroid receptors and genes associated with ciliary and neuroplasticity in the hippocampus, an area of the brain associated with stress response, learning, and memory.
Source: University of Bristol.
Chronic stress is a well-known cause of mental health disorders. New research has moved a step forward in understanding how glucocorticoid hormones (‘stress hormones’) act upon the brain and what their function is. The findings could lead to more effective strategies in the prevention and treatment of mental health disorders.


Some mutations that disable SCN2A, one of the genes most strongly linked to autism, can unexpectedly make neurons hyperexcitable, a study in mice shows. The findings may help explain why a sizeable proportion of autistic children with mutations in SCN2A experience epileptic seizures.
Deleterious mutations in an autism-associated gene can make neurons hyperexcitable, raising the risk of epileptic seizures.
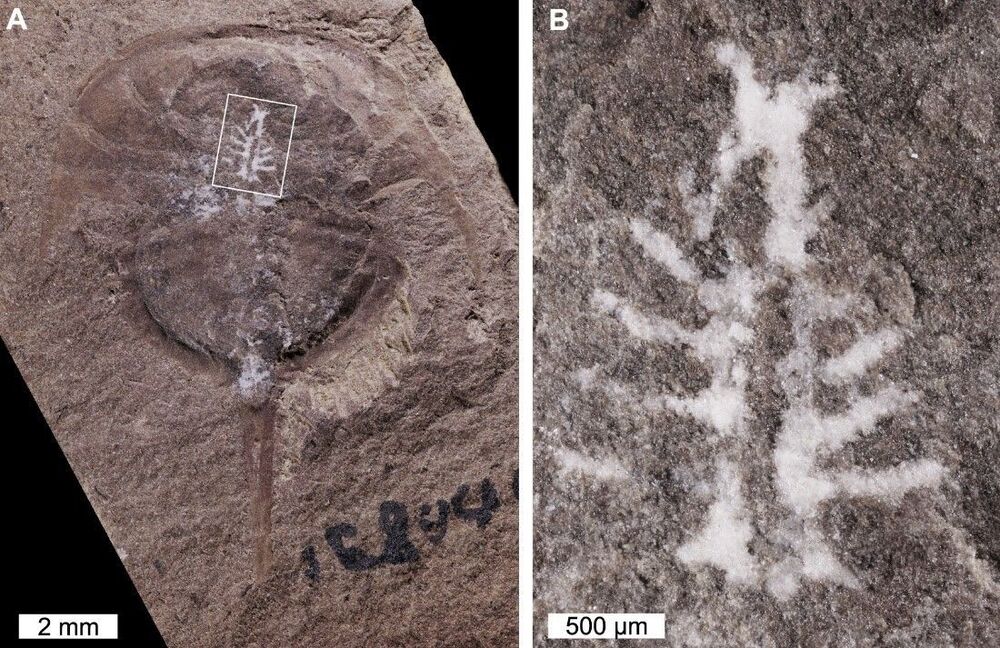

Researchers have discovered one of the oldest and best-preserved brains in the fossil record. A 310-million-year-old horseshoe crab was found with its complete brain intact, thanks to a previously unknown preservation method.
The majority of our knowledge of ancient creatures comes from bones – soft tissues don’t fossilize very well. Some mechanisms are better than others at preserving these fragile tissues though, most famously amber. Scientists can then scan amber-encased creatures to image their brains and other organs.
But that record only goes back so far. The oldest amber inclusions date back about 230 million years ago, to the Triassic period. Burgess Shale-type deposits, however, extend as far back as 520 million years ago, to the early Cambrian. These mudstone deposits can also preserve soft tissues as carbon films – most commonly the gut, but on rare occasions imprints of parts of the nervous system can be found.

As a cardiac electrophysiologist, Deeptankar DeMazumder has worked for years with people at risk for sudden cardiac arrest (SCA). Despite the latest medical advances, less than 10 percent of individuals stricken with an SCA will survive this highly dangerous condition in which irregular heart rhythms, or arrhythmias, cause the heart suddenly to stop beating.
In his role as a physician, DeMazumder keeps a tight focus on the electrical activity in their hearts, doing his best to prevent this potentially fatal event. In his other role, as a scientist at the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine, DeMazumber is also driven by a life-saving aspiration: finding ways to identify at-risk individuals with much greater accuracy than currently possible—and to develop better ways of protecting them from SCAs. He recently received a 2020 NIH Director’s New Innovator Award to pursue one of his promising ideas.
SCAs happen without warning and can cause death within minutes. Poor heart function and abnormal heart rhythms are important risk factors, but it’s not possible today to predict reliably who will have an SCA. However, doctors already routinely capture a wealth of information in electrical signals from the heart using electrocardiograms (ECGs). They also frequently use electroencephalograms (EEGs) to capture electrical activity in the brain.