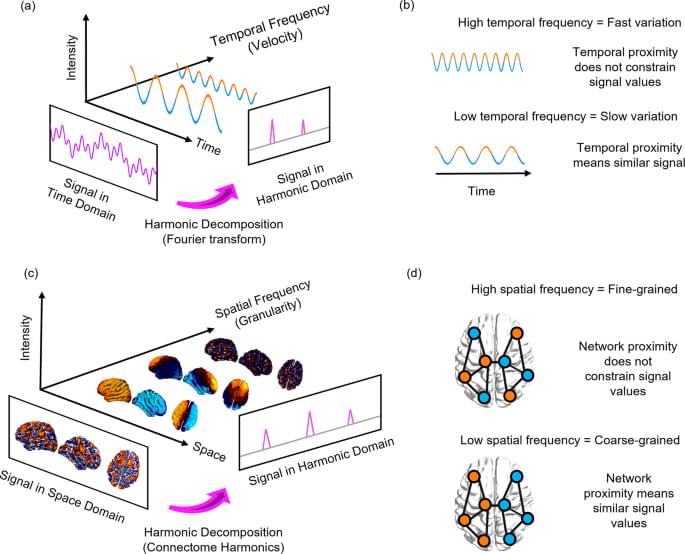
Connectome harmonic decomposition (CHD) generalises the mathematics of the Fourier transform to the network structure of the human brain. The traditional Fourier transform operates in the temporal domain (Fig. 1a): decomposition into temporal harmonics quantifies to what extent the signal varies slowly (low-frequency temporal harmonics) or quickly (high-frequency temporal harmonics) over time (Fig. 1b). Analogously, CHD re-represents a spatial signal in terms of harmonic modes of the human connectome, so that the spatial frequency (granularity) of each connectome harmonic quantifies to what extent the organization of functional brain signals deviates from the organization of the underlying structural network (Fig. 1c, d). Therefore, CHD is fundamentally different from, and complementary to, traditional approaches to functional MRI data analysis. This is because CHD does not view functional brain activity as composed of signals from discrete spatial locations, but rather as composed of contributions from distinct spatial frequencies: each connectome harmonic is a whole-brain pattern with a characteristic spatial scale (granularity)—from an entire hemisphere to just a few millimetres.
On one hand, this means that CHD is unsuitable to address questions pertaining to spatial localisation and the involvement of specific neuroanatomical regions; such questions have been extensively investigated within the traditional framework of viewing brain activity in terms of spatially discrete regions, and several previous studies have implicated specific neuroanatomical regions in supporting consciousness33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49. On the other hand, CHD enables us to consider how brain activity across states of consciousness is shaped by the brain’s distributed network of structural connections, reflecting the contribution of global patterns at different spatial scales—each arising from the network topology of the human connectome. We emphasise that neither approach is inherently superior, but rather they each provide a unique perspective on brain function: one localised, the other distributed.