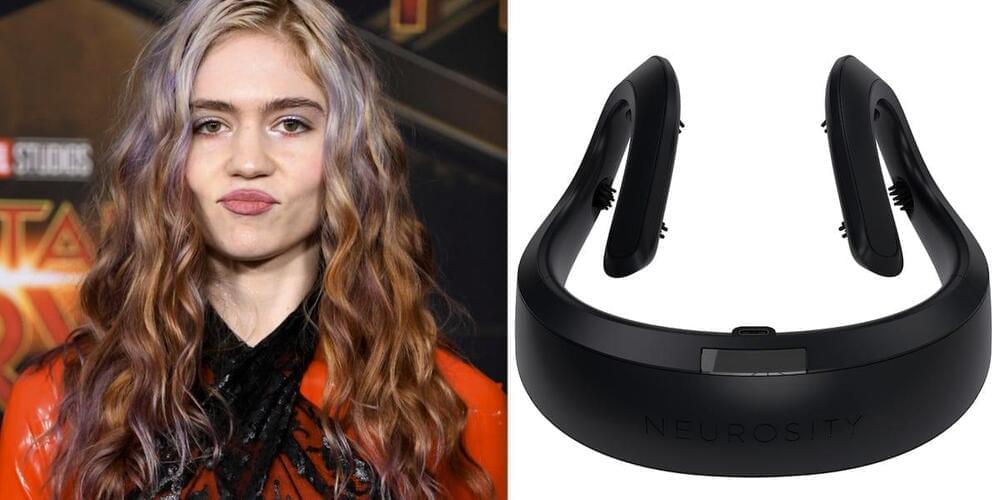
Neurosity’s headset uses electroencephalogram technology, or EEG, to measure brain activity by placing small metal electrodes on a person’s scalp. If the electrodes detect decreased electrical activity in the brain, the Crown plays music and sounds, or pulses vibrations, hoping those actions will help the user focus.
But some developers, it seems, have taken Neurosity’s tech a step further, turning the Crown into a more traditional brain computer interface that can allow users to control a computer using only their mind.
One owner of the gadget claimed they’ve used it to drive a Tesla, moving the electric car short distances by doing some mental math, which signals to the device that the person wearing it is exerting a lot of cognitive effort.
Grimes got a new brain gadget for her 35th birthday.
“Getting a non invasive brain computer interface for my birthday (!!!!?),” she tweeted Friday. “Yeah it’s a good time to be alive.”
Neurosity CEO AJ Keller confirmed that the singer, named Claire Boucher, had asked for one of the company’s headsets, known as the Crown, in a custom white color.