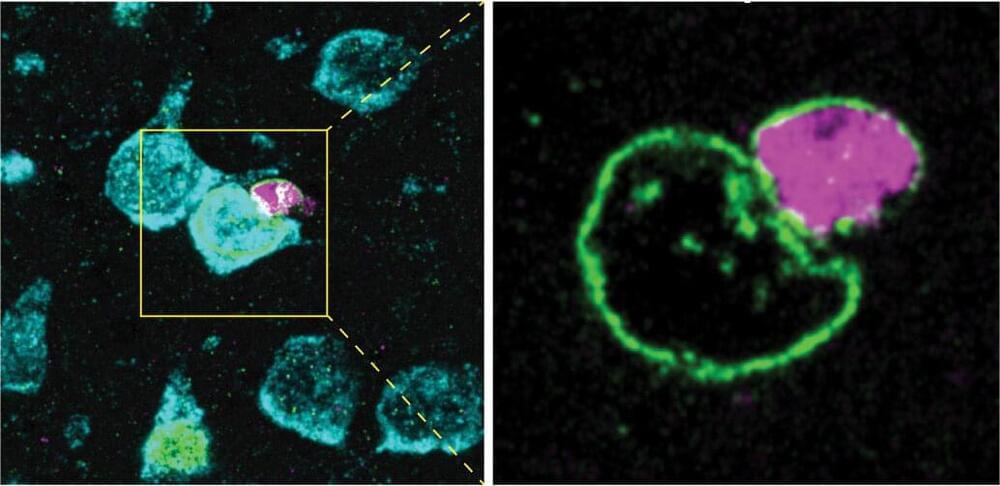
Researchers at UC Davis are the first to report how a specific type of brain cells, known as oligodendrocyte-lineage cells, transfer cell material to neurons in the mouse brain. Their work provides evidence of a coordinated nuclear interaction between these cells and neurons. The study was published today in the Journal of Experimental Medicine.
“This novel concept of material transfer to neurons opens new possibilities for understanding brain maturation and finding treatments for neurological conditions, such as Alzheimer’s disease, cerebral palsy, Parkinson’s and Huntington’s disease,” said corresponding author Olga Chechneva is an assistant project scientist at UC Davis Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Medicine and independent principal investigator in the Institute for Pediatric Regenerative Medicine at Shriners Children’s Northern California.
Oligodendrocyte-lineage cells, also called oligodendroglia, are a type of glial cells found in the central nervous system. From birth onward, these glial cells arise to support neural circuit maturation. They are mostly known for their role in myelination—the formation of the insulating myelin sheath around nerve axons.



 עברית (Hebrew)
עברית (Hebrew)