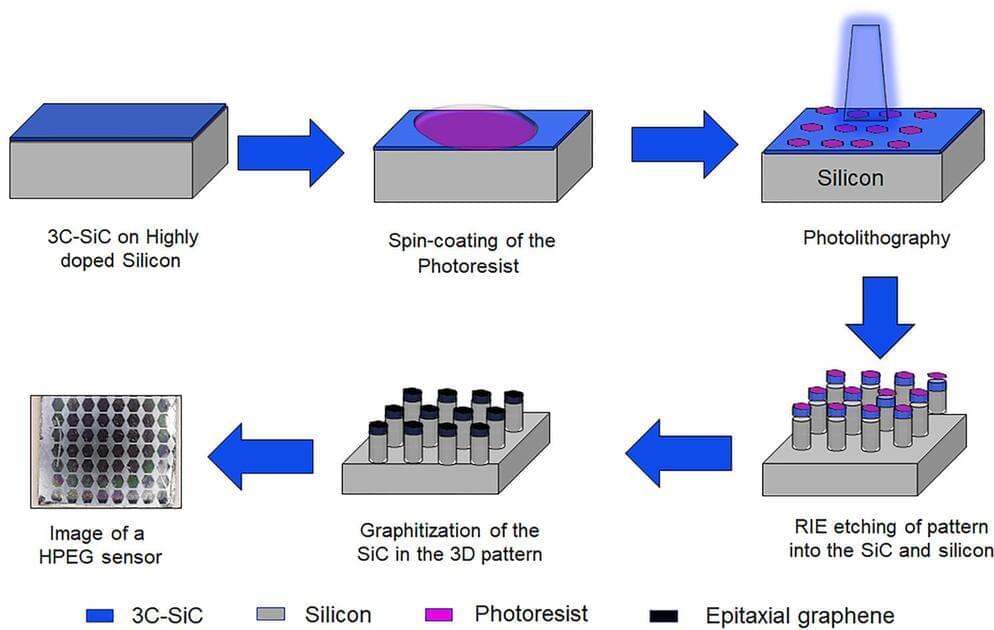
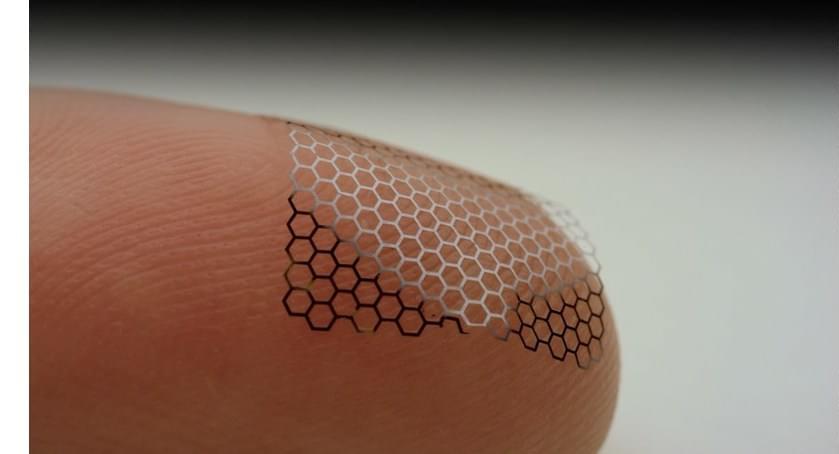
As fun as brain-computer interfaces (BCI) are, for the best results they tend to come with the major asterisk of requiring the cutting and lifting of a section of the skull in order to implant a Utah array or similar electrode system. A non-invasive alternative consists out of electrodes which are placed on the skin, yet at a reduced resolution. These electrodes are the subject of a recent experiment by [Shaikh Nayeem Faisal] and colleagues in ACS Applied NanoMaterials employing graphene-coated electrodes in an attempt to optimize their performance.
Although external electrodes can be acceptable for basic tasks, such as registering a response to a specific (visual) impulse or for EEG recordings, they can be impractical in general use. Much of this is due to the disadvantages of the ‘wet’ and ‘dry’ varieties, which as the name suggests involve an electrically conductive gel with the former.
This gel ensures solid contact and a resistance of no more than 5 – 30 kΩ at 50 Hz, whereas dry sensors perform rather poorly at 200 kΩ at 50 Hz with worse signal-to-noise characteristics, even before adding in issues such as using the sensor on a hairy scalp, as tends to be the case for most human subjects.