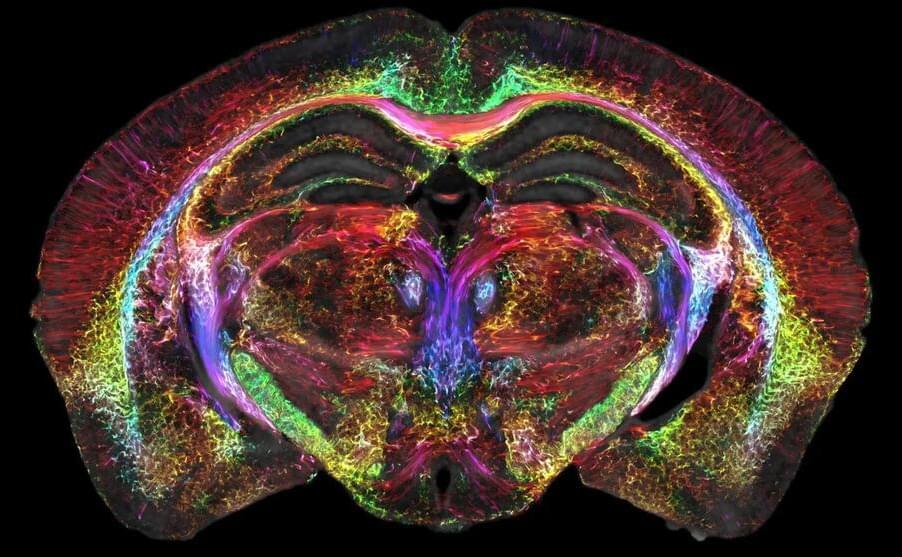
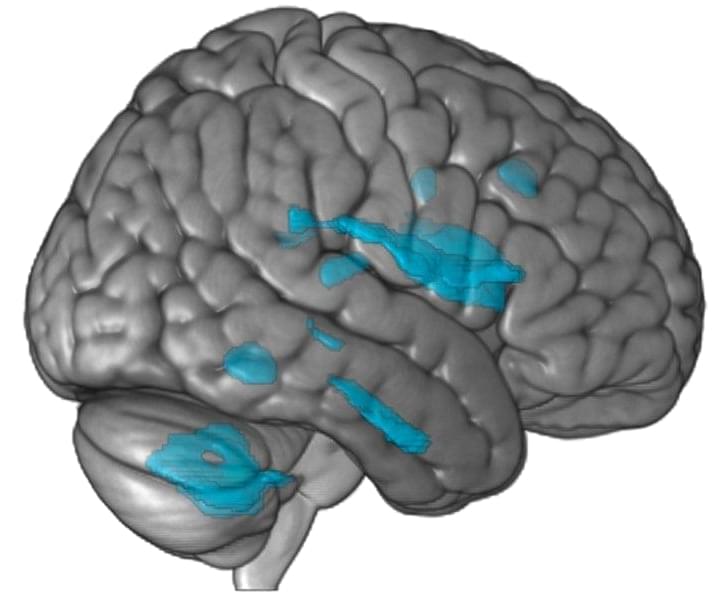
Findings point to brain areas that integrate planning, purpose, physiology, behavior, and movement.
Calm body, calm mind, say the practitioners of mindfulness. A new study by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis indicates that the idea that the body and mind are inextricably intertwined is more than just an abstraction. The study shows that parts of the brain area that control movement are plugged into networks involved in thinking and planning, and in control of involuntary bodily functions such as blood pressure and heartbeat. The findings represent a literal linkage of body and mind in the very structure of the brain.
The research, published on April 19 in the journal Nature, could help explain some baffling phenomena, such as why anxiety makes some people want to pace back and forth; why stimulating the vagus nerve, which regulates internal organ functions such as digestion and heart rate, may alleviate depression; and why people who exercise regularly report a more positive outlook on life.