That, in a nutshell, is The perceived sensation of pain that you know as heartburn, the smell that draws you to a steak on the grill, the sight of magenta streaked across the sky at sunset—all are instances of conscious experience.
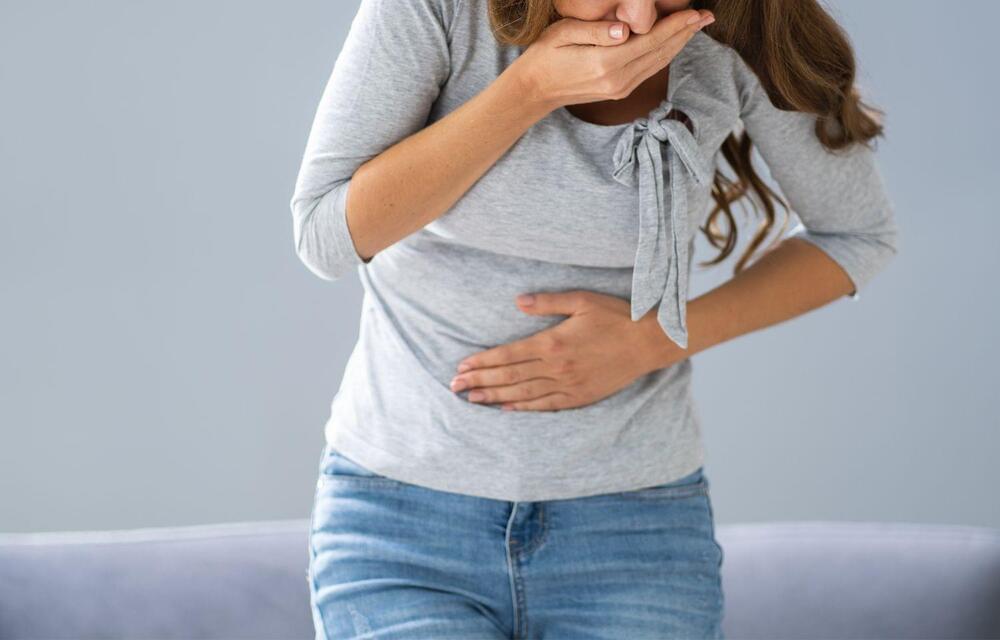



A study from Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago demonstrated that Botulinum toxin (Botox) injected in the pylorus during endoscopy improves chronic nausea and vomiting in children who have a disorder of gut-brain interaction (DGBI). These debilitating symptoms not attributed to a defined illness have previously been called functional gastrointestinal disorders before the newer DGBI classification. The study’s findings point to a novel understanding of the condition’s pathology – pylorus that is failing to relax and allow food to effectively pass into the small intestine resulting in symptoms of nausea, vomiting, early satiety and bloating.
Results were published in the Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition.
“Our results suggest that chronic nausea and vomiting might be caused by pyloric dysfunction, rather than abnormal peristalsis, which is the rhythmic contraction and relaxation of digestive tract muscles needed to move foods and liquids through the gastrointestinal system,” said lead author Peter Osgood, MD, gastroenterologist at Lurie Children’s and Assistant Professor of Pediatrics at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine. “This is a paradigm shift in our understanding of mechanistic pathology. Importantly, it opens the door to a more targeted use of Botox specifically in children who are found to have pyloric dysfunction during endoscopy, and for whom the current medications are not effective.”
Scientists have discovered new insights into how our brain stores episodic memories—a type of long-term, conscious memory of a previous experience—that could be critical to the development of new neuroprosthetic devices to help patients with memory problems, like Alzheimer’s disease and dementia.
The new study—led by the University of Glasgow, in collaboration with the University of Birmingham and University of Erlangen—used special electrodes, implanted directly into the brains of epilepsy patients requiring surgery, to allow scientists to observe the activity of individual neurons in the hippocampus region of the brain.
The hippocampus is a challenging area to study, due to its location deep within the brain, yet this area is critical for our memory, acting as the librarian to the memory library in our brain.
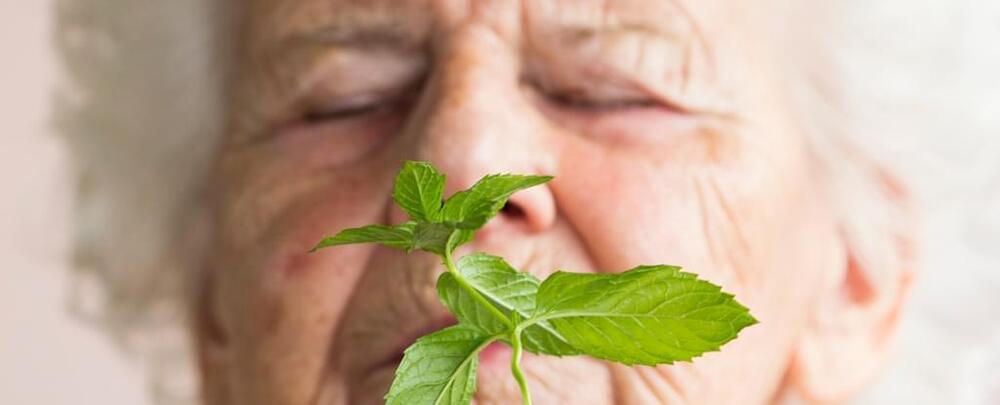

A recent study reports something strange: When mice with Alzheimer’s disease inhale menthol, their cognitive abilities improve. It seems the chemical compound can stop some of the damage done to the brain that’s usually associated with the disease.
In particular, researchers noticed a reduction in the interleukin-1-beta (IL-1β) protein, which helps to regulate the body’s inflammatory response – a response that can offer natural protection but one that leads to harm when it’s not controlled properly.
The team behind the study, which was published in April 2023, says it shows the potential for particular smells to be used as therapies for Alzheimer’s. If we can figure out which odors cause which brain and immune system responses, we can harness them to improve health.
Combining two cutting-edge technologies, researchers revealed the impact of a multitude of genes that are associated with neurodevelopmental disorders, including autism, but whose effects on human brain development were previously unknown.