The strange science experiment that blew a worm’s head off… and blew our minds.
This interview is an episode from @The-Well, our publication about ideas that inspire a life well-lived, created with the @JohnTempletonFoundation.
Watch Michael Levin’s next interview ► https://youtu.be/XHMyKOpiYjk.
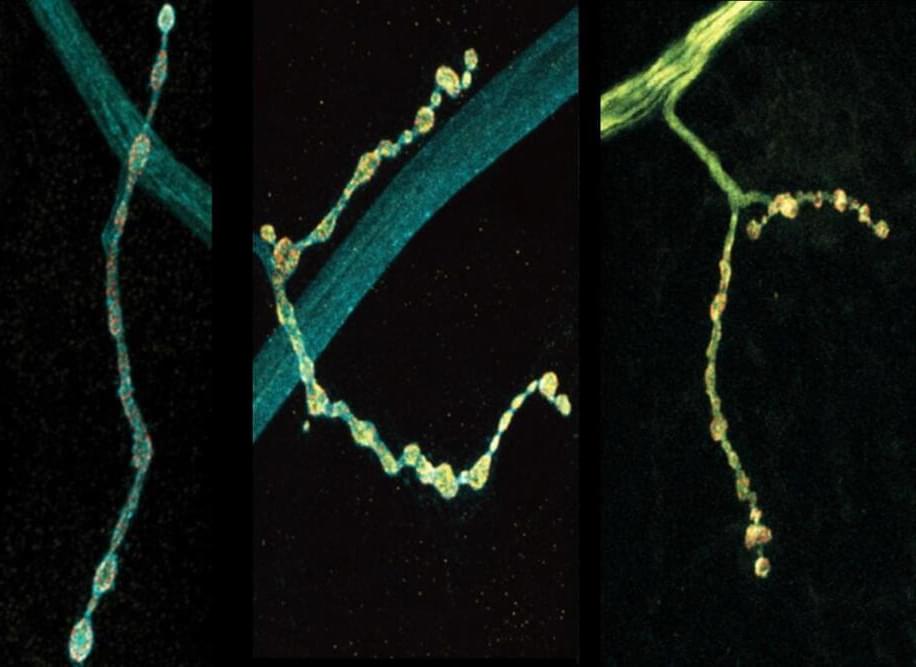
Michael Levin, a developmental biologist at Tufts University, challenges conventional notions of intelligence, arguing that it is inherently collective rather than individual.
Levin explains that we are collections of cells, with each cell possessing competencies developed from their evolution from unicellular organisms. This forms a multi-scale competency architecture, where each level, from cells to tissues to organs, is solving problems within their unique spaces.
Levin emphasizes that properly recognizing intelligence, which spans different scales of existence, is vital for understanding life’s complexities. And this perspective suggests a radical shift in understanding ourselves and the world around us, acknowledging the cognitive abilities present at every level of our existence.