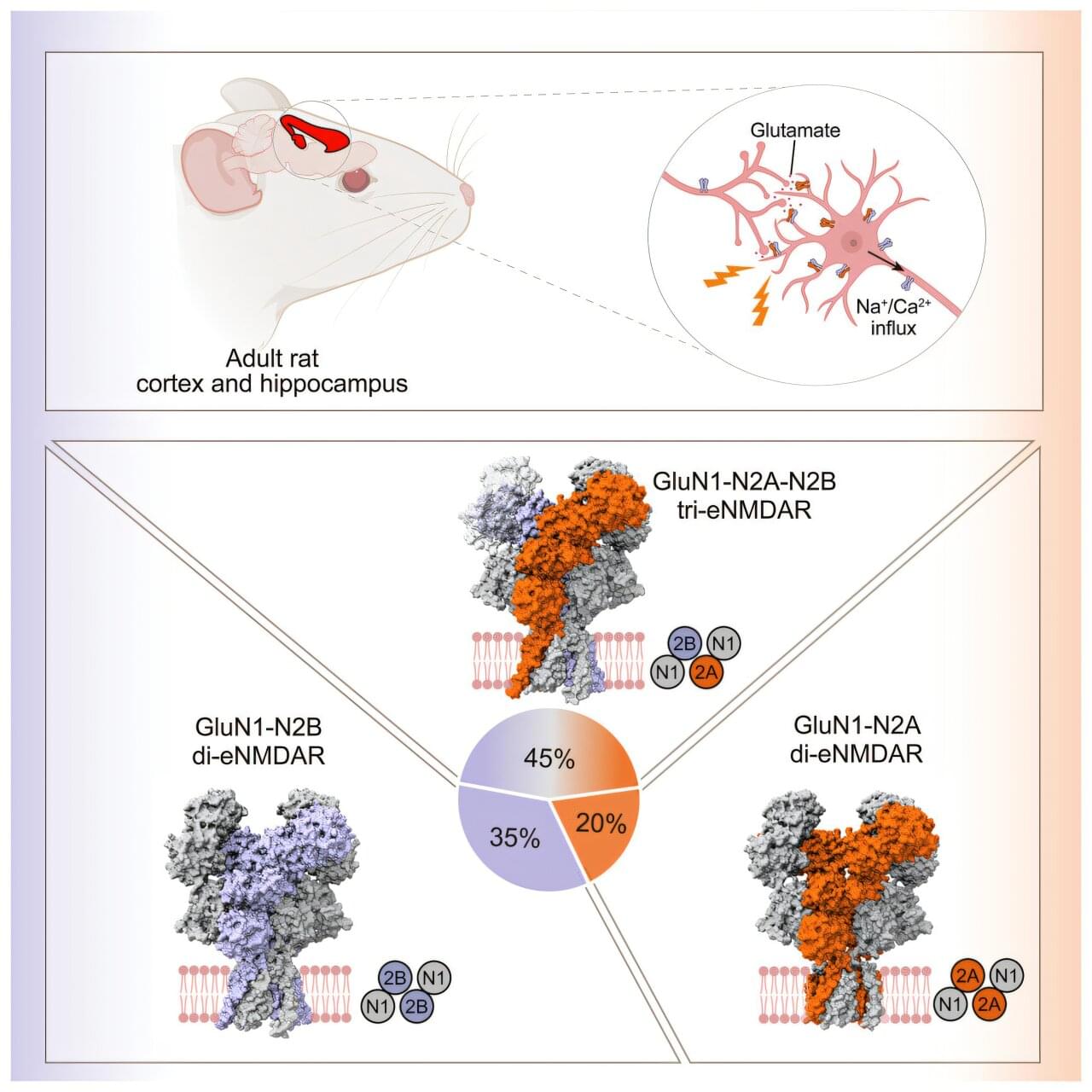
In a study published in Cell, a research team led by Zhu Shujia from the Center for Excellence in Brain Science and Intelligence Technology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), along with Li Yang from the Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica of CAS, has dissected the assembly and architecture of endogenous N-methyl-ᴅ-aspartate receptors (eNMDARs) in the adult mammalian cerebral cortex and hippocampus.
Learning and memory are fundamental brain functions that underlie human cognition and perception of the world, which rely on development-and activity-dependent synaptic plasticity. NMDA receptors, members of the excitatory ionotropic glutamate receptor family, are essential to these processes.
They regulate the strength of synaptic connections, playing a critical role in advanced brain functions. In higher brain structures involved in cognition, such as the cerebral cortex and hippocampus, they are especially vital for cognitive function.