Cecile G. Tamura Lifeboat Foundation An effective treatment for depression from a systematic review of 200 unique RCTs:
Exercise.
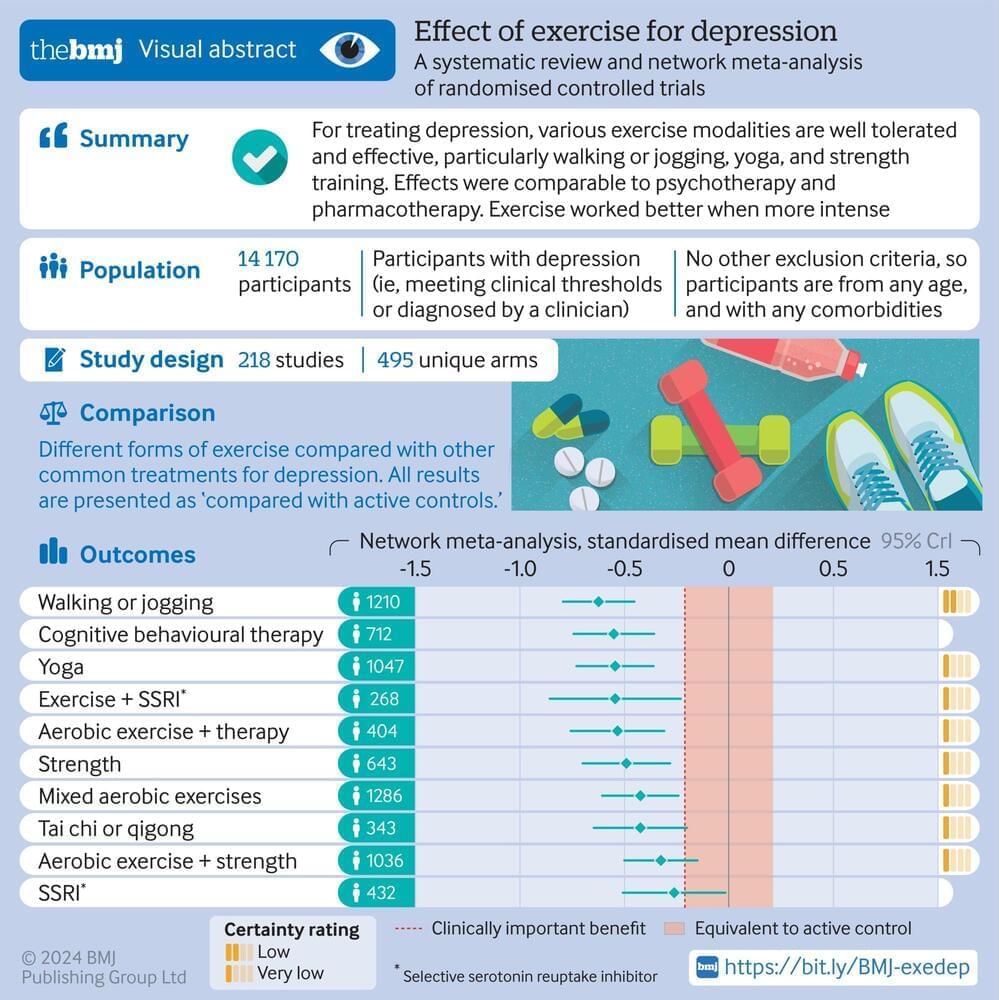
Objective To identify the optimal dose and modality of exercise for treating major depressive disorder, compared with psychotherapy, antidepressants, and control conditions.
Design Systematic review and network meta-analysis.
Methods Screening, data extraction, coding, and risk of bias assessment were performed independently and in duplicate. Bayesian arm based, multilevel network meta-analyses were performed for the primary analyses. Quality of the evidence for each arm was graded using the confidence in network meta-analysis (CINeMA) online tool.
Data sources Cochrane Library, Medline, Embase, SPORTDiscus, and PsycINFO databases.