Khan, M.U., Hassan, B., Alazzam, A. et al. Brain inspired iontronic fluidic memristive and memcapacitive device for self-powered electronics. Microsyst Nanoeng 11, 37 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41378-025-00882-x.
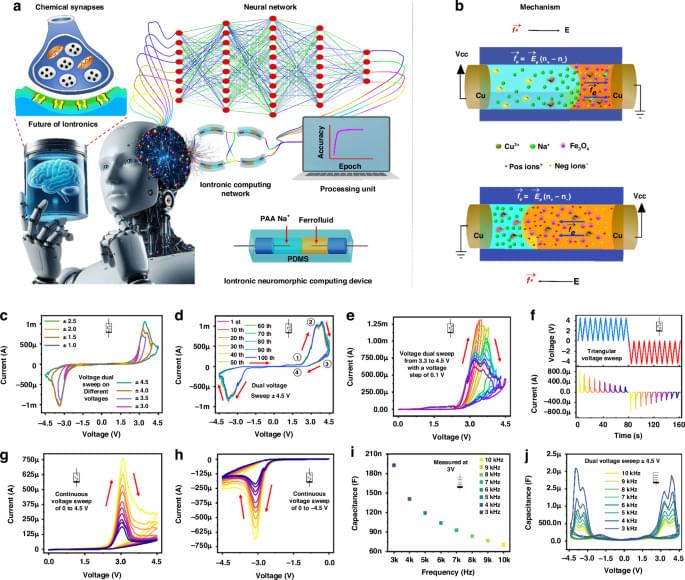

Khan, M.U., Hassan, B., Alazzam, A. et al. Brain inspired iontronic fluidic memristive and memcapacitive device for self-powered electronics. Microsyst Nanoeng 11, 37 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41378-025-00882-x.
This is the prophesied follow-up to my fastpunch through humanism, covering some 20th century reactions to humanist thought. I hypothesize that we’re at something of a standoff between humanism and posthumanism, as our political and educational institutions are struggling to terms with changing technical contexts.
If you like the work there’s more at https://spoti.fi/3f0OIXD and / plasticpills.
Addendum: Sometimes posthumanism is confused with transhumanism, which I had planned to cover in this video but it was getting too long. Transhumanism is often humanistic in that it privileges the same capacities that humanism does–intellect, memory, progress, consciousness–and proposes that our bodies can be technologically or genetically augmented to improve these capacities in new stages of human develepment– uploading our consciousness into the cloud or staving off mortality. Posthumanists, by and large, tend to de-emphasize the supposed value of those ends in the first place, although there is some overlap.
Thanks for watching!
Sources Used:
Nietzsche’s Twilight of the Idols (https://amzn.to/37GFyw7) and Human, All Too Human (https://amzn.to/2OQsdbQ)
Deleuze and Guattari, A Thousand Plateaus (https://amzn.to/33l4AgP)
Bernard Stiegler, Technics and Time (https://amzn.to/2qQoJOF)
Donna Haraway (https://amzn.to/2pPVxqy)
Timecode:
MIT 6.868J The Society of Mind, Fall 2011
View the complete course: http://ocw.mit.edu/6-868JF11
Instructor: Marvin Minsky.
In this lecture, students discuss Barry Schwartz’s 2000 piece on the psychology of hope. They also look at ethical dilemmas for positive psychology, and who has the right to meddle with top-level goals or induce happiness.
License: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA
More information at http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
More courses at http://ocw.mit.edu
Summary: A new study reveals that human accelerated regions (HARs)—segments of DNA that evolved much faster than expected—may be key to the brain’s advanced cognitive abilities. Researchers compared human and chimpanzee neurons and found that HARs drive the growth of multiple neural projections, which enhance communication between brain cells.
When human HARs were introduced into chimp neurons, they also grew more projections, suggesting a direct link between HARs and neural complexity. However, these same genetic changes may also contribute to neurodevelopmental disorders like autism, highlighting the delicate balance of human brain evolution.
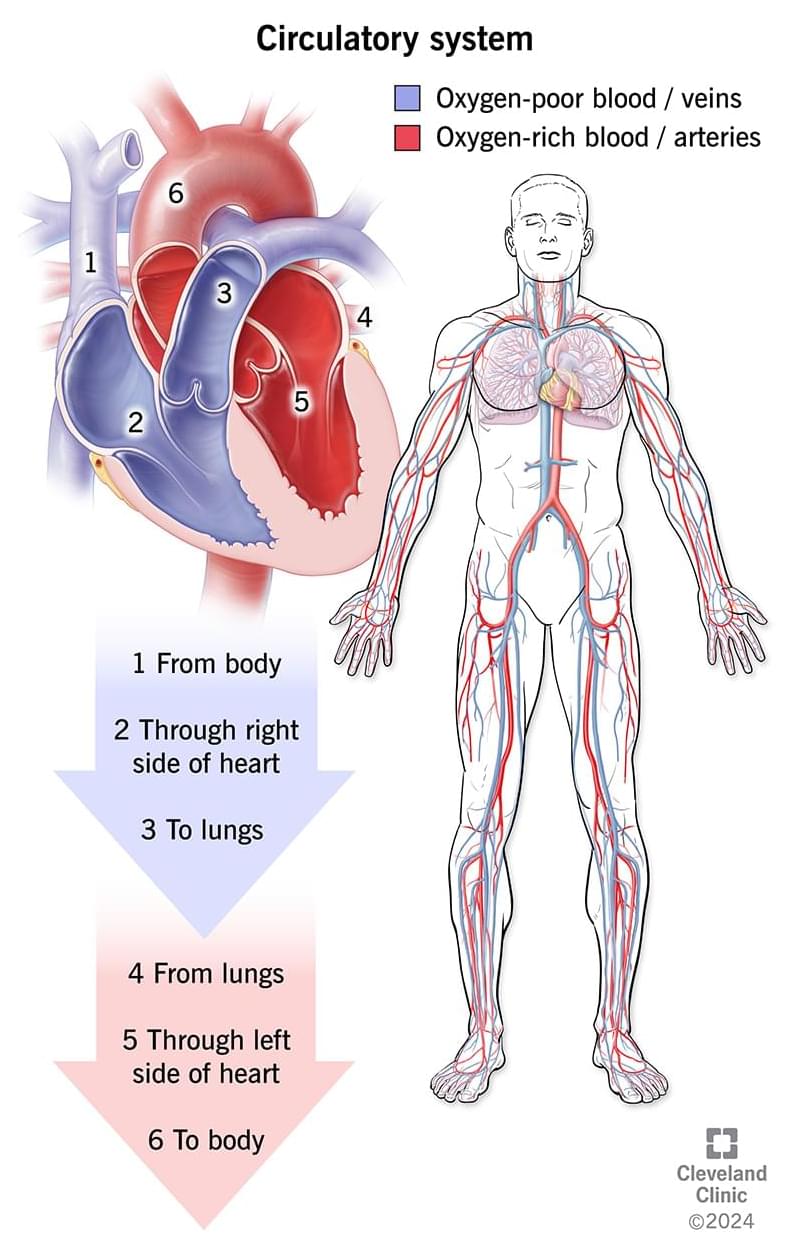
The astounding numbers of the human body:
Your body consists of 37 trillion cells divided into 200 different types.
100 billion cells make up the skin, which is the largest organ in your body. 100 billion neurons in the brain allow you to process as many as 60,000 thoughts per day.
You also have 127 million retinal cells that allow you to see the world in as many as 10 million different colors. You have 30 trillion red blood cells, 42 billion blood vessels, and 6 liters (1.6 gallons) of blood in your body. Your blood makes up approximately 10% of your body weight. Your nose has 1,000 olfactory receptors that allow you to distinguish 50,000 different smells.
Your lungs allow you to breathe 23,040 breaths per day, while your heart beats around 115,200 heartbeats per day or 42 million heartbeats per year. You have 640 muscles, 360 joints, 206 bones and 100,000 hair follicles. You produce around 23,000 liters (6,075 gallons) of saliva in your lifetime, which is enough to fill two swimming pools.
Your circulatory system (cardiovascular system) includes your heart and blood vessels. Your heart pumps oxygen-rich blood after your lungs add oxygen to your blood.
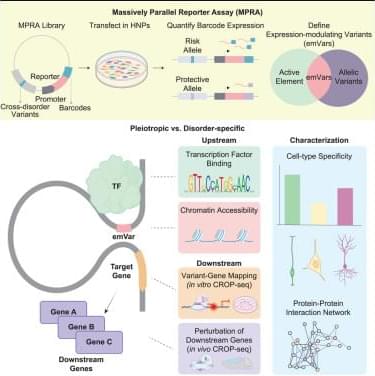
Researchers just found common genes linked to autism, ADHD, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder, Tourette syndrome, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and anorexia.
These disorders all share common genetic variants that influence brain development.
Researchers found that these genetic differences impact multiple stages of brain growth and are involved in complex protein interactions. This discovery could explain why many of these conditions often appear together in individuals and families, offering a fresh perspective on mental health connections.
By identifying 683 genetic variants that regulate brain development, scientists hope to pave the way for new treatments targeting these shared genetic factors. This research challenges traditional classifications of psychiatric disorders and suggests that a single therapy could potentially address multiple conditions. With nearly 1 billion people worldwide affected by mental health disorders, these findings mark a significant step toward more effective, genetically-informed treatments.
High-throughput experimental validation of genetic variants linked to eight psychiatric disorders reveals the regulatory mechanisms underlying variants with pleiotropic and disorder-specific effects.
https://search.app/?link=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=faI…cover/m5/4
Closer to truth aspects of consciousness.
Like Closer To Truth on Facebook and discover daily videos, updates, announcements, and more: https://shorturl.at/tak4l.
We offer distinctive approaches to consciousness, including cognitive science, phenomenology, and even the implications of aesthetics like fiction and films. We observe the richness of consciousness studies.
Make a tax-deductible donation of any amount to help Closer To Truth continue exploring the world’s deepest questions: https://shorturl.at/OnyRq.
Dr. Zorana Ivcevic Pringle studies the role of emotion and emotional intelligence in creativity and well-being, as well as how to use the arts (and art-related institutions) to promote emotion and creativity skills.

A large study of 18,740 dementia patients found that those taking antidepressants experienced faster cognitive decline compared to those who were not medicated.
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), particularly escitalopram, citalopram, and sertraline, were associated with the greatest deterioration.
Mirtazapine, which works differently from SSRIs, had a milder impact on cognitive function.
While depression itself can worsen dementia symptoms, it remains unclear whether the decline is due to the medication or the underlying condition.
Researchers emphasize the need for more individualized treatment approaches to balance mental health benefits with potential cognitive risks.
Future studies will explore whether specific dementia types or biomarkers influence antidepressant effects.