Could your driving habits reveal your mental health? Research shows AI can analyze driving data to identify depression risk in older adults.


Get a Wonderful Person Tee: https://teespring.com/stores/whatdamathMore cool designs are on Amazon: https://amzn.to/3QFIrFXAlternatively, PayPal donations ca…
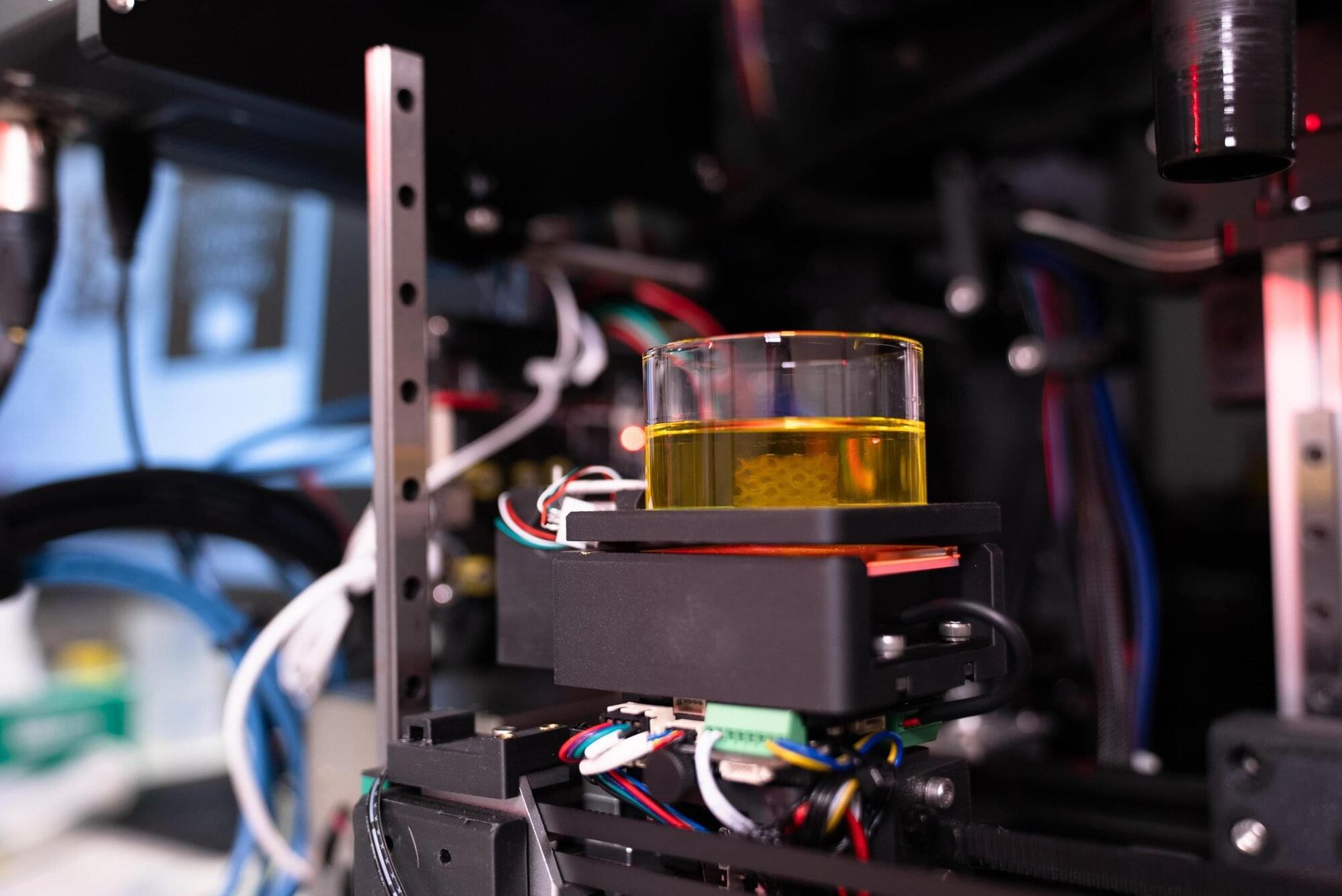
Biomedical engineers at the University of Melbourne have developed a 3D bioprinting system capable of creating structures that closely replicate various human tissues, ranging from soft brain tissue to more rigid materials like cartilage and bone.
This innovative technology provides cancer researchers with a powerful tool for replicating specific organs and tissues, enhancing their ability to predict drug responses and develop new treatments. By offering a more accurate and ethical approach to drug discovery, it also has the potential to reduce reliance on animal testing.
Head of the Collins BioMicrosystems Laboratory at the University of Melbourne, Associate Professor David Collins said: In addition to drastically improving print speed, our approach enables a degree of cell positioning within printed tissues. Incorrect cell positioning is a big reason most 3D bioprinters fail to produce structures that accurately represent human tissue.
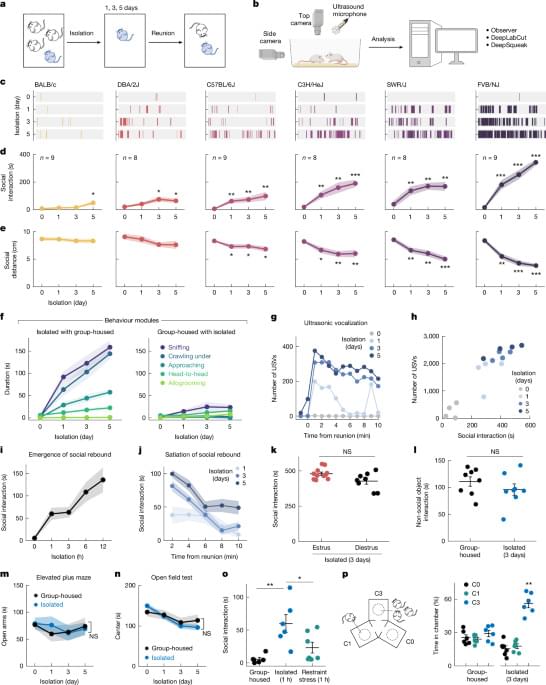
Scientists at the La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) have identified a potential new target for Parkinson’s disease treatment. Their research highlights the role of a specific brain cell protein in triggering the disease and may explain why Parkinson’s is more prevalent in men.
Recent studies from LJI suggest that autoimmunity plays a key role in Parkinson’s onset. Their latest findings, published in The Journal of Clinical Investigation, reveal that the protein PINK1 may label certain brain cells for attack by the immune system, contributing to disease progression.
“This research allows us to better understand the role of the immune system in Parkinson’s disease,” says LJI Professor Alessandro Sette, Dr. Biol. Sci., senior author of the recent study.
Links:
- Patreon (Support the channel directly!): https://www.patreon.com/Asianometry.
- X: https://twitter.com/asianometry.
- Bluesky: https://bsky.app/profile/asianometry.bsky.social.
- Newsletter & Podcast (available through Stratechery Plus): https://asianometry.passport.online/
- LinkedIn (feel free to connect): www.linkedin.com/in/jon-y-asianometry
Summary: A new study challenges the long-held belief that the striatum is responsible for selecting actions. Researchers found that instead of making decisions, the striatum and motor cortex work together to specify movement details, such as how to reach for an object.
Using a novel “reach-to-pull” system, they recorded neural activity in mice and found that both regions were active during movement execution, not decision-making. These findings could reshape our understanding of motor control and help improve treatments for movement disorders like Parkinson’s and Huntington’s disease.
Slides here: http://bit.ly/MZMmdp — Whole Brain Emulation & Computational Neuroscience Synopsis Within a few decades, I believe it will be possible to construct working simulations of an entire human brain. In this talk I will explain why I believe this, with reference to recent work in Computational Neuroscience, extrapolations of Moore’s Law, and other such matters. I will also address some common criticisms leveled against whole brain emulation, and briefly discuss some of the many ways I believe this technology will drastically change the face of society in the near future.
I’ll basically be presenting selected material from this publication, with some updates and additions of my own.
http://www.fhi.ox.ac.uk/brain-emulation-roadmap-report.pdf.
Science, Technology & the Future — By Design.

Summary: Scientists have developed e-Taste, a novel technology that digitally replicates taste in virtual environments. Using chemical sensors and wireless dispensers, the system captures and transmits taste data remotely, enabling users to experience sweet, sour, salty, bitter, and umami flavors.
In tests, participants distinguished different taste intensities with 70% accuracy, and remote tasting was successfully initiated across long distances. Beyond gaming and immersive experiences, this breakthrough could enhance accessibility for individuals with sensory impairments and deepen our understanding of how the brain processes taste.

Two remarkable innovations coming together to tackle prion disease: AAVs that leverage human receptors to cross the blood-brain-barrier + a way of epigenetically silencing the gene encoding prions. I recall reading those cited papers and both are amazing!
BOSTON and NEW YORK, Feb. 28, 2025 /PRNewswire/ — Apertura Gene Therapy, a biotechnology company focused on innovative gene therapy solutions, supports the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, and the Whitehead Institute in advancing a gene therapy approach for the treatment of prion disease. The project is led by the Vallabh-Minikel lab at the Broad Institute which is focused on finding a cure for prion disease, and their approach leverages two cutting-edge technologies developed at the Institutes of both the Broad and Whitehead: the CHARM platform designed in Dr. Jonathan Weismann’s lab, and TfR1 capsid, an engineered AAV designed in the lab of Dr. Ben Deverman, Director of Vector Engineering at the Broad Institute and scientific founder of Apertura.
Prion disease is a rare, fatal, neurodegenerative disorder caused by misfolded proteins. The new gene therapy aims to address the root cause by using CHARM (Coupled Histone tail for Autoinhibition Release of Methyltransferase) to target and silence the gene that codes for the disease-causing protein1. This payload will be combined with Apertura’s TfR1 capsid, an adeno-associated virus (AAV) capsid engineered to efficiently cross the blood-brain barrier by binding to the human TfR1 receptor, which facilitates iron transport into brain cells2. Together, these technologies represent a transformative approach to tackling CNS diseases.
“We are thrilled to see the progress being made in the development of this innovative therapy for prion disease,” said Dr. Sonia Vallabh, co-leader of the group at the Broad working on preventative therapies for prion disease. “The collaborative efforts between Apertura, the Broad Institute and the Whitehead mark a significant milestone toward addressing unmet needs in neurodegenerative disorders.”