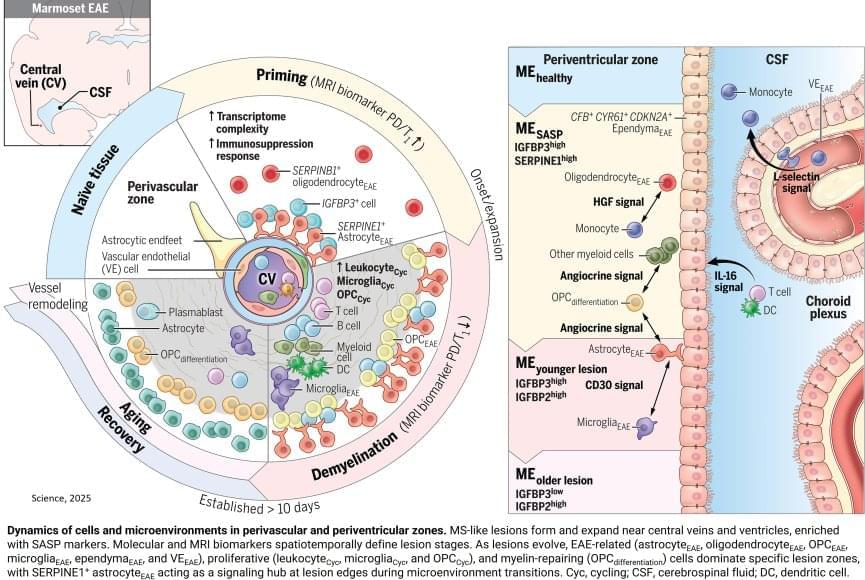
To mimic the conditions of the human brain, the researchers opted not to use a mouse model for MS, instead advancing a model that uses the marmoset, a nonhuman primate. Compared to mouse brains, marmoset and human brains have a higher ratio of white matter (the “wires” of the brain) to gray matter (neuronal cell bodies). The marmoset model creates multiple lesions that closely resemble those seen in human MS and that can be tracked in real time using MRI imaging. Because these lesions can be induced experimentally, the model offers a look at the earliest stages of inflammation and immune responses that lead to MS-like demyelination.
One key player identified was a specific type of astrocyte, one of the support cell types in the brain, that turns on a gene called SERPINE1 or plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI1). They found SERPINE1-expressing astrocytes in vulnerable brain borders before visible damage occurs, clustering near blood vessels and the fluid-filled ventricles of the brain and signaling future areas of lesion development. These astrocytes also appeared to influence the behavior of other cells near the lesion area, including the ability of immune cells to enter the brain and contribute to inflammation, as well as the precursor cells involved in myelin repair.
Given that SERPINE1-expressing astrocytes accumulated at the edges of growing lesions, where damage happens but healing also begins, their potential dual role in coordinating signals that could lead to either tissue repair or further damage was an unexpected wrinkle that will require further study. It’s possible that the earliest responses could be a part of a protective mechanism that becomes overwhelmed as the injury progresses. It’s also possible that the same mechanism could itself become disease-causing.
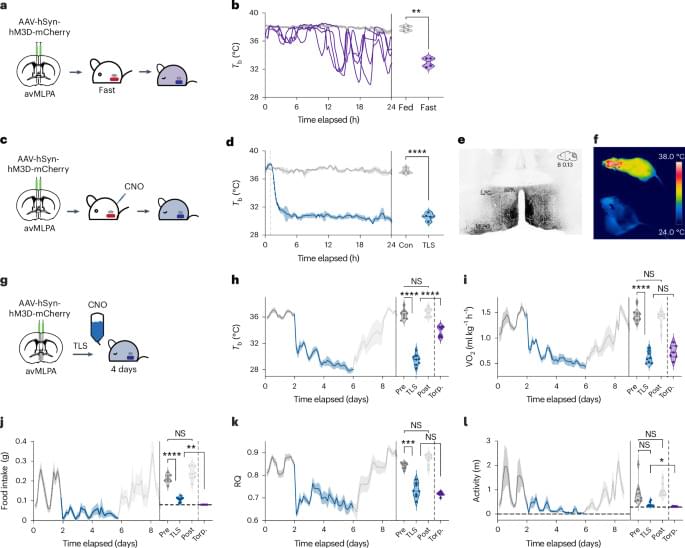
Using an animal model of multiple sclerosis (MS), researchers have created a four-dimensional brain map that reveals how lesions similar to those seen in human MS form. These findings, published in Science, provide a window into the early disease state and could help identify potential targets for MS treatments and brain tissue repair.
The researchers combined repeated MRI imaging with brain-tissue analysis, including gene expression, to track the onset and development of MS-like lesions. They uncovered a new MRI signature that can help detect brain regions at risk for damage weeks before any visible lesions occur. They also identified “microenvironments” within affected brain tissue based on observed patterns of neural function, inflammation, immune and support cell responses, gene expression, and levels of damage and repair.
“Identifying the early events that occur after inflammation and teasing apart which are reparative versus which are damaging, can potentially help us identify MS disease activity sooner and develop treatments to slow or stop its progression,” said the author.