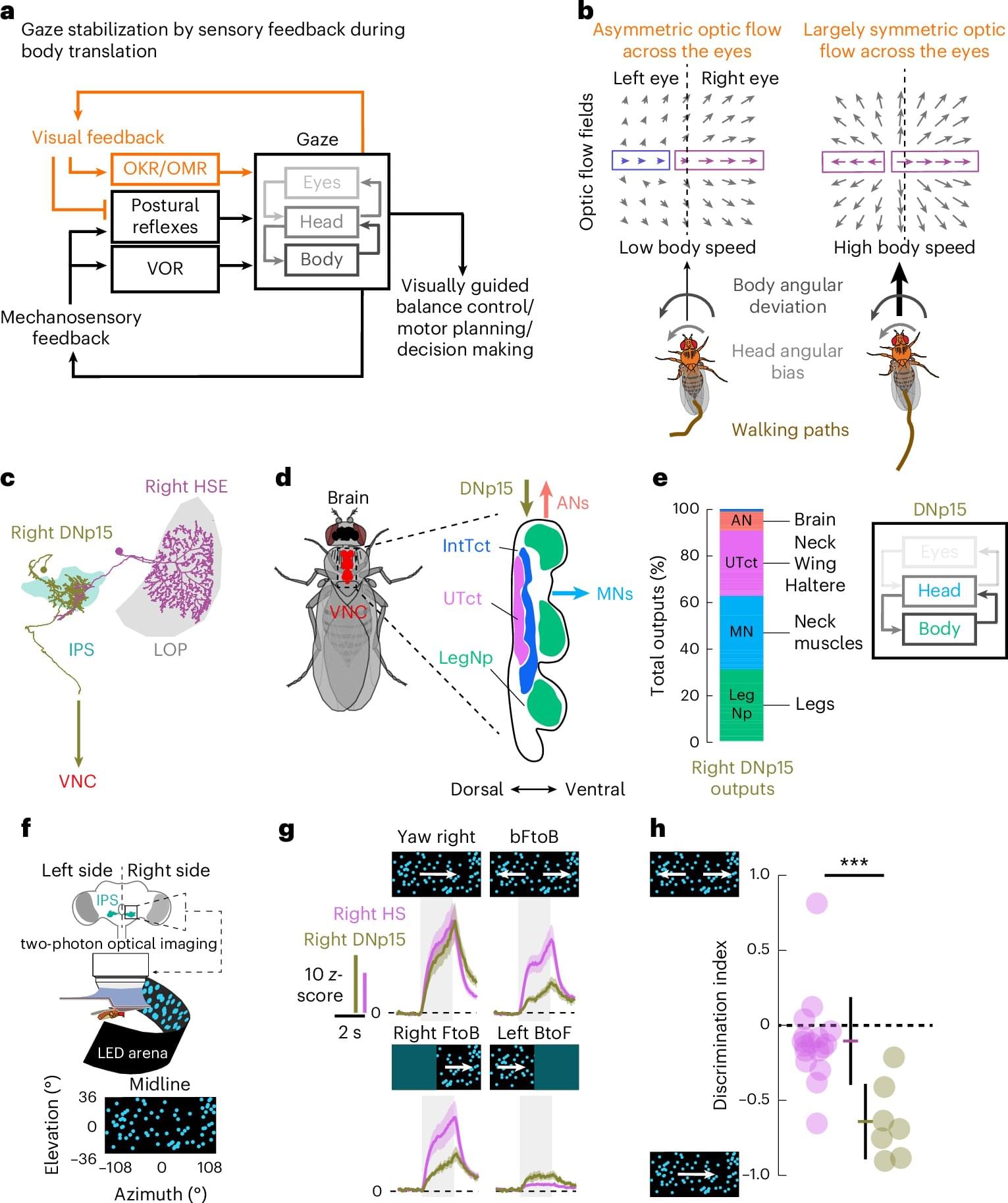
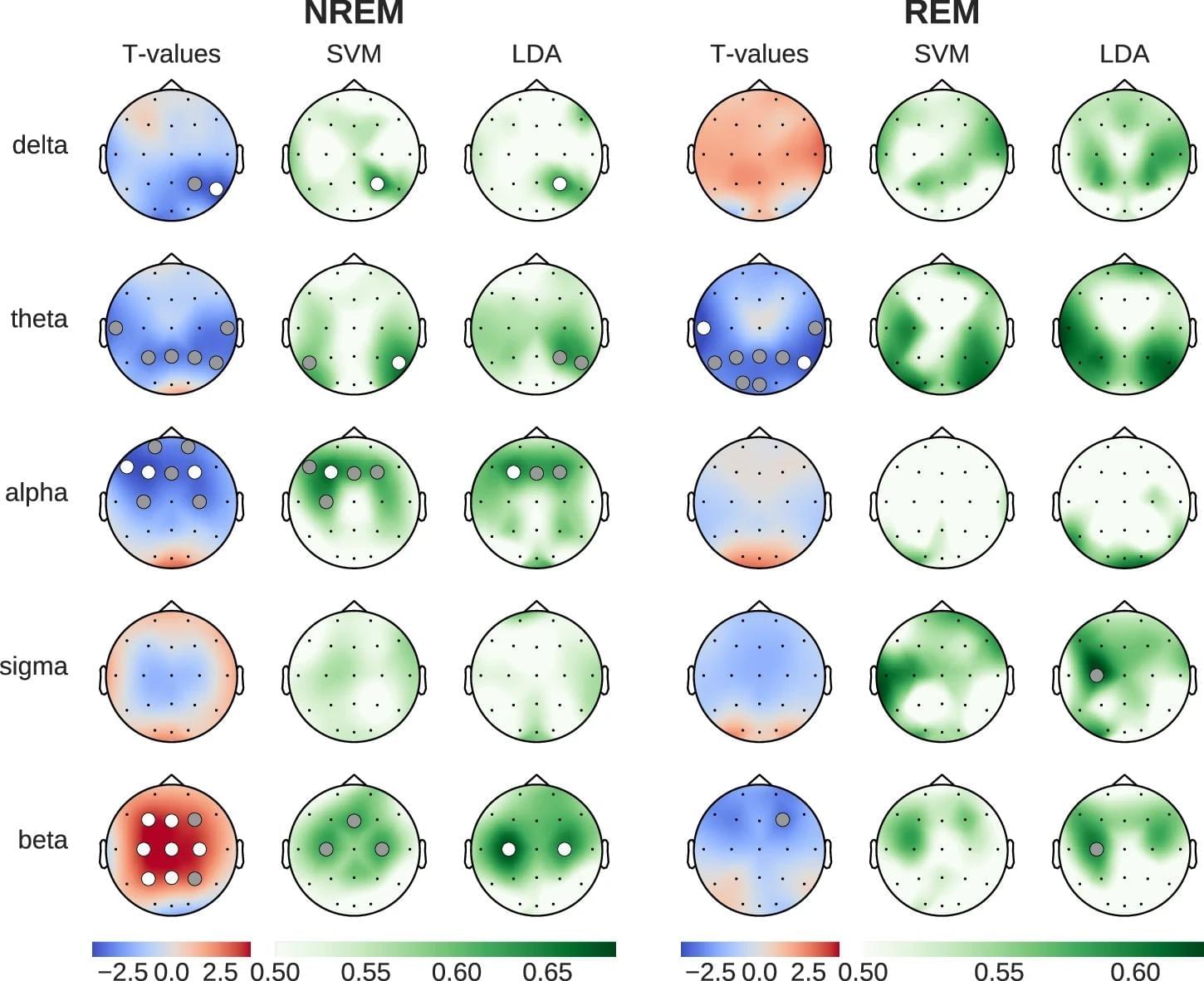
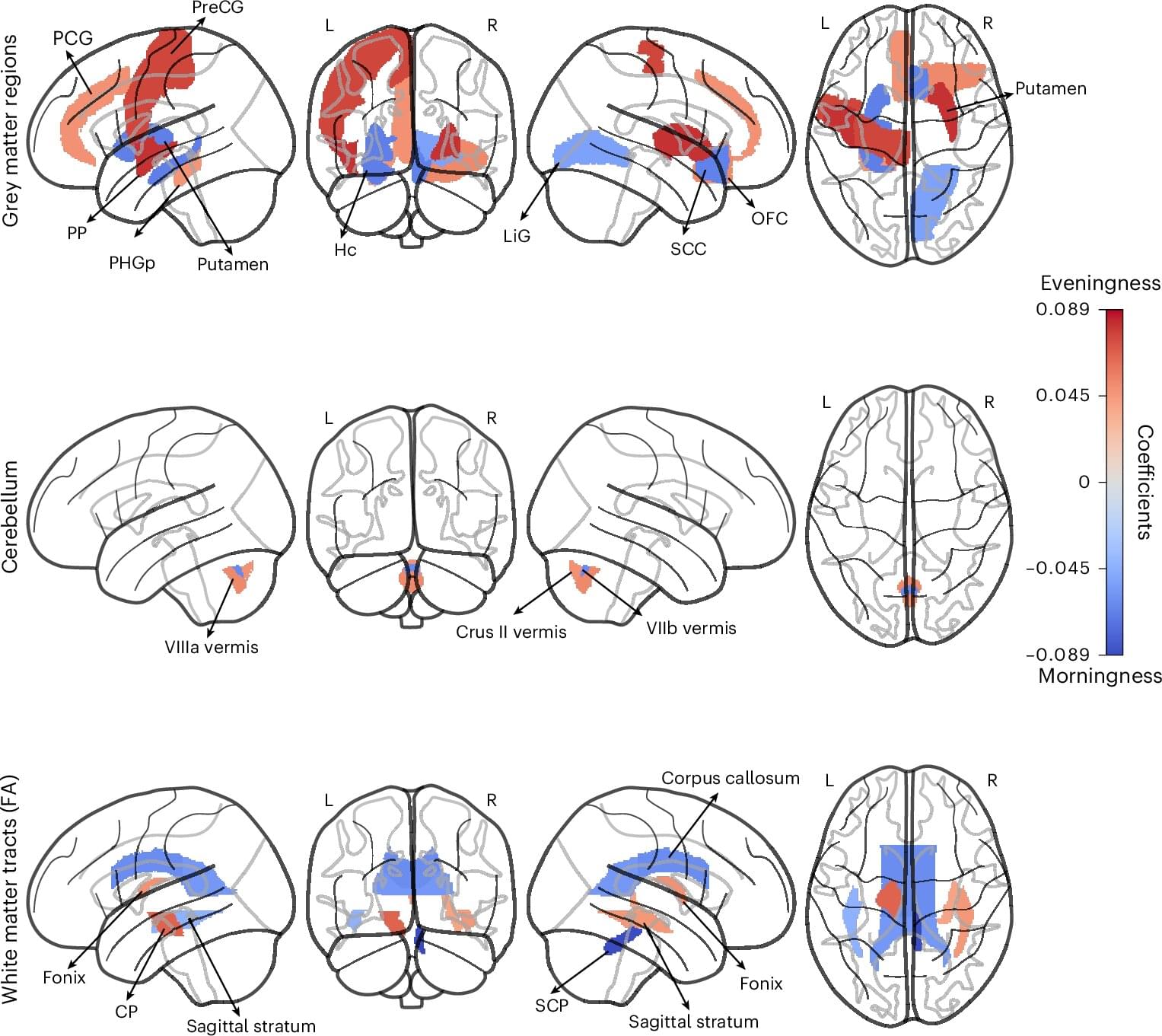
Insomnia, depression, and anxiety are the most common mental disorders. Treatments are often only moderately effective, with many people experiencing returning symptoms. This is why it is crucial to find new leads for treatments. Notably, these disorders overlap a lot, often occurring together. Could there be a shared brain mechanism behind this phenomenon?
Siemon de Lange, Elleke Tissink, and Eus van Someren, together with their colleagues from the Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam, investigated brain scans of more than 40,000 participants from the UK Biobank. The research is published in the journal Nature Mental Health.
Tissink says, “In our lab, we explore the similarities and differences between insomnia, anxiety, and depression. Everyone looks at this from a different perspective: some mainly look at genetics and in this study, we look at brain scans. What aspects are shared between the disorders, and what is unique to each one?”