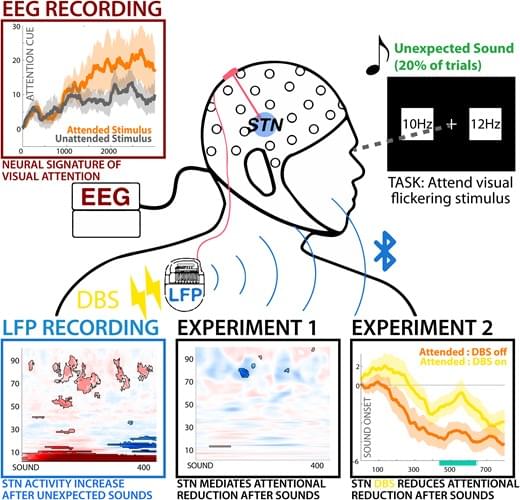
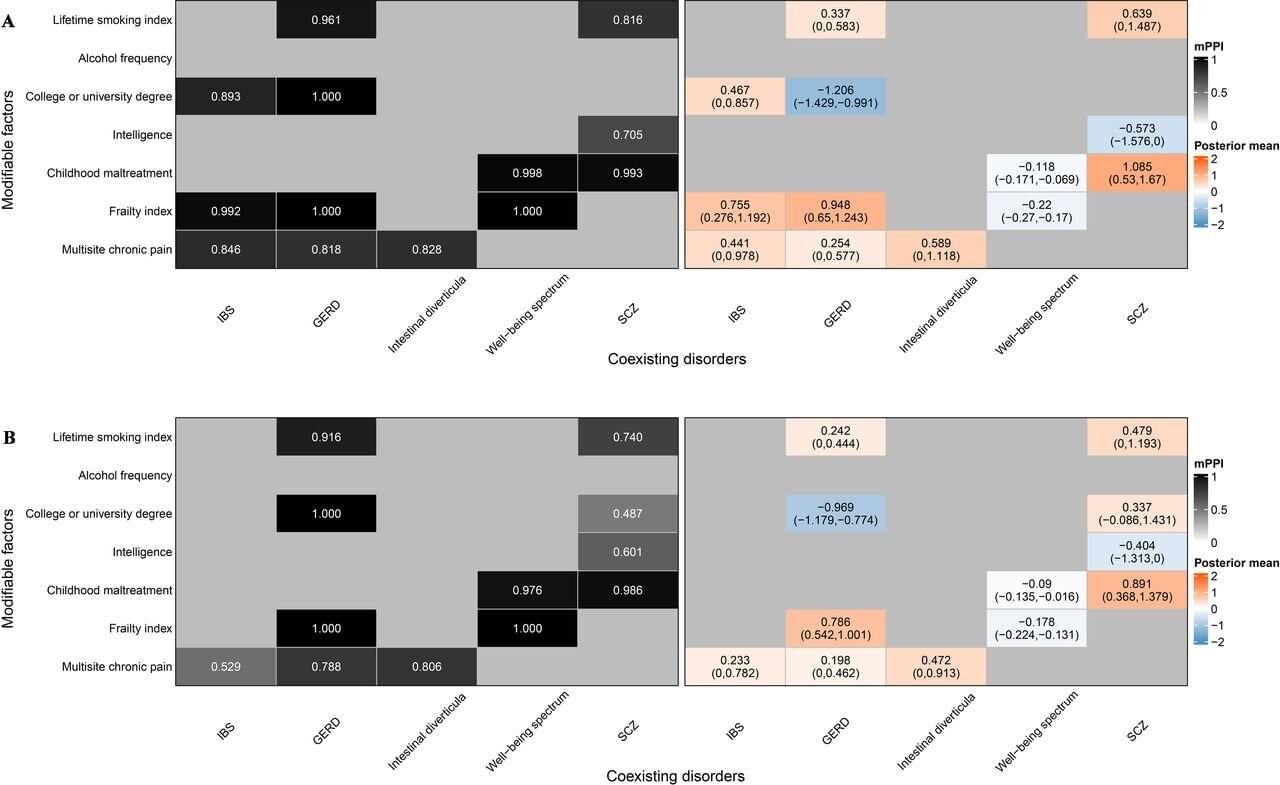
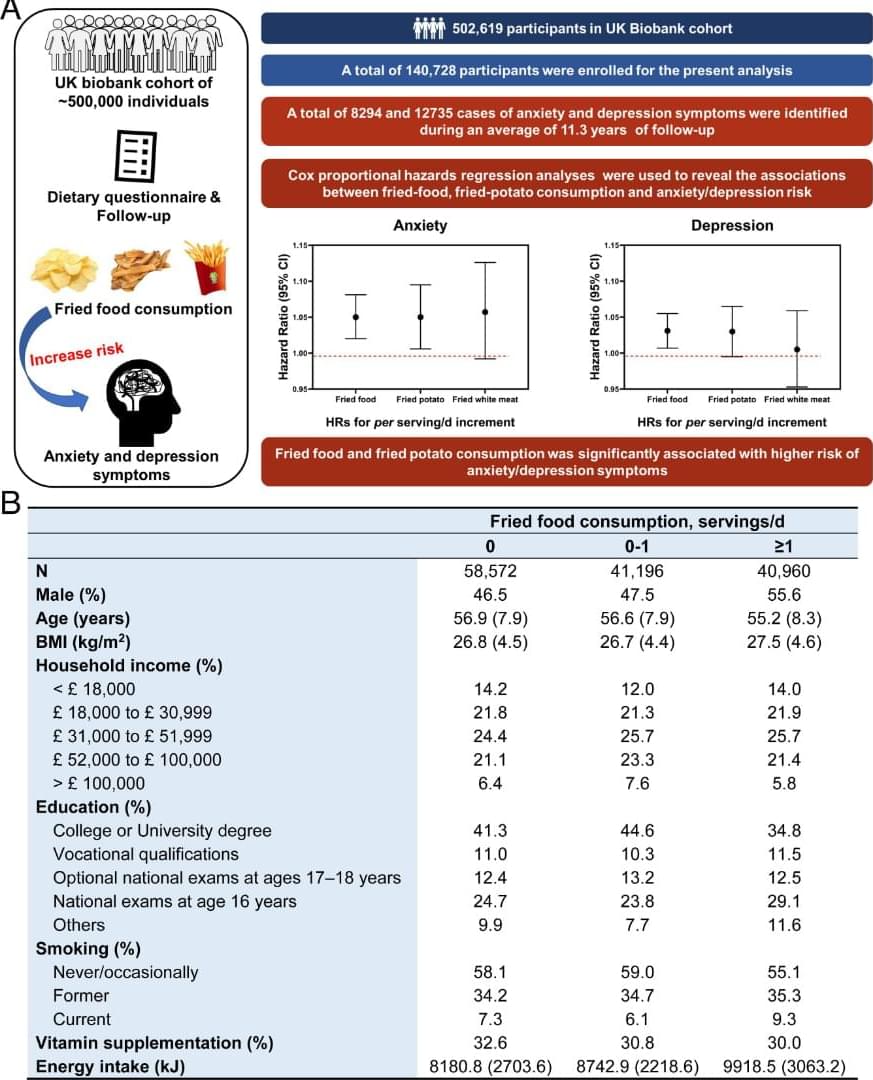
There is a curious tension between the notion of information as zero dimensional and the very fabric of the universe that is measured in finite increments such as the Planck length, often considered the smallest meaningful unit of space (10⁻³⁵ m). From the day our earliest models of communication were formalized, theorists have wrestled with the idea that information might be weightless, formless, and without dimensional extension, even as all signals we use to transmit and store it require tangible, measurable structures. As a matter of conceptual elegance, zero-dimensional descriptions of information promise simplicity and universality, yet collide with the physical reality of a world that consists of definite quantum-scale granularity. While Gregory Bateson alluded to information as a “difference that makes a difference” (Bateson, 1972, p. 459), the question remains whether this difference is truly independent of spatial and temporal constraints, or forever bound to them in ways that challenge the zero-dimensional ideal.
When the classic figures of communication theory described the fundamentals of information, there was a sense that the symbol or “bit” itself was neither physical nor extended in space. Claude Shannon (1948) famously called the problem of communication one of “reproducing at one point either exactly or approximately a message selected at another point” (p. 379). Such an abstract conceptualization pushed any question of dimensional extension into the background, because the focus rested on logical patterns rather than the medium. Yet, even in these logical patterns, one finds references to signals, channels, and potential distortions that are inseparable from physical processes. A memory device — whether neural or silicon-based — still requires a physically instantiated substrate to encode these abstract messages. Norbert Wiener (1954), whose work helped launch cybernetics, was strikingly prescient when he declared, “Information is information, not matter or energy.