Do our minds have quantum structures that give rise to consciousness? Sir Roger Penrose, one of the world’s most famous scientists, believes this and can explain how it works.
Category: neuroscience – Page 1,096

Green and privileged childhoods signal better adult mental
As greenery round the childhood residence shrunk, risk of mental illness as an adolescent and adult went up. Kids who grew up in plots with the least vegetation had a 15 to 50% greater incidence of a range of psychiatric problems, including depression, eating disorders, anxiety and obsessive compulsive disorder.
Two studies link parks and poshness to lower depression and cognitive decline, for reasons still unclear. Paul Biegler reports.
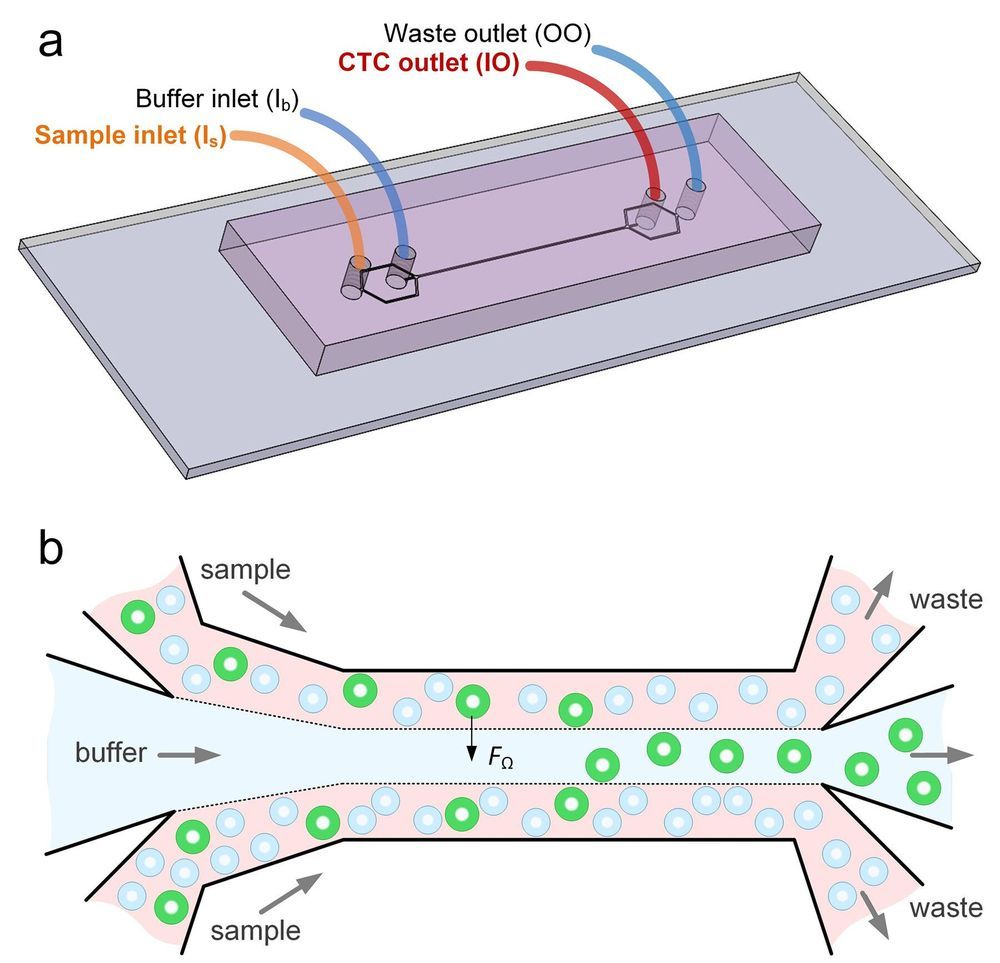
New microfluidics device can detect cancer cells in blood
Researchers at the University of Illinois at Chicago and Queensland University of Technology of Australia, have developed a device that can isolate individual cancer cells from patient blood samples. The microfluidic device works by separating the various cell types found in blood by their size. The device may one day enable rapid, cheap liquid biopsies to help detect cancer and develop targeted treatment plans. The findings are reported in the journal Microsystems & Nanoengineering.
“This new microfluidics chip lets us separate cancer cells from whole blood or minimally-diluted blood,” said Ian Papautsky, the Richard and Loan Hill Professor of Bioengineering in the UIC College of Engineering and corresponding author on the paper. “While devices for detecting cancer cells circulating in the blood are becoming available, most are relatively expensive and are out of reach of many research labs or hospitals. Our device is cheap, and doesn’t require much specimen preparation or dilution, making it fast and easy to use.”
The ability to successfully isolate cancer cells is a crucial step in enabling liquid biopsy where cancer could be detected through a simple blood draw. This would eliminate the discomfort and cost of tissue biopsies which use needles or surgical procedures as part of cancer diagnosis. Liquid biopsy could also be useful in tracking the efficacy of chemotherapy over the course of time, and for detecting cancer in organs difficult to access through traditional biopsy techniques, including the brain and lungs.

The foods that might help with dementia
I wonder how diet mixed with CBD oil treatment can work on neurodegenerative diseases? A man has told of how he “got his mum back” after a diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease, in part, by getting her to follow a diet high in berries and leafy green vegetables.
One man has ‘got his mum back’ from the ravages of Alzheimer’s, partly…

The Effect of Cannabis on Dementia Related Agitation and Aggression
#ClinicalTrial The most common syndrome in patients with severe dementia is agitated behavior, which is often characterized by a combination of violent behavior (physical or verbal), restlessness, and inappropriate loudness. The treatment options for this syndrome are limited and lead to severe side effects. In vivo experiments on animals and clinical studies on adults show that cannabinoids could have a beneficial effect on behavioral disorders in general, and in dementia-related disorders in particular.
Full Text View.
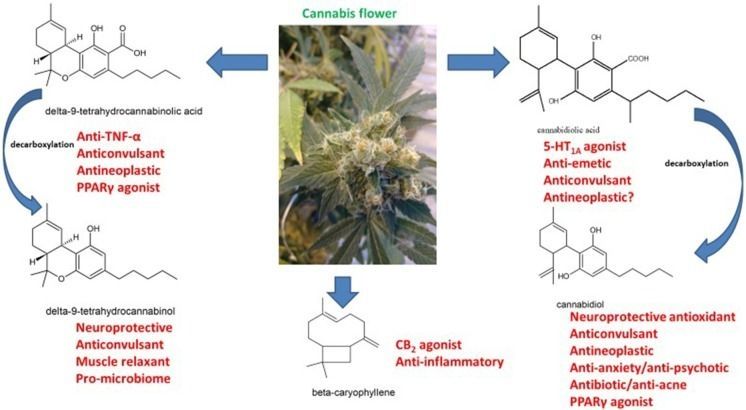
Cannabis Therapeutics and the Future of Neurology
Neurological therapeutics have been hampered by its inability to advance beyond symptomatic treatment of neurodegenerative disorders into the realm of actual palliation, arrest or reversal of the attendant pathological processes. While cannabis-based medicines have demonstrated safety, efficacy and consistency sufficient for regulatory approval in spasticity in multiple sclerosis (MS), and in Dravet and Lennox-Gastaut Syndromes (LGS), many therapeutic challenges remain. This review will examine the intriguing promise that recent discoveries regarding cannabis-based medicines offer to neurological therapeutics by incorporating the neutral phytocannabinoids tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), cannabidiol (CBD), their acidic precursors, tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) and cannabidiolic acid (CBDA), and cannabis terpenoids in the putative treatment of five syndromes, currently labeled recalcitrant to therapeutic success, and wherein improved pharmacological intervention is required: intractable epilepsy, brain tumors, Parkinson disease (PD), Alzheimer disease (AD) and traumatic brain injury (TBI)/chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE). Current basic science and clinical investigations support the safety and efficacy of such interventions in treatment of these currently intractable conditions, that in some cases share pathological processes, and the plausibility of interventions that harness endocannabinoid mechanisms, whether mediated via direct activity on CB1 and CB2 (tetrahydrocannabinol, THC, caryophyllene), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPARγ; THCA), 5-HT1A (CBD, CBDA) or even nutritional approaches utilizing prebiotics and probiotics. The inherent polypharmaceutical properties of cannabis botanicals offer distinct advantages over the current single-target pharmaceutical model and portend to revolutionize neurological treatment into a new reality of effective interventional and even preventative treatment.
Keywords: cannabis, pain, brain tumor, epilepsy, Alzheimer disease, Parkinson disease, traumatic brain injury, microbiome.
Cannabis burst across the Western medicine horizon after its introduction by William O’Shaughnessy in 1838 (O’Shaughnessy, 1838–1840; Russo, 2017b), who described remarkable successes in treating epilepsy, rheumatic pains, and even universally fatal tetanus with the “new” drug. Cannabis, or “Indian hemp,” was rapidly adopted by European physicians noting benefits on migraine by Clendinning in England (Clendinning, 1843; Russo, 2001) and neuropathic pain, including trigeminal neuralgia by Donovan in Ireland (Donovan, 1845; Russo, 2017b). These developments did not escape notice of the giants of neurology on both sides of the Atlantic, who similarly adopted its use in these indications: Silas Weir Mitchell, Seguin, Gowers and Osler (Mitchell, 1874; Seguin, 1877; Gowers, 1888; Osler and McCrae, 1915).


New ‘interspecies communication’ strategy between gut bacteria and mammalian hosts uncovered
A study published today in Cell describes a form of “interspecies communication” in which bacteria secrete a specific molecule — nitric oxide — that allows them to communicate with and control their hosts’ DNA, and suggests that the conversation between the two may broadly influence human health.
The researchers out of Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center, and Harvard Medical School tracked nitric oxide secreted by gut bacteria inside tiny worms (C. elegans, a common mammalian laboratory model). Nitric oxide secreted by gut bacteria attached to thousands of host proteins, completely changing a worm’s ability to regulate its own gene expression.
The study is the first to show gut bacteria can tap into nitric oxide networks ubiquitous in mammals, including humans. Nitric oxide attaches to human proteins in a carefully regulated manner — a process known as S-nitrosylation — and disruptions are broadly implicated in diseases such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, asthma, diabetes, heart disease, and cancer.