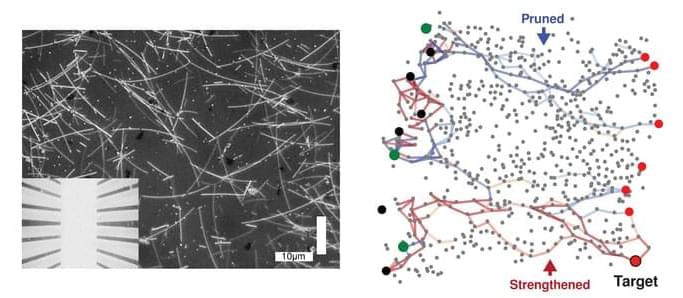
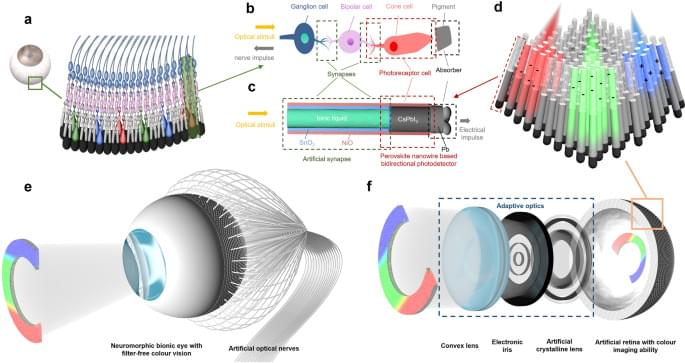
Cameras for machine vision and robotics are essentially bionic devices mimicking human eyes. These applications require advanced color imaging systems to possess a number of attributes such as high resolution, large FoV, compact design, light-weight and low energy consumption, etc1. Conventional imaging systems based on CCD/CMOS image sensors suffer from relatively low FoV, bulkiness, high complexity, and power consumption issues, especially with mechanically tunable optics. Recently, spherical bionic eyes with curved image sensor retinas have triggered enormous research interest1,2,3,4,5,6,7. This type of devices possess several appealing features such as simplified lens design, low image aberration, wide FoV, and appearance similar to that of the biological eyes rendering them suitable for humanoid robots8,9,10,11,12,13. However, the existing spherical bionic eyes with curved retinas typically only have fixed lens and can only acquire mono color images. Fixed lenses cannot image objects with varying distances. On the other hand, conventional color imaging function of CCD/CMOS image sensors are achieved by using color filter arrays, which add complexity to the device fabrication and cause optical loss14,15,16,17,18,19. Typical absorptive organic dye filters suffer from poor UV and high-temperature stabilities, and plasmonic color filters suffer from low transmission20,21,22. And it is even more challenging to fabricate color filter arrays on hemispherical geometry where most traditional microelectronic fabrication methods are not applicable.
Herein, we demonstrate a novel bionic eye design that possesses adaptive optics and a hemispherical nanowire array retina with filter-free color imaging and neuromorphic preprocessing abilities. The primary optical sensing function of the artificial retina is realized by using a hemispherical all-inorganic CsPbI3 nanowire array that can produce photocurrent without external bias leading to a self-powered working mode. Intriguingly, an electrolyte-assisted color-dependent bidirectional synaptic photo-response is discovered in a well-engineered hybrid nanostructure. Inspired by the vertical alignment of a color-sensitive cone cell and following neurons, the device structure vertically integrates a SnO2/NiO double-shell nanotube filled with ionic liquid in the core on top of a CsPbI3/NiO core-shell nanowire. It is found that the positive surrounding gate effect of NiO due to photo hole injection can be partially or fully balanced by electrolyte under shorter (blue) or longer (green and red) wavelength illuminations, respectively. Thus, the device can yield either positive or negative photocurrent under shorter or longer wavelength illumination, respectively. The carriers can be accumulated in SnO2/NiO structure, giving rise to the bidirectional synaptic photo-response. This color-sensitive bidirectional photo-response instills a unique filter-free color imaging function to the retina. The synaptic behavior-based neuromorphic preprocessing ability, along with the self-powered feature, effectively reduce the energy consumption of the system23,24,25,26,27,28. Moreover, the color selectivity of each pixel can be tuned by a small external bias to detect more accurate color information. We demonstrate that the device can reconstruct color images with high fidelity for convolutional neural network (CNN) classifications. In addition, our bionic eye integrates adaptive optics in the device, by integrating an artificial crystalline lens and an electronic iris based on liquid crystals. The artificial crystalline lens can switch focal length to detect objects from different distances, and the electronic iris can control the amount of light reaching the retina which enhances the dynamic range. Both of the optical components can be easily tuned by the electric field, which are fast, compact, and much more energy efficient compared to the conventional mechanically controlled optics reported hitherto. (Supplementary Table 1 compares our system with some commercial zoom lenses.) The combination of all these unique features makes the bionic eye structurally and functionally equivalent to its biological counterpart.