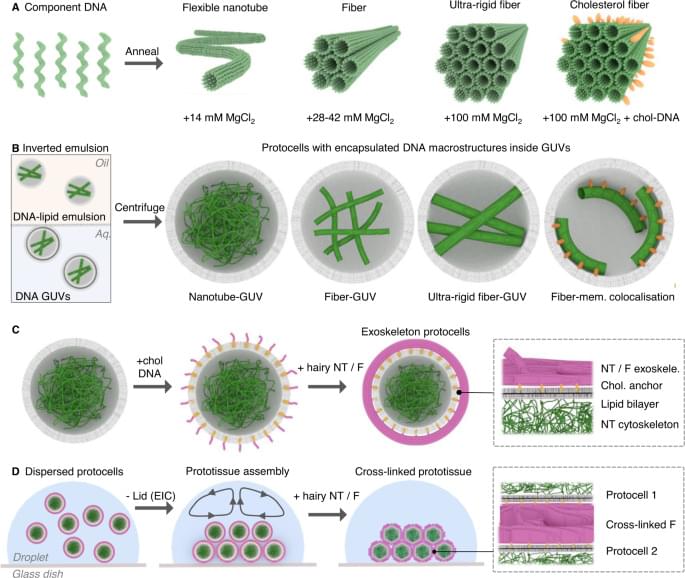
Legitimately awesome paper wherein Arulkumaran et al. assemble DNA nanotubes and use them to build artificial ‘cytoskeletons’ inside of giant unilamellar vesicles. They go on to make a variety of fun variations on this theme and eventually build artificial ‘tissues’ made up of these synthetic cell-like vesicles and an ‘extracellular matrix’ that is also made of DNA nanotubes. I find this paper impressive due to how performs precise engineering at the nanoscale and builds up layers of complexity until macroscale specimens are created in a fashion reminiscent of biological systems, yet unique in its own way. #biotechnology #nanotechnology #cellbiology #bioengineering
Building synthetic protocells and prototissues hinges on the formation of biomimetic skeletal frameworks. Here, the authors harness simplicity to create complexity by assembling DNA subunits into structural frameworks which support membrane-based protocells and prototissues.