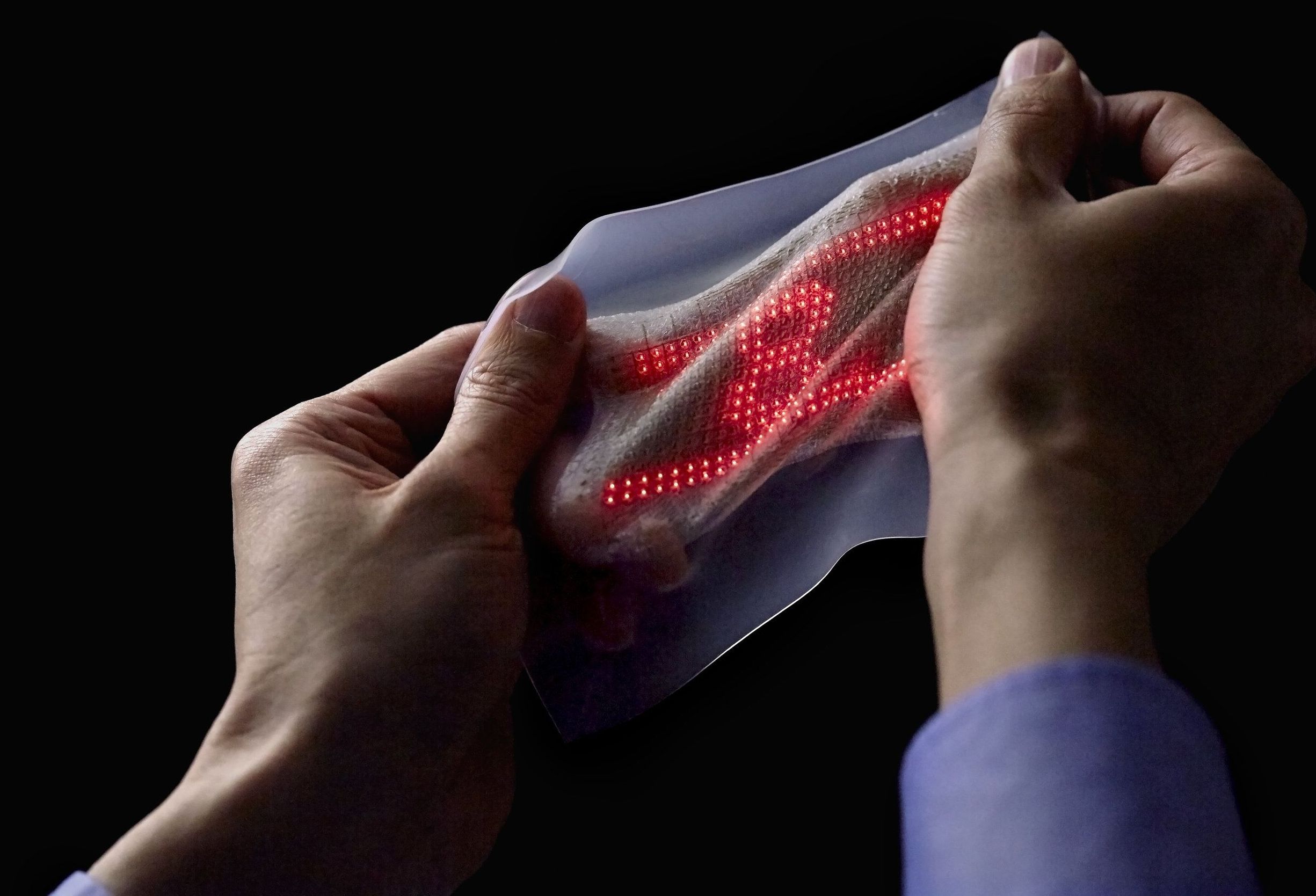
A new ultrathin elastic display that fits snugly on the skin can show the moving waveform of an electrocardiogram recorded by a breathable, on-skin electrode sensor. Combined with a wireless communication module, this integrated biomedical sensor system, called “skin electronics,” can transmit biometric data to the cloud.
This latest research by a Japanese academic-industrial collaboration, led by Professor Takao Someya at the University of Tokyo’s Graduate School of Engineering, is slated for a news briefing and talk at the AAAS Annual Meeting in Austin, Texas on February 17th.
Thanks to advances in semiconductor technology, wearable devices can now monitor health by measuring vital signs or taking an electrocardiogram, and then transmitting the data wirelessly to a smartphone. The readings or electrocardiogram waveforms can be displayed on the screen in real time, or sent to the cloud or a memory device where the information is stored.